
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
Newton's Laws and Uniform Circular Motion Q5: Please answer and explain step by step in detail

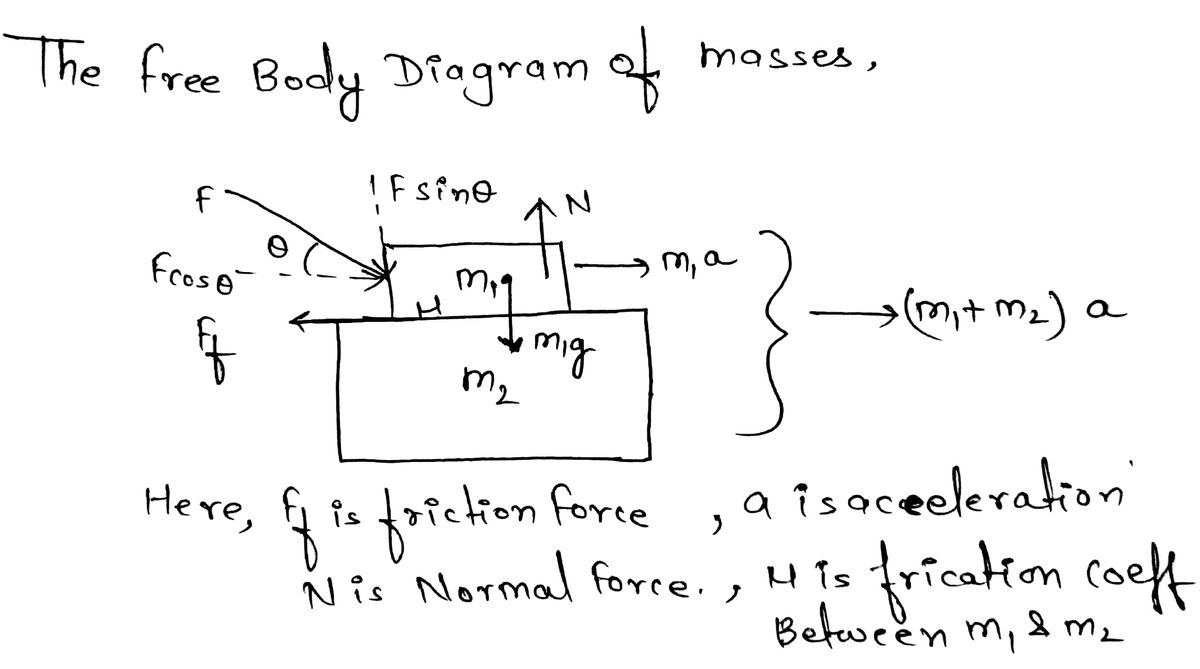
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 5: Two blocks are stacked as shown to the right and rest on a frictionless surface.
There is friction between the two blocks (coefficient of friction µ). An external force is
applied to the top block at an angle 0 to the horizontal.
M.
M2
What is the maximum force F that can be applied for the two blocks to move together? Give your answer in terms of the variables from the
problem statement in addition to g for gravitational acceleration.
Expression :
F =
Select from the variables below to write your expression. Note that all variables may not be required.
cos(a), cos(o), cos(0), sin(a), sin(0), sin(0), y, µ, 0, d, g, m1, m2, n, q
Problem 6: Displayed to the right are two carts connected by a cord that passes over a small
frictionless pulley. Each cart rolls freely with negligible friction. Consider the mass of the cart to be
m, and the angle the first cart sits on to be 01, while the mass of the second cart as m, and the angle it
sits on to be 02.
mi
m2
01
Part (a) Considering the positive x direction to be pointing as it is in the image, write an equation for the acceleration that the two blocks
experience in terms of the mass of the first block m1, the angle 0,, the mass of the second block m,, the angle 0,, and the acceleration due to
gravity g.
Expression :
a =
Select from the variables below to write your expression. Note that all variables may not be required.
cos(a), cos(4), cos(01), cos(02), sin(a), sin(4), sin(01), sin(02), a, g, k, m¡, m2, n, q
Part (b) What is the equation for tension in regards to the rope coming from the second block? Answer in terms of the mass
the block m2, the
acceleration due to gravity g, the angle 02, and the acceleration of the blocks found previously a.
Expression :
T =
Select from the variables below to write your expression. Note that all variables may not be required.
cos(a), cos(4), cos(0,), cos(02), k, q, sin(æ), sin(4), sin(0,), sin(0,), a, g, m1, m2, n
Problem 7: Two blocks, which can be modeled as point masses, are connected by a
massless string which passes through a hole in a frictionless table. A tube extends out
of the hole in the table so that the portion of the string between the hole and M1
remains parallel to the top of the table. The blocks have masses M, = 1.4 kg and M, =
2.7 kg. Block 1 is a distance r = 0.85 m from the center of the frictionless surface.
Block 2 hangs vertically underneath.
M
1 of 1
M,
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Ball tied to the end of a 1 m long twine as shown it oscillates around a vertical circle under the influence of gravity. When the string makes an angle of 0 = 90 ° with the vertical, the ball has a velocity of 5 m / s. Find the radial component of the acceleration. aarrow_forwardLearning Goal: To understand Newton's law of universal gravitation and be able to apply it in two-object situations and (collinear) three-object situations; to distinguish between the use of G and g. In the late 1600s, Isaac Newton proposed a rule to quantify the attractive force known as gravity between objects that have mass, such as those shown in the figure. (Figure 1) Newton's law of universal gravitation describes the magnitude of the attractive gravitational force Fg between two objects with masses m₁ and m₂ as F₁ = G ( m₂ where r is the distance between the centers of the two objects and G is the gravitational constant. Figure m1m2 The gravitational force is attractive, so in the figure it pulls to the right on m₁ (toward m₂) and toward the left on m2 (toward m₁). The gravitational force acting on m₁ is equal in magnitude to, but exactly opposite in direction from, the gravitational force acting on m2, as required by Newton's third law. The magnitude of both forces is…arrow_forwardThe first linear graph shows that the Force of Gravity depends is directly proportional to the mass of an object at a given location. The second linear graph shows that the Force of Gravity is proportional to the Inverse Square of the distance between two bodies. Research Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation, and explain.arrow_forward
- What would be the acceleration of gravity (in m/s2) at the surface of a world with seven times Earth's mass and nine times its radius? HINT m/s2arrow_forwardA very dedicated physics student decides to ride the elevator in Strode while standing on a scale. The student weighs 700 N. Determine the apparent weight the student reads on the scale for the following 3 situations:a. The elevator is accelerating upwards at 3 m/s^2.b. The elevator is moving upwards at 7 m/s. c. The elevator is accelerating downwards at 4 m/s^2. Please include known values, a diagram, and implied values so I can better understand.arrow_forwardWhat would be the acceleration of gravity (in m/s2) at the surface of a world with five times Earth's mass and eight times its radius? HINT m/s2arrow_forward
- Explain why astronauts float in space and describe the state of weightlessness.arrow_forwardI Review The Attraction of Ceres Ceres, the largest asteroid known, has a mass of roughly 8.7 x 1020kg. Part A If Ceres passes within 1.2x104 km of the spaceship in which a 66 kg astronaut is traveling, what force does it exert on she? (Treat the astronaut and the asteroid as point objects.) Express your answer using two significant figures. ? F = N Submit Request Answerarrow_forwardDescribe the relationship between Mass and Acceleration - is this linear? Why or why not? Use your graph and your data table as evidence to support your answer.arrow_forward
- es. Use the information below to answer parts a-c. The International Space Station (ISS) orbits the Earth at an altitude (distance above the surface of the Earth) of 408 km, conducting various experiments in a "weightless" environment. ISC and MENG UI an ob questio11 IS b) Calculate the acceleration of the ISS. (Any constant values needed for your calculation can be found on your Physics 20 data sheets.)arrow_forwardPlease explain and solve the given questionarrow_forwardplease indicate answer choice as i.e A,B,C,D or Earrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON