
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
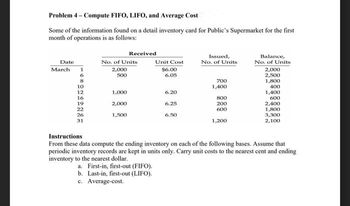
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 4- Compute FIFO, LIFO, and Average Cost
Some of the information found on a detail inventory card for Public's Supermarket for the first
month of operations is as follows:
Date
March 1
6
8
10
12
16
19
22
26
31
No. of Units
2,000
500
1,000
2,000
Received
1,500
Unit Cost
$6.00
6.05
6.20
6.25
6.50
Issued,
No. of Units
700
1,400
800
200
600
1,200
Balance,
No. of Units
2,000
2,500
1,800
400
1,400
600
2,400
1,800
3,300
2,100
Instructions
From these data compute the ending inventory on each of the following bases. Assume that
periodic inventory records are kept in units only. Carry unit costs to the nearest cent and ending
inventory to the nearest dollar.
a. First-in, first-out (FIFO).
b. Last-in, first-out (LIFO).
c. Average-cost.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- January 1 January 12 January 24 January 28 Balance: 30 units @ 40 units @ 3 units @ 50 units @ $35 per unit $36 per unit $36 per unit $50 per unit Purchases: Purchase Return: Sales: The company uses the last in first out (LIFO) method of accounting for inventory. All purc and sales are done on account. Record all required entries related to inventory movemer order of occurrence using the period method (NOT THE PERPETUAL). Action/Date Periodic Method Beginning 1/1 Purchase 1/12 Return 1/24 Sales 1/28 Adjustment 1/31arrow_forwardQuestion-based on, "using Weighted Average cost"... I have tried it but unable to get the correct answer. Any help would be appreciated.arrow_forwardAy 3. item Beta. Units. Cost The following three identical units of items PX2T are purchased during April April 2 Purchase 1 $104 April 15 Purchase 1 108 April 20. Purchase. 1. 112 Total. 3. $324 Average cost per unit. $108. ($324 ~ 3 units) Assume that one unit is sold on April 27 for $152. Determine the gross profit for April and ending inventory on April 30 using the (a) first -in, first-out (FIFO); (b) last-in, first-out (LIFO); and (c)weighted average cost method a. First-in, first-out (FIFO). Gross Profit. Ending Inventory b. Last-in, first-out (LIFO) c. Weighted average carrow_forward
- Date Nov. 1 Nov. 10 Nov. 15 Nov. 20 November 1 Nov. 24 Nov. 30 10 15 20 24 30 15 X Inventory 27 units at $88 The business maintains a perpetual inventory system, costing by the first-in, first-out method. Sale a. Determine the cost of the goods sold for each sale and the inventory balance after each sale, presenting the data in the form illustrated in Exhibit 3. Under FIFO, if units are in inventory at two different costs, enter the units with the LOWER unit cost first in the Cost of Goods Sold Unit Cost column and in the Inventory Unit Cost column. Purchase Sale Sale Purchase 59 units at $81 48 units. 33 units at $84 17 units 18 units. Quantity Purchases Purchases Purchased Unit Cost Total Cost Cost of the Goods Sold Schedule First-in, First-out Method DVD Players Cost of Cost of Quantity Goods Sold Goods Sold Inventory Inventory Inventory Sold Unit Cost Total Cost Quantity Unit Cost Total Cost O UD 000 8 00 00arrow_forwardQuestion 3 Use the following information for question 3 (i) and (ii). (i) Beacon Factory, Inc. uses a perpetual inventory system. The company's beginning inventory and purchases of a particular product during the month of May were as follows: Quantity Unit Cost ($) Beginning inventory (1 May) 32 5 Purchases (11 May.) 46 7.5 Purchase (25 May.) 28 6 On 24 May, Beacon Factory, Inc. sold 50 units of this product. The other units remained in inventory at 3 1 May. (i) Refer to the above data. Assuming that Beacon Factory uses the FIFO flow assumption, the ending inventory at 31 May is: A: $268. B: $295. C: $378. D: $405. (ii) Refer to the above data. Assuming that Beacon Factory uses the weighted average cost flow assumption, the cost of goods sold to be recorded at 24 May is: A: $323. B: $308. C: $273 D: $347.arrow_forwardPerpetual Inventory Using LIFO The following units of a particular item were available for sale during the calendar year: Jan. 1 Inventory 3,800 units at $41 Apr. 19 Sale 2,500 units June 30 Purchase 4,600 units at $45 Sept. 2 Sale 4,900 units Nov. 15 Purchase 1,800 units at $48 The firm maintains a perpetual inventory system. Determine the cost of goods sold for each sale and the inventory balance after each sale, assuming the last-in, first-out method. Present the data in the form illustrated in Exhibit 4. Under LIFO, if units are in inventory at two or more different costs, enter the units with the LOWER unit cost first in the Inventory Unit Cost column. Schedule of Cost of Goods Sold LIFO Method Pukchases Cost of Goods Sold Inventory Date Quantity Unit Cost Total Cost Quantity Unit Cost Total Cost Quantity Unit Cost Total Cost Jan. 1 Apr. 19 June 30 Sept. 2arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education