
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
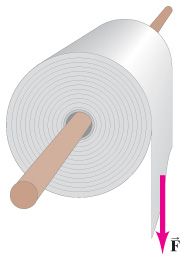
Problem 11 : The radius of the roll of paper shown in the figure (Figure 1) is 7.5 cm and its moment of inertia is I = 3.5×10−3 kg⋅m2 . A force of 2.5 N is exerted on the end of the roll for 1.0 s , but the paper does not tear so it begins to unroll. A constant friction torque of 0.12 m⋅N is exerted on the roll which gradually brings it to a stop.
Part A
Assuming that the paper's thickness is negligible, calculate the length of paper that unrolls during the time that the force is applied (1.0 s ).
Express your answer using two significant figures.
Part B
Assuming that the paper's thickness is negligible, calculate the length of paper that unrolls from the time the force ends to the time when the roll has stopped moving.
Express your answer using two significant figures.
Transcribed Image Text:F
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Problem 2: When a 3.75-kg fan, having blades 22.5 cm long, is turned off, its angular speed decreases uniformly from 11.0 rad/s to 7.20 rad/s in 6.00 s. (a) What is the magnitude of the angular acceleration of the fan? (2 pts) (b) Through what angle (in degrees) does it turn while it is slowing down during the 6.00 s? (1 pt) (c) If its angular acceleration does not change, how long after it is turned off does it take the fan to stop.arrow_forwardCalculate the rotational inertia of a meter stick, with mass 0.642 kg, about an axis perpendicular to the stick and located at the 38.3 cm mark. (Treat the stick as a thin rod.)arrow_forwardProblem 6 A figure skater enters into a spin with arms outstretched. This body position gives them a moment of inertia of 2.4 kg m². They're initially spinning through 1.2 revolutions per second. Then, with no external torques acting on them, they pull their arms in close to their body, reducing their moment of inertia to 0.4 kg m². What is their angular velocity after they pull their arms in? Don't forget units! cadarrow_forward
- The outstretched hands and arms of a figure skater preparing for a spin can be considered a slender rod pivoting about an axis through its center (Figure 1). When his hands and arms are brought in and wrapped around his body to execute the spin, the hands and arms can be considered a thin-walled hollow cylinder. His hands and arms have a combined mass 8.0 kg. When outstretched, they span 1.7 m; when wrapped, they form a thin- walled hollow cylinder of radius 23 cm. The moment of inertia about the rotation axis of the remainder of his body is constant and equal to 0.4 kg. m². For related problemsolving tips and strategies, you may want to view a Video Tutor Solution of Anyone can be a ballerina. Figure 1 of 1 TI Part A If his original angular speed is 0.50 rev/s, what is his final angular speed? Express your answer in revolutions per second. 15| ΑΣΦ W2 = 1.03 Submit Previous Answers Request Answer X Incorrect; Try Again; 8 attempts remaining Provide Feedback ? rev/sarrow_forward5 A rigid body is undergoing planar motion with the velocity of its center of mass vc = 2 m/s i + 5 m/s j and an angular velocity of 10 rad/s k. If a force of 10N i and a couple of 2 Nm k is applied to the body, what is the rate of its kinetic energy change with respect to time? 40 W 54 W 74 W 20 Warrow_forwardThe triceps muscle in the back of the upper arm extends the forearm. This muscle in a professional boxer exerts a force of 2967 N with an effective perpendicular lever arm of 3.40 cm, producing an angular acceleration of the forearm of 130.0 rad / s². What is the moment of inertia of the boxer's forearm? moment of inertia: kg m? Question Credit: OpenStax College Physicsarrow_forward
- A solid uniform spherical boulder travels down a hill. At the top of the hill the boulder is rolling with a horizontal speed of 5 m/s. The top half of the hill is rough, so that the boulder continues to roll without slipping. The bottom half of the hill and the valley is covered in smooth ice, so that there is no static friction between the boulder and the hill. How fast is the boulder moving when it gets to the bottom of the hill? What is its rotational speed in the valley if the boulder has a radius of 10 cm? Rough 50.0 m Smootharrow_forwardThe fly wheel is an important mechanical element in machines that is used to increase the moment of inertia of the machine and store rotational kinetic energy. A fly wheel of an engine starts rotating about a fixed axis from rest to 102 rad/s in 6.3 seconds. The wheel has a radius of 0.5 meters and mass of 88 kg. Calculate the net torque acting on the fly wheel during the time interval t = 0; 6.3 s measured in Nm (Enter the number only).arrow_forwardA 270-g mass hangs from a string that is wrapped around a pulley, as shown in the figure. The pulley is suspended in such a way that it can rotate freely. When the mass is released, it accelerates toward the floor as the string unwinds. Model the pulley as a uniform solid cylinder of mass 1.00 kg and radius 5.00 cm. Assume that the thread has negligible mass and does not slip or stretch as it unwinds. Determine the magnitude a of the pulley's angular acceleration. 344 rad/s? Incorrect Determine the magnitude of the acceleration a of the descending weight. a = m/s? Question Source: Freedman College Physics 3e | Publarrow_forward
- The wheel of radius R shown below consists of a hoop of massm and two thin rods, each of mass M. Calculate the moment of inertia of the wheel about an axis going through its center, perpendicular to the plane of the hoop, for the values listed below. Express your answer in kg m2 to three significant figures. R= 2.28 m m = 0.372 kg M= 0.288 kgarrow_forwardThe triceps muscle in the back of the upper arm extends the forearm. This muscle in a professional boxer exerts a force of 1559 N with an effective perpendicular lever arm of 3.25 cm, producing an angular acceleration of the forearm of 110.0 rad / s?. What is the moment of inertia of the boxer's forearm? moment of inertia: kg m?arrow_forwardA rope with a negligible mass has two blocks that are suspended over a pulley, m, and M, as shown in the image. The pulley can be considered as a uniform solid cylindrical disk. What is the equation for the net torque on the disc? Assume acceleration of blocks are a=(1/2)(9.8m/s2). What is the moment of inertia for this shape? (using the net torque equation from the above question, substitute the moment of inertia) The angular acceleration is correlated to the linear acceleration as α=r. Make the substitution into the torque equation in order to get the equation in terms of acceleration, α only.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON