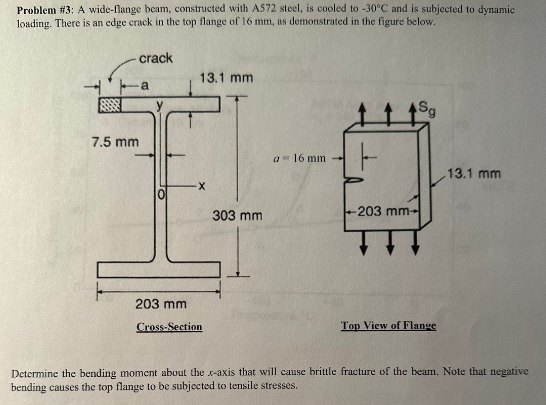
Problem #3: A wide-flange beam, constructed with A572 steel, is cooled to -30°C and is subjected to dynamic loading. There is an edge crack in the top flange of 16 mm, as demonstrated in the figure below. 7.5 mm crack a y 13.1 mm -X 203 mm Cross-Section 303 mm a = 16 mm 203 mm- Sg Top View of Flange 13.1 mm Determine the bending moment about the x-axis that will cause brittle fracture of the beam. Note that negative bending causes the top flange to be subjected to tensile stresses.
Problem #3: A wide-flange beam, constructed with A572 steel, is cooled to -30°C and is subjected to dynamic loading. There is an edge crack in the top flange of 16 mm, as demonstrated in the figure below. 7.5 mm crack a y 13.1 mm -X 203 mm Cross-Section 303 mm a = 16 mm 203 mm- Sg Top View of Flange 13.1 mm Determine the bending moment about the x-axis that will cause brittle fracture of the beam. Note that negative bending causes the top flange to be subjected to tensile stresses.
Chapter2: Loads On Structures
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Problem #3: A wide-flange beam, constructed with A572 steel, is cooled to -30°C and is subjected to dynamic
loading. There is an edge crack in the top flange of 16 mm, as demonstrated in the figure below.
Hints:
4
●
7.5 mm
crack
a
y
13.1 mm
X
203 mm
Cross-Section
303 mm
a = 16 mm
ㅏ
↑
203 mm-
Sg
Top View of Flange
Determine the bending moment about the x-axis that will cause brittle fracture of the beam. Note that negative
bending causes the top flange to be subjected to tensile stresses.
13.1 mm
As illustrated in the figure above, treat the top flange as an edge-cracked tension member. Use the
simplified expression for computing K, but still verify that it applies.
The average stress in the top flange can be determined by an My/I calculation, as opposed to a P/A
calculation from previous problems. Compute y based on the mid-depth of the top flange.
Ignore the "fillets" (i.e., the rounded portions of the I-section) when calculating the moment of inertia, I.
Expert Solution
Step 1 : Data
Step by step
Solved in 6 steps with 11 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780134610672
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780134610672
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780073398006
Author:
Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305156241
Author:
Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning