
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696527
Author: J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
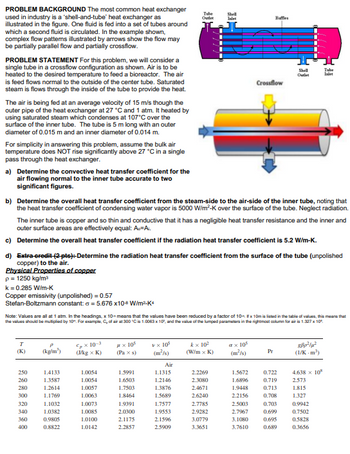
Transcribed Image Text:PROBLEM BACKGROUND The most common heat exchanger
used in industry is a 'shell-and-tube' heat exchanger as
illustrated in the figure. One fluid is fed into a set of tubes around
which a second fluid is circulated. In the example shown,
complex flow patterns illustrated by arrows show the flow may
be partially parallel flow and partially crossflow.
PROBLEM STATEMENT For this problem, we will consider a
single tube in a crossflow configuration as shown. Air is to be
heated to the desired temperature to feed a bioreactor. The air
is feed flows normal to the outside of the center tube. Saturated
steam is flows through the inside of the tube to provide the heat.
The air is being fed at an average velocity of 15 m/s though the
outer pipe of the heat exchanger at 27 °C and 1 atm. It heated by
using saturated steam which condenses at 107°C over the
surface of the inner tube. The tube is 5 m long with an outer
diameter of 0.015 m and an inner diameter of 0.014 m.
For simplicity in answering this problem, assume the bulk air
temperature does NOT rise significantly above 27 °C in a single
pass through the heat exchanger.
a) Determine the convective heat transfer coefficient for the
air flowing normal to the inner tube accurate to two
significant figures.
Tube
Shell
Outlet
Inlet
Baffles
Shell
Outlet
Tube
Crossflow
b) Determine the overall heat transfer coefficient from the steam-side to the air-side of the inner tube, noting that
the heat transfer coefficient of condensing water vapor is 5000 W/m²-K over the surface of the tube. Neglect radiation.
The inner tube is copper and so thin and conductive that it has a negligible heat transfer resistance and the inner and
outer surface areas are effectively equal: Ao-Ai.
c) Determine the overall heat transfer coefficient if the radiation heat transfer coefficient is 5.2 W/m-K.
d) Extra credit (2 pts):-Determine the radiation heat transfer coefficient from the surface of the tube (unpolished
copper) to the air.
Physical Properties of copper
p = 1250 kg/m³
k = 0.285 W/m-K
Copper emissivity (unpolished) = 0.57
Stefan-Boltzmann constant:
5.676x10-8 W/m²-K4
Note: Values are all at 1 atm. In the headings, x 10+ means that the values have been reduced by a factor of 10 x10m is listed in the table of values, this means that
the values should be multiplied by 10". For example, C, of air at 300 °C is 1.0063 x 10°, and the value of the lumped parameters in the rightmost column for air is 1.327 x 10".
T
(K)
(kg/m³)
5px 10-3
(J/kg xK)
*x 10³
(Pax s)
vx 105
(m²/s)
kx 10²
(W/m x K)
ax 10³
(m²/s)
Pr
(1/K m³)
Air
250
1.4133
1.0054
1.5991
1.1315
2.2269
1.5672
0.722
4.638 x 10
260
1.3587
1.0054
1.6503
1.2146
2.3080
1.6896
0.719
2.573
280
1.2614
1.0057
1.7503
1.3876
2.4671
1.9448
0.713
1.815
300
1.1769
1.0063
1.8464
1.5689
2.6240
2.2156
0.708
1.327
320
1.1032
1.0073
1.9391
1.7577
2.7785
2.5003
0.703
0.9942
340
1.0382
1.0085
2.0300
1.9553
2.9282
2.7967
0.699
0.7502
360
0.9805
1.0100
2.1175
2.1596
3.0779
3.1080
0.695
0.5828
400
0.8822
1.0142
2.2857
2.5909
3.3651
3.7610
0.689
0.3656
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 1 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- In a chemical production facility, a mixture containing 80% acetone and 20% water by mol will be transported through the pipeline. This mixture can be transported in liquid form or in vapor form. Transport of the steam mixture through the pipeline is carried out by a centrifugal pump. In order for the pump vanes to be unaffected by wear and to continue their operation without interruption, the mixture must have only a vapor structure. Determine the highest pump fluid pressure value at which the mixture will not form liquid, based on the temperature of the mixture in the pump being 100 °C. The mixture can be well represented by the following activity coefficient model (van Laar model): 4₁2 = 2.05 In y₁ = A₁₂ 1+ = diz[14 A₂ = 1.50 A₁2 x₁ A21 X₂ In 7₂ = A21 An ( 1 + Aj X₂ A₁2 X₁ 12arrow_forwardProblem 4. In order not to damage the resistance in the kettles, the difference between the temperature of the heater and the fluid should not exceed 25 °C. If the heat transfer area between the fluid and the heater is 78.5 cm² and the heat transfer coefficient is 400 W/m².K, find the maximum allowable power of the heater in order to boil water?arrow_forwardParts a-c please.arrow_forward
- A hydraulic fluid preheater consists of a single tube with a diameter of D = 0.5 in and a length of L= 5 m. The tube surface is maintained at Ts = 200°F by hot combustion gases flowing past the outside surface. The hydraulic fluid enters at To = 80°F and a mass flow rate of 370 lbm/h. (a) Determine the convection heat transfer coefficient for the hydraulic fluid flowing through the tube. (b) Determine the hydraulic fluid exit temperature. (c) Determine the heat transfer rate to the hydraulic fluid. (d) Determine the power required to pump the hydraulic fluid through the tube.arrow_forwardConsider a 10 m length of 2 cm-I.D tube. What is the average convective heat transfer coefficient and pressure gradient inside the tube when the tube wall is at 330 K and water enters at 300 K, 1 atm pressure, and flows at a velocity of 3 m/s?arrow_forwardAir at 300 K flows across one side of a flat plate at a velocity of 15 m/s. The plate measures 2.0 m in the direction of flow and 1.0 m wide. If the surface temperature is 400 K, find the convective heat transfer. How much of the plate experiences laminar flow?arrow_forward
- 1) Consider the infinitely tall, annular mixing tank. The fluid to be mixed is Fluid between the inner cylinder and the outer wall. The fluid is mixed by a Fluid spinning the inner cylinder at an angular velocity of n (s-1). The tank has an inner radius of R (m) and the R. inner cylinder has a diameter of k (m). Fluid There is no net flow in the vertical or radial directions. Top view Answer the following questions about Side view this sytem:arrow_forward2. Adjacent Flow of Two Immiscible Power Law Fluids Two immiscible fluids are contained in the space between two infinite parallel plates. The upper plate, at y = h, is in motion with a velocity U. Initially there is no pressure gradient in the x-direction. We have already solved for the velocity profile between the two plates for a number of different conditions, now we are going to make fluid II non-Newtonian. U Fluid II Interface Between Two Immiscible Fluids ah Fluid I d) Go back to your old assignment (b), but now let's let Fluid II be non-Newtonian. Specifically, model the fluid as a power law fluid with n =ky". Solve for the velocity profile across the channel and sketch the result for a shear thinning and shear thickening fluid as the velocity on the top plate is systematically increased. e) Now remove the velocity of the top plate and instead apply a pressure gradient. What is the velocity profile look like now?arrow_forwardAccording to nature of flow, convective heat transfer is classified into natural convection and forced convection. By taking specific examples, explain how the natural convection and forced convection arises in them.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The