
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Can you answer problem 1 in this image?
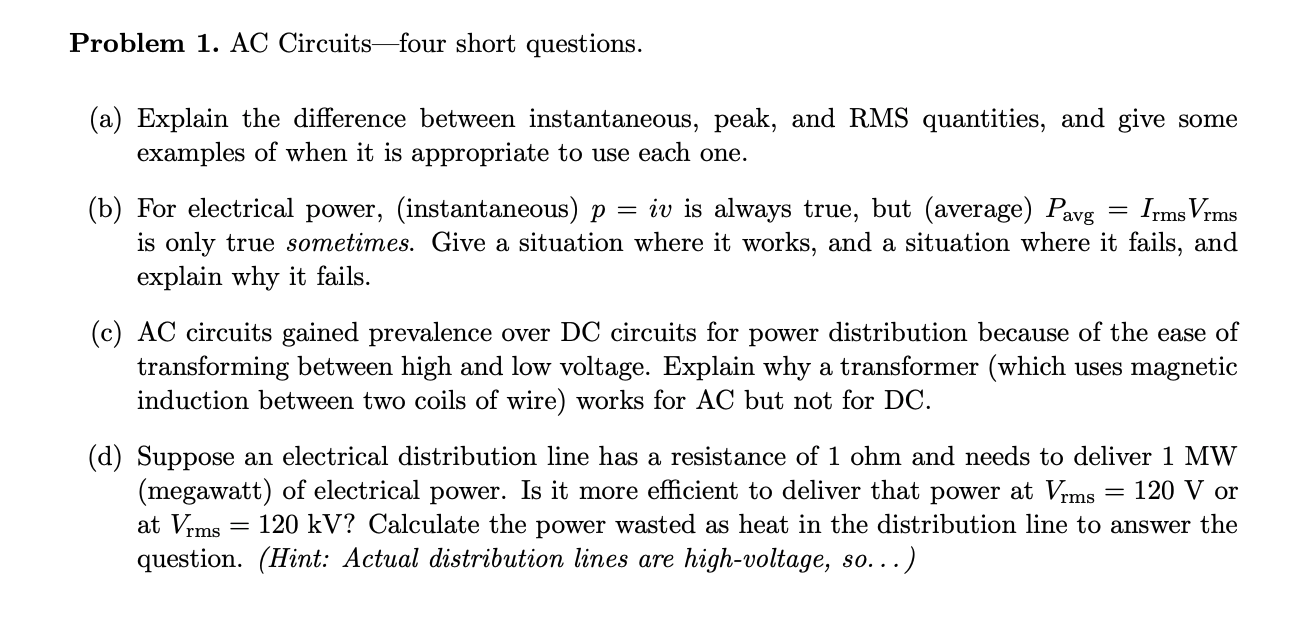
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 1. AC Circuits-four short questions.
(a) Explain the difference between instantaneous, peak, and RMS quantities, and give some
examples of when it is appropriate to use each one.
(b) For electrical power, (instantaneous) p
is only true sometimes. Give a situation where it works, and a situation where it fails, and
explain why it fails.
= iv is always true, but (average) Pavg
Irms Vrms
(c) AC circuits gained prevalence over DC circuits for power distribution because of the ease of
transforming between high and low voltage. Explain why a transformer (which uses magnetic
induction between two coils of wire) works for AC but not for DC.
(d) Suppose an electrical distribution line has a resistance of 1 ohm and needs to deliver 1 MW
(megawatt) of electrical power. Is it more efficient to deliver that power at Vrms
at Vrms
question. (Hint: Actual distribution lines are high-voltage, so...)
= 120 V or
120 kV? Calculate the power wasted as heat in the distribution line to answer the
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 12 cm tall bbject is placed 15 cm away from a convex miror of radius of curvature r=60 cm. How tall is the resulting image? Select one: t of Oa. -18 cm b. 18 cm O c. -8 cm O d. 8 cmarrow_forwardA2.71-cm-high insect is 1.24 m from a 135-mm-focal-length lens. Where is the image? O in front the lens O behind the lens How high is the image? Express your answer with the appropriate units. ? h = Value Unitsarrow_forwardWhich option is best to do among (a-d)? USE IMAGE AS REFERENCE.arrow_forward
- Please answer question 2, answer 1 is in the 2nd imagearrow_forwardAn air bubble inside a plastic ball with a diameter of 20.0 cm is 7.0 cm from the surface. When you look at the ball in the configuration in the figure below (observer, center of the ball, and bubble are on the same straight line), at what distance from the center of the ball will the image form? Consider nₚₗₐₛₜ=1.6 and nₐᵣ = 1 a)5.85 cm to the right of the center of the ball b)5.85 cm left of center of ball c)4.85 cm right from center of ball d)4.85 cm left from center of ball e)3.85 cm right from center of ball f)3.85 cm left from center of ball g)6.85 cm right from center of ball h)6.85 cm left from center of ball i)7.85 cm right from center of ball j)7.85 cm left from center of ballarrow_forwardChapter 34, Problem 034 SN When an object is placed a distance p in front of a spherical refracting surface with radius of curvature r, the image distance is i. If the index of refraction of the surrounding material Is n1, what is the index of refraction of the refracting material? State your answer in terms of the given variables. n2 = 2 Editarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON