
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
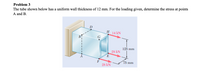
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 3
The tube shown below has a uniform wall thickness of 12 mm. For the loading given, determine the stress at points
A and B.
D
Н 14 kN
G
125 mm
28 kN
E
F
28 kN
75 mm
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 3. A tube 2 mm thick has the shape shown in the figure Find the shearing stress caused by a torque of 600 N m. (Practice at Home) 10 mm - 80 mm 10 mmarrow_forwardThe copper pipe shown in the figure has an outside diameter of 4.000 in. and a wall thickness of 0.363 in. The pipe is subjected to a uniformly distributed torque of t = 80 lb-ft/ft along its entire length. Using a = 2.00 ft, b = 4.00 ft, and c = 7.5 ft, calculate (a) the shear stress at A on the outer surface of the pipe. (b) the shear stress at B on the outer surface of the pipe. a b Answers: (а) ТА i psi (b) Тв- i psiarrow_forwardA strain gage is mounted at an angle of 30° with respect to the longitudinal axis of the cylindrical pressure. The pressure vessel is fabricated from aluminum [E = 10,000 ksi; v=0.33], and it has an inside diameter of 54 in. and a wall thickness of 1.00 in. If the internal pressure in the cylinder is 706 psi, determine the maximum shear strain on the outer surface of the cylinder. Ο Ο Ο Ο 1049 με 1714 με 1600 με 1268 με 1167 μεarrow_forward
- A high-strength steel [E = 188 GPa] tube having an outside diameter of 67 mm and a wall thickness of 4.1 mm is bent into a circular curve having a 42-m radius of curvature. Determine the maximum magnitude of the bending stress max developed in the tube. Answer: Omax = i MPa.arrow_forwardQ..c,.arrow_forwardRequired information The tube shown has a uniform wall thickness of 12 mm. Take P = 19 kN. D HP E 28 KN 28 KN Determine the stress at points A and B. 16.11 MPa. The stress at point A is The stress at point B is MPa. 125 mm 75 mmarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning