
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
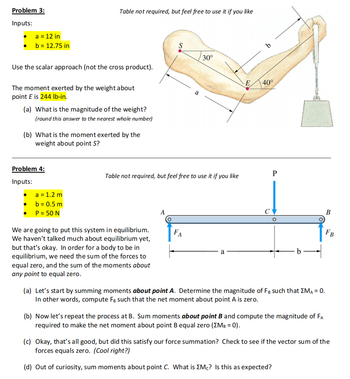
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 3:
Inputs:
a = 12 in
b = 12.75 in
Use the scalar approach (not the cross product).
The moment exerted by the weight about
point E is 244 lb-in.
Table not required, but feel free to use it if you like
(a) What is the magnitude of the weight?
(round this answer to the nearest whole number)
(b) What is the moment exerted by the
weight about point S?
Problem 4:
Inputs:
a = 1.2 m
b = 0.5 m
P = 50 N
We are going to put this system in equilibrium.
We haven't talked much about equilibrium yet,
but that's okay. In order for a body to be in
equilibrium, we need the sum of the forces to
equal zero, and the sum of the moments about
any point to equal zero.
S
A
Table not required, but feel free to use it if you like
a
FA
30°
a
E
b
40°
P
b
(a) Let's start by summing moments about point A. Determine the magnitude of FB such that EMA = 0.
In other words, compute FB such that the net moment about point A is zero.
(b) Now let's repeat the process at B. Sum moments about point B and compute the magnitude of FA
required to make the net moment about point B equal zero (XMB = 0).
B
FB
(c) Okay, that's all good, but did this satisfy our force summation? Check to see if the vector sum of the
forces equals zero. (Cool right?)
(d) Out of curiosity, sum moments about point C. What is Mc? Is this as expected?
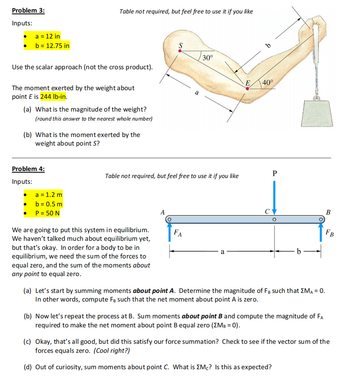
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 3:
Inputs:
a = 12 in
b = 12.75 in
Use the scalar approach (not the cross product).
The moment exerted by the weight about
point E is 244 lb-in.
Table not required, but feel free to use it if you like
(a) What is the magnitude of the weight?
(round this answer to the nearest whole number)
(b) What is the moment exerted by the
weight about point S?
Problem 4:
Inputs:
a = 1.2 m
b = 0.5 m
P = 50 N
We are going to put this system in equilibrium.
We haven't talked much about equilibrium yet,
but that's okay. In order for a body to be in
equilibrium, we need the sum of the forces to
equal zero, and the sum of the moments about
any point to equal zero.
S
A
Table not required, but feel free to use it if you like
a
FA
30°
a
E
b
40°
P
b
(a) Let's start by summing moments about point A. Determine the magnitude of FB such that EMA = 0.
In other words, compute FB such that the net moment about point A is zero.
(b) Now let's repeat the process at B. Sum moments about point B and compute the magnitude of FA
required to make the net moment about point B equal zero (XMB = 0).
B
FB
(c) Okay, that's all good, but did this satisfy our force summation? Check to see if the vector sum of the
forces equals zero. (Cool right?)
(d) Out of curiosity, sum moments about point C. What is Mc? Is this as expected?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 4) Determine the total moment caused by the forces Fp4 and Fca about the plate diagonal that goes through point B (the dashed line). Write your answer in cartesian vector notation. FCA= 500 lb 14 ft FRA = 350 Ib FDA= 400 lb 3 ft-> 3 ft 3 ft 2 t 6 ftarrow_forwardFind the Nominal force, N in kilo Newtons (kN). What is the shear force, V in kilo Newtons (kN). Find the bending moment, M in kilo Newton metres (kNm).arrow_forwardNeeds Complete typed solution with 100 % accuracy.arrow_forward
- Pivot A constant density bar with mass m and length Lis held in place as shown. Use the usual x,y,z coordinates for the following questions. Celling Cable 12. Measuring from the pivot, in the space below draw the torque-pic for the weight force exerted on the bar. Be sure your torque-pic includes both an expression for r in terms of L and also the value for the angle between r and weight force. Bar 350 Length = Larrow_forwardShow work step by step by hand calculations clearlyarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY