
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A fiberglass pipe is lifted by a sling, as shown in the figure. The outer
diameter of the pipe is 6,0 in., its thickness is 0.25 in,, and its weight
density is 0,053 1b/in3 the length of the pipe is L = 36 ft and the distance
between lifting points is s = 11 ft.
a. Determine the maximum bending stress in the pipe due to its own
weight,
b. Find the spacing s between lift points which minimizes the
bending stress. What is the minimum bebding stress?
c. What spacing s leads to maximum bending stress? What is that
stress?
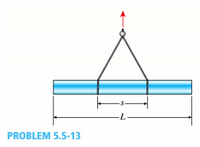
Transcribed Image Text:PROBLEM 5.5-13
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Q2. In the extruded profile shown in the figure, the maximum allowable stress in tension is 120 MPa and the maximum allowable stress in compression is 150 MPa. Find the maximum bending moment that can be applied to this profile. 20mm 40mm 20 mm 54mm yc 40 mm A= bh h %3D C. Rectangular area A = %3D Triangular areaarrow_forwardA triangular dam is shown in the figure, base is 6-m and height is 8-m. Compute for the factor of safety against sliding and overturning. Unit weight of concrete is 23.54 kN/cu.m. Consider 1 meter length strip. Disregard hydrostatic uplift pressure. The coefficient between the dam and the foundation is 0.8. harrow_forwardA 38-mm-diameter solid steel shaft supports loads PA = 1230 N and Pc = 2170 N, as shown. Assume LAB = 82 mm, LBc = 203 mm, and LCD = 152 mm. The bearing at B can be idealized as a roller support and the bearing at D can be idealized as a pin support. Determine the magnitude omax and location x (measured positive to the left from D) of the maximum bending stress in the shaft. Answers: o max || PA LAB B LBC MPa, x = C Pc LCD D mm.arrow_forward
- A column with a wide-flange section has a flange width b = 200 mm , height h = 200 mm , web thickness tw = 8 mm , and flange thickness tf = 12 mm (Figure 1). Calculate the stresses at a point 75 mm above the neutral axis if the section supports a tensile normal force N = 2.9 kN at the centroid, shear force V = 4.6 kN , and bending moment M = 4.8 kN⋅m as shown (Figure 2). Part A - Normal stress Calculate the normal stress at the point due to the internal normal force on the section. σnormal =? Part B - Shear stress Calculate the magnitude of the shear stress at the point due to the internal shear on the section. τ =?arrow_forwardCalculate the normal stress and shear stress acting on an element G, 150 mm from the top surface of the beam, in the section to the left of the point load (water tank load) as shown in the bottom figure and then determine the principal planes and the principal stresses.arrow_forwardD=100mm d=80mm p=1.9kPaarrow_forward
- A railroad tie (or sleepe1) is subjected to two rail loads, each of magnitude P=175 kN, acting as shown in the figure. The reaction q of the ballast is assumed to be uniformly distributed over the length of the tie,which has cross-sectional dimensions b =300 mm and h =250 mm. Calculate the maximum bending stress 111ma inthe tie due to the loads P, assuming the distance L =1500 mm and the overhang length a =500 mm.arrow_forwardNOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. Several forces are acting on a bolt as shown in the diagram below. It is desired to determine the resultant of all of the forces acting on the bolt. The axis of the bolt is at a 45° angle with respect to the x-axis. The line of action of force Pis parallel to the x-axis. The magnitudes of the forces and the angles labeled are as follows: P = 35 N S = 60 N T = 31 N a = 15⁰ Q = 53 N 0 = 25⁰ B = 65° y P T S xarrow_forwardA railroad tie (or sleeper) is subjected to two rail loads, each of magnitude P = 177 kN, acting as shown in the figure. L 9 £a The reaction q of the ballast is assumed to be uniformly distributed over the length of the tie, which has cross-sectional dimensions b 300 mm and h = 250 mm. Calculate the maximum bending stress o (in MPa) in the tie due to the loads P, assuming the distance L = 1,500 mm and the overhang length a = 495 mm. (Enter the magnitude.) max MPaarrow_forward
- P=6 M=4 W=0.7 L=12arrow_forwardFind the maximum bending compressive stress in psi, caused by the load P=1100 lbsarrow_forwardA cylindrical pressure vessel with flat ends is subjected to a torque 7 and a bending moment M (see figure). ot oc max Zo = M yo The outer radius is 12.2 in. and the wall thickness is 1.0 in. The loads are T = 800 kip-in., M = 1,000 kip-in., and the internal pressure p = 840 psi. Determine the maximum tensile stress, maximum compressive stress and maximum shear stress Tmax in the wall of the cylinder. (Enter the magnitudes in psi. Assume that the structure behaves linearly elastically and that the stresses caused by two or more loads may be superimposed to obtain the resultant stresses acting at a point. Consider both in-plane and out-of-plane shear stresses unless otherwise specified.) T M psi хо 11474.4981 X Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. psi 0 psiarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY