
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
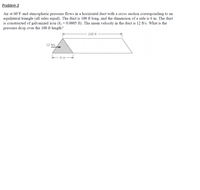
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 3
Air at 60°F and atmospheric pressure flows in a horizontal duct with a cross section corresponding to an
equilateral triangle (all sides equal). The duct is 100 ft long, and the dimension of a side is 6 in. The duct
is constructed of galvanized iron (k; = 0.0005 ft). The mean velocity in the duct is 12 ft/s. What is the
pressure drop over the 100 ft length?
- 100 ft
12 ft/s
f 6 in -
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A joining elbow on horizontal plane is shown in the figure. The fluid is water and assumed to be ideal. Pipe 2 is open to the atmosphere. The flow velocity of pipe 2 is given as Uz = [2+ (k/10)] m/s, and pressure at pipe 3 is p3 = 1.6 + k/ 4 kPa. (k=5) a) Calculate the flow velocity at pipe 3 (u3 = ?) b) Calculate the discharge and flow velocity of pipe 1 (Q = ?, ui = ?). c) Calculate the pressure at pipe 1 (p. = ?). d) Calculate the x and y components of the net force acting on the joining elbow by the fluid. Draw the force vector. Atmosfer dz-25 cm d;=40 cm d;=25 cm 3 300arrow_forwardHeavy machine tool lubricating oil (ref. Appendix C applied fluid mechanics) is pumped through six rectangular slots in a heat exchanger (oil flows in the white rectangles in section view a-a) as shown below. You may assume that the oil flows through the heat exchanger with a constant temperature of 40°C. If the flow rate from A to B is 3 cm³/sec determine the Reynolds number for the oil flow. Is the flow laminar or turbulent?arrow_forwardQuestion 2A large vat contains water, which contains a drainage pipe at a height h1, as shown infigure 2. The drainage pipe has a length L. = 0.4 m, and a radius R = 15 mm, and releaseswater to the atmosphere at a flow rate Q. The connection between the pipe and the vatwall has a loss coefficient of KL = 0.8.Point A is in the middle of the tank at a height, hi.You can assume that the flow in the drainage pipe is fully developed and laminar. The density of water is p = 1000 kg/m° and the viscosity is u = 1 mPa.s. The acceleration due to gravity is 9.81 m/s? a) Find an expression for the pressure at point A.b) Find an expression in terms of Q, L, d, K, p and u for the pressure losses along the pipe (including the losses at the inlet and exit).c) If the flowrate out of the drainage tank is Q = 50 L/min, find ho. You may assumeany change of ho with time is negligible.arrow_forward
- Problem 5. A horizontal rough pipe with surface roughness of 1.5 × 104 m is used to transport pressurized air at a flow rate of 7 × 102 m³/s. The design guidance requires that the pressure drop must be no more than 4.2 kPa per 50 m length of the pipe. Determine the minimum diameter of the pipearrow_forwardThe diagram shown illustrates the flow in a circular metal duct 20 feet long. The duct has a sudden contraction at the inlet and sudden expansion at the outlet. The diameter of the duct is 10 inches and the flow rate is 600 cfm. The duct is such that both ends have area ratio of 0.6. Thus A2/A1 = A3/A4 = 0.6. Calculate: Total pressure loss in the duct (in. wg.).arrow_forwardProblem 1 – A laminar flow fluid of known density (ρ) and viscosity (μ) flows between twoparallel plates with different velocities in the same direction. The top plate has a velocity Utop inthe positive x direction. The bottom plate has a velocity Ubot in the positive x direction. The twoplates are a distance of “a” apart. There is a pressure gradient in the x direction ( ). Derivean expression of the velocity and shear stress profiles between the two platesarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY