
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780078022159
Author: Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
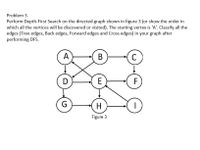
Transcribed Image Text:**Problem 3**
Perform Depth-First Search on the directed graph shown in Figure 3 (or show the order in which all the vertices will be discovered or visited). The starting vertex is ‘A’. Classify all the edges (Tree edges, Back edges, Forward edges, and Cross edges) in your graph after performing DFS.
**Figure 3 Description:**
The graph consists of the following vertices and directed edges:
- Vertices: A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I
- Directed edges:
- A to B
- A to D
- B to C
- C to F
- D to E
- E to B
- E to F
- E to H
- G to D
- G to H
- H to I
To perform Depth-First Search (DFS) starting from vertex A, we follow the paths down to the deepest nodes and backtrack. The classification of edges involves:
- **Tree Edges**: Part of the DFS tree, leading to a new vertex.
- **Back Edges**: Point back to ancestors in the DFS tree.
- **Forward Edges**: Point to descendants that aren't direct children in the DFS.
- **Cross Edges**: All other edges, which connect vertices in the same level or across different branches, not in the DFS tree path.
Proceed with these definitions to perform DFS and classify the edges accordingly.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Single mistake will dislikearrow_forwardRelaxing the Edges |V|+1 times on a directed graph will compute whether the graph has negative cycle or not True or Falsearrow_forwardHow many entries would the adjacency list representation for the following graph contain? (Assume that the array slots for each vertex count as one entry, and the linked list nodes for edges each count as one entry as well.) D B E A F Garrow_forward
- We have the following directed graph G, where the number on each edge is the cost of the edge. 1. Step through Dijkstra’s Algorithm on the graph starting from vertex s, and complete the table below to show what the arrays d and p are at each step of the algorithm. For any vertex x, d[x] stores the current shortest distance from s to x, and p[x] stores the current parent vertex of x. 2. After you complete the table, provide the returned shortest path from s to t and the cost of the path.arrow_forwardConsider the following graph: a Specify a simple cycle. Use only lower case letters. If the graph has any cycles which are not simple and which have no repeated edges, specify one. If there are none enter none Use only lower case letters.arrow_forward1. Run DFS-with-timing on this graph G: give the pre and post number of each vertex. Whenever there is a choice of vertices to explore, always pick the one that is alphabetically first. 2. Draw the meta-graph of G. 3. What is the minimum number of edges you must add to G to make it strongly connected (i.e., it consists of a single connected component after adding these edges)? Give such a set of edges. b.arrow_forward
- One can model a maze by having a vertex for a starting point, a finishing point, dead ends, and all the points in the maze where more than one path can be taken, and then connecting the vertices according to the paths in the maze. a. Construct such a graph for the following maze. 鷗 b. Which traversal DFS or BFS- would you use if you found yourself in a maze and why?arrow_forwardAlert dont submit AI generated answer. Write a program that reads a weighted graph and an initial vertex.The program must print on the screen the minimum paths obtained by Dijkstra's algorithm. Input: Receives n, m and s; n is the total number of vertices, m the total number of arcs and s is the initial vertex.Next, m lines, each line with a trio of integers, corresponding to the beginning and end of the arc, followed by the weight of the arc.(Vertices are identified from 0 to n-1.) Output: Prints the shortest paths obtained by Dijkstra's algorithm. Exemple: Input: 5 10 00 1 100 4 51 2 11 4 22 3 43 2 63 0 74 1 34 2 94 3 2 Output: [0, 8, 9, 7, 5][-1, 4, 1, 4, 0]arrow_forward2. Consider the graph G2(V2, E2) below. 2a. Find the MST of this graph with Kruskal’s algorithm. Draw the MST, and show the table [edge] [w(u, v)] [mark]. 2b. Find the MST of this graph with Prim’s algorithm starting at vertex 'a'. Draw the MST and list the vertices in order you added them to the MST. 2c. Would you get a different MST if you repeat 2b starting at vertex 'e'? Why or why not?arrow_forward
- A. Let G be a graph on 17 vertices. We know that G contains at most one cycle. How many edges can G contain at the most? B. The expression r is written in post-order notation (also referred to as RPN). What value does r evaluate to? r = 1 6 7 + - 5 3 + 2 * +arrow_forwardPlease make a graph by hand for each step. no codearrow_forwardWrite a function that returns true (1) if there is an edge between two vertices u and v in an adjacency-listed directed graph.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education