
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
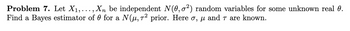
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 7. Let X₁,..., Xn be independent N(0,0²) random variables for some unknown real 0.
Find a Bayes estimator of 0 for a N(µ,7² prior. Here σ, µ and □ are known.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- QUESTION 6 Suppose we know that X and Y are random variables with var(X) = 2, var(Y) = 3, and cov(X,Y) = -1. Find var (2X – Y). Round to 4 decimal places if needed.arrow_forward3. If x1, X2, X3, ..., Xn is a random sample from a normal 1 distribution N (µ, 1) show that t= E xí is an unbiased estimator of n i = 1 H² + 1.arrow_forward1. Random variable X has p.d.f -6z 6e fx(z) otherwise and let Y = eX. Calculate E(X)arrow_forward
- Complete the following multiple choice questions. No work will be graded in the bonus problem. (a) E(X²)= 16. Compute E[-X(3X – 2)]. Assume that X is a random variable with E(X)= -3 and | (i) -54 (ii) -48 (iii) -33 (iv) -27arrow_forwardSuppose X and S2 are calculated from a random sample X₁,..., Xn drawn from a population with finite variance o2. We know that ES2 = o². Prove that ES ≤ 0, and if o2 > 0, then ESarrow_forward4. A particle moves on the x- axis starting at x = 0. With equal probability, the particle moves to the left or right one unit. Let X denote the position on the x- axis after four moves. (a) Find px(x). Notice that X can take on -4,-2,0, 2, 4. Fill out the table below. xPx(x) (b) What is the expected position of the particle after four moves. That is, compute E(X). Express your answer as a fraction in lowest terms.arrow_forward
- Q 6.1. Suppose Z = (Z₁, Z2, Z3) is a standard multi-variate Gaussian random variable i.e., for i ≤ 3, Zi~ N(0, 1) are i.i.d. random variables. Each of the random variables, (a)–(d), on the left is equal in distribution to exactly one random variables, (1)–(4), on the right. Pair up according to "equal in distribution" and explain briefly your reasoning. X₁ (a) X₂ (b) (x₂) - (2) (c) (x²) - (¹/1² 1/√²) (2₁) (3/√2 = √2 = (V2) Z₁ (d) (x) - (1) (²) X2 Y₁ (9)-(-) (2) (1=1) Y₂ (1) Y₁ (²) (4) - (1/² (3) (1/√√2 1/√2-1/√2) (x₁) = (²₁ ² ✓/³²) (3) 2 2 √2 1 Z3 Y₁ → ()-()) (4) = Y₂ 1/2) (2) 1) (2)arrow_forward2. Suppose one has n non-degenerate random variables X1, X2,, X, so that X1+ X2 + · · · + Xn = L for some constant L. (Recall that a random variable is non-degenerate if it is not a constant in disguise.) Show that there must be at least one pair of indices i j so that p(X;, X;) < 0.arrow_forwardQ 6.1. Suppose Z = (Z1, Z2, Z3) is a standard multi-variate Gaussian random variable i.e., for i ≤ 3, Zi~ N(0, 1) are i.i.d. random variables. Each of the random variables, (a)-(d), on the left is equal in distribution to exactly one random variables, (1)-(4), on the right. Pair up according to "equal in distribution" and explain briefly your reasoning. (a) (X₂) (¹) (X) = (2) 1/√2 (Ⓒ) (x₂) - (3/1² ¹1/1²) (2) (c = 2 0 = 2 Z₁ 1) (²) 3 (4¹) (X) = (²¹) (1) (2) (3) Y₁ 1 (29) - ()) (2) = Y₂ 1 Y₁ (121) = (1/² √₂) (2) (1/√2 1/√2 /2 −1/√√2, Y₂ X₁ X₂ = 22 1 1 2 0 Y₁ 2 1 (4) (2)) = (²) (²) 1 1 Z₁ Z₂ Z3arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman