
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
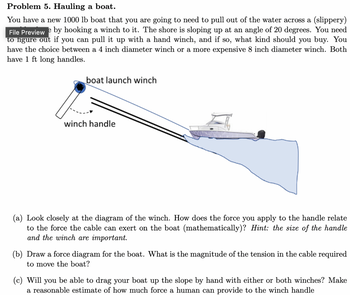
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 5. Hauling a boat.
You have a new 1000 lb boat that you are going to need to pull out of the water across a (slippery)
File Preview e by hooking a winch to it. The shore is sloping up at an angle of 20 degrees. You need
to figure out if you can pull it up with a hand winch, and if so, what kind should you buy. You
have the choice between a 4 inch diameter winch or a more expensive 8 inch diameter winch. Both
have 1 ft long handles.
boat launch winch
winch handle
(a) Look closely at the diagram of the winch. How does the force you apply to the handle relate
to the force the cable can exert on the boat (mathematically)? Hint: the size of the handle
and the winch are important.
(b) Draw a force diagram for the boat. What is the magnitude of the tension in the cable required
to move the boat?
(c) Will you be able to drag your boat up the slope by hand with either or both winches? Make
a reasonable estimate of how much force a human can provide to the winch handle
SAVE
AI-Generated Solution
info
AI-generated content may present inaccurate or offensive content that does not represent bartleby’s views.
Unlock instant AI solutions
Tap the button
to generate a solution
to generate a solution
Click the button to generate
a solution
a solution
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A 3.00-kg stone is tied to a thin, light wire wrapped around the outer edge of the uniform 8.00-kg cylindrical pulley. The inner diameter of the pulley is 55.0 cm, while the outer diameter is 1.00 m. The system is released from rest, and there is no friction at the axle of the pulley. a) Find the acceleration of the stone and the tension of the wire. b) Find the angular acceleration of the pulley.arrow_forwardWhen you carry shopping bags, rather than grasp the handles with your hand as in Q8.14a, you might choose to put them over your arm and slide the handle toward your elbow as in Q8.14b. Explain why this leads to less muscle effort to carry the bags and less force in your elbow joint.arrow_forwardASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER The chewing muscle, the masseter, is one of the strongest in the human body. It is attached to the mandible (lower jawbone) as shown in figure (a). The jawbone is pivoted about a socket just in front of the auditory canal. The forces acting on the jawbone are equivalent to those acting on the curved bar in figure (b). DETAILS SERCP11 8.3.P.033. Mandible magnitude of R magnitude of Masseter Need Help? -7.50 cm - 3.50 cm is the force exerted by the food being chewed against the jawbone, is the force of tension in the masseter, and is the force everted by the socket on the mandible. Find and i (in N) for a person who bites down on a piece of steak with a force of 53.5 N MY NOTESarrow_forward
- How do you solve problem? I'm confused about which equations to use and which variables go where. How should I think about what is going on? You have a pulley 14.6 cm in diameter and with a mass of 1.9 kg. You get to wondering whether the pulley is uniform. That is, is the mass evenly distributed, or is it concentrated toward the center or the rim? To find out, you hang the pulley on a hook, wrap a string around it several times, and suspend your 1.2 kg physics book 1.5 m above the floor. With your stopwatch, you can find that it takes 0.62 s for your book to hit the floor. Use g=9.8 m/s2. a) What is the moment of inertia if the pulley is uniform? b) What is the actual moment of inertia of the pulley based on your measurement? c) Is the pulley uniform (within 1% of uniform), is the mass of the pulley concentrated toward the center, or is the mass concentrated toward the rim?arrow_forward3.) A cube of brass has sides of 0.12 m. a. Draw the situation. b. Determine the applied tangential force to displace the top of the block 1.2 x 10-5 m given that Sbrass = 3.5 x 101⁰ N/m².arrow_forward1. The figure below shows the normal configuration of the head with proper posture. The center of mass for the weight of the skull is labeled W and the muscles that attach to the back of the skull are labeled M. Assume all quantities are correct to 2 significant figures. M W a) Determine the mechanical advantage of the skull muscles when d₁ 20 mm and d₂ = 26 mm. Hint: Which force on the fulcrum (rotation point) is the effort, and which is the load? Enter to 2 significant figures Mechanical Advantage: b) Improper posture and positioning of the head can lead to muscle tension headaches. If the head begins to shift forward while studying or reading, the center of mass moves further from the fulcrum or pivot point. It is a subtle change, but the figure below shows the head shifted forward. The center of mass for the weight of the skull is labeled W and the muscles that attach to the back of the skull are labeled M. Determine the new mechanical advantage of the skull muscles when d₁ = 16 mm…arrow_forward
- A group of physics students, each of whom can pull with 100lb of force, is planning to topple a 9600lb statue that the school built for the meanest teacher. Assume the statue does not slide.Answer all questions relative to the rotation point. How much torque is caused by the statue's weight? How much tension must the students generate to "barely balance" the statue? What is the minimum number of students (whole number) needed to topple the statue?arrow_forwardHelp me pleasearrow_forward3. Consider two thin-walled beams of the same wall thickness with cross- sections as shown in Figure 2. Applied torque is the same for both beams. Beams are twisted such that twisting angles are equal to each other. Find the relation between R2 and R₁ for the case = π/3. What will be this relation if we double the center angle o? R₁ R₁ R₂ FIGURE 2. Cross-sections of two thin-walled beams.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON