
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
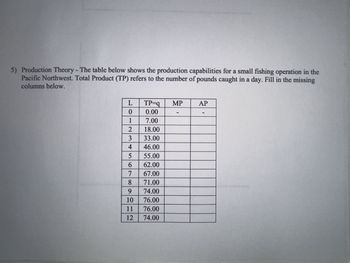
Transcribed Image Text:5) Production Theory - The table below shows the production capabilities for a small fishing operation in the
Pacific Northwest. Total Product (TP) refers to the number of pounds caught in a day. Fill in the missing
columns below.
L
0
1
2
3
4
456700
8
9
10
11
12
TP-q
0.00
7.00
18.00
33.00
46.00
55.00
62.00
67.00
71.00
74.00
76.00
76.00
74.00
MP
AP
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Spot the economics in the following cases by identifying the concept described within the scenario and then briefly articulating your answers When parking violations in San Francisco were $100, there were 250,000 tickets given out. When violations went up to $175 there were 200,000 violations given. Ford produces trucks and loses ⅓ of a sedan for each truck produced. When it produces sedans, it loses 2 trucks per sedan produced. Driving down Mendocino Blvd, you notice a street crew working near campus. One worker is jackhammering away, while another removes the rubble. Both are extremely productive. Two workers are talking and having a smoke, while another three are having some coffee all while watching the first two workers. Recently, I attempted to cancel my SiriusXM subscription. I logged into their website and clicked on the “cancel subscription” link which I had a hard time finding because it was hidden in some obscure menu. When I clicked on cancel, a window popped up…arrow_forward6 workers and 4 machines are required to produce 2 computers. 2 workers and 2 machines are required to produce 2 units of tomato. A. Find the labor and capital requirement per one computer and 1 unit of tomato? B. Which industry is a labor intensive? Capital intensive?arrow_forwardCom 120.000 D 80.000 40.000 Robots 5.000 10.000 15.000 In the graph above, the resources in this economy arearrow_forward
- The table below shows Lanark's production possibilities. Wheat Cars A 0 95 B 90 90 C 158 81 204 63 226 F 235 36 a. If Lanark is producing 72 cars, it can produce approximately b. If Lanark is currently producing combination C, the cost of 46 more wheat is (Click to select) c. If Lanark is currently producing combination D, the approximate per unit cost of an additional car is necessary, round your answers to 1 decimal place. Remember to round 0.05 up to 0.10. wheat. (Click to select). Ifarrow_forwardThe biggest problem of production to be solved is: Deciding how much of a business’s production budget should be invested in lobbying congress for policies favorable to the business. Deciding how best to allocate a business’s limited manpower and resources so as to produce what consumers most want. To create as many jobs as possible. To produce as many goods as possible.arrow_forwardCountry JKL has a maximum of 50 labour(hours). The tab shows maximum quantity of wheat and cotton the Country produce with different labour (hours) used. Combination A B C D E F Corn 15 14 12 9 5 0 Wheat 0 2 4 6 8 10 A) If Country JKL produces 8,000 kg of wheat and 5,000 kg cotton a week, does it face trade-off? Why? B) Suppose Country JKL has successfully brought in an adv technology that improves the production of cotton by 20% from its original combinations. Sketch a diagram that shows the changes of the PPC for Country JKLarrow_forward
- For an economist, a technology is: A method of combining resources to make goods and services. 8 8 8 A computer. A capital-intensive method of production. Any production technique that is patented.arrow_forwardShow full answers and steps to part a) b) & c)arrow_forwardProvide a diagram showing the inefficient or underemployed resources in a hypothetical economyarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education