Question
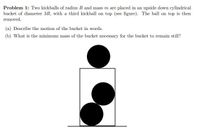
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 1: Two kickballs of radius R and mass m are placed in an upside down cylindrical
bucket of diameter 3R, with a third kickball on top (see figure). The ball on top is then
removed.
(a) Describe the motion of the bucket in words.
(b) What is the minimum mass of the bucket necessary for the bucket to remain still?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A ball weighing 800 grams and having a radius of 2cm moves in the direction of the positive x-axis at a speed of 5m/s. It collides with another stationary ball weighing 500 grams and also having a radius of 2cm. The collision occurs off-center, with the vertical components of the centers of the balls differing by 1cm. Following the collision, the lighter ball attains a speed of 3m/s. Determine the velocity of the heavier ball after the collision and calculate the amount of energy lost during the collision.arrow_forwardA meteoroid is moving towards a planet. It has mass m = 0.54×109 kg and speed v1 = 4.7×107 m/s at distance R1 = 1.6×107 m from the center of the planet. The radius of the planet is R = 0.78×107 m. The mass of the planet is M = 5.6×1025kg. There is no air around the planet. a)Enter an expression for the total energy E of the meteoroid at R, the surface of the planet, in terms of defined quantities and v, the meteoroid’s speed when it reaches the planet’s surface. Select from the variables below to write your expression. Note that all variables may not be required.α, β, θ, d, g, G, h, m, M, P, R, R1, t, v, v1 b)Enter an expression for v, the meteoroid’s speed at the planet’s surface, in terms of G, M, v1, R1, and R. c)Calculate the value of v in meters per second.arrow_forwardA conical pendulum is set up with a bob whose mass is 6.0 kg. When it is set in motion, at a speed of 0.60 m/s, the string makes a 12.0 degree angle with the vertical. a) Find the radius of the horizontal circle the conical pendulum traces out. b) Find the length of the string.c) Find the magnitude of the tension in the string.arrow_forward
- Please do part barrow_forwardA package of mass 7 kg sits at the equator of an airless asteroid of mass 4.0 1020 kg and radius 5.9 105 m. We want to launch the package in such a way that it will never come back, and when it is very far from the asteroid it will be traveling with speed 188 m/s. We have a large and powerful spring whose stiffness is 2.1 105 N/m. How much must we compress the spring?arrow_forward2. A 45.0 kg boy is initially seated on the top of a hemispherical ice mound of radius 20.0 m. He begins to slide down the ice, with a negligible initial speed. Assume the ice is frictionless. a. At what height does the boy lose contact with the ice. b. What is acting as a radial force?arrow_forward
- Two blocks, which can be modeled as point masses, are connected by a massless string which passes through a hole in a frictionless table. A tube extends out of the hole in the table so that the portion of the string between the hole and M1 remains parallel to the top of the table. The blocks have masses M1 = 1.4 kg and M2 = 2.1 kg. Block 1 is a distance r = 0.85 m from the center of the frictionless surface. Block 2 hangs vertically underneath. a) Assume that block two, M2, does not move relative to the table and that block one, M1, is rotating around the table. What is the speed of block one, M1, in meters per second? b) How much time, in seconds, does it take for block one, M1, to make one revolution?arrow_forwardProblem 1: The figure shows a small sphere of mass m a distance D from the edge of a uniform rod of length L and mass M placed perpendicularly to the rod. The left edge of the rod is placed at the origin of an xy coordinate system. The x-direction points to the right, and the y-direction points up in the figure shown.The rod has a mass of 6.1 kg and the small sphere's mass is half the mass of the rod. The distance D = 1.4 m and the rod has a length of 1.4 m. What is the magnitude of the gravitational force, in newtons, of the ball?arrow_forwardTwo blocks, which can be modeled as point masses are connected by a massless string which passes through a hole in a frictionless table. A tube extends out of the hole in the table so that the portion of the string between the hole and M1 remains parallel to the top of the table l. The blocks have masses M1 = 1.2 kg and M2 = 2.5 kg. Block 1 is a distance r = 0.85 m from the center of the frictionless surface. Block 2 hangs vertically underneath Assume that block two, M2 does not move relative to the table and that the block one M1 is rotating around the table. What is the speed of block one, M1, in meters per second?arrow_forward
- The Moon is 60 Earth radii (i.e. 60 rEarth) from the center of the Earth and has a mass of 0.012 Earth masses (i.e. 0.012 mEarth) a. How many Earth radii is the center of mass (the “barycenter”) of the Earth-Moon system from the center of the Earth? b. Is the center of mass inside the Earth or outside the Earth? c. What point along the line from the center of the Earth to the center of the Moon orbits the barycenter of the Solar System in a (nearly) circular orbit (e.g. the center of the Earth, the barycenter of the Earth-Moon system, the midpoint, the center of the Moon)?arrow_forwardYou have a summer internship at NASA and are working on plans for a new space station to be launched into orbit around the Earth. The design of the space station is shown. i It is to be constructed in the shape of a hollow ring of mass 52,000 kg. The structures other than the ring shown in the figure have negligible mass compared to the ring. Members of the crew will walk on a deck formed by the inner surface of the outer cylindrical wall of the ring, with radius r = 140 m. The thickness of the ring is very small compared to the radius, so we can model the ring as a hoop. At rest when constructed, the ring is to be set rotating about its axis so that the people standing inside on this deck experience an effective free-fall acceleration equal to g. The rotation is achieved by firing two small rockets attached tangentially to opposite points on the rim of the ring. Your supervisor asks you to determine the following: (a) the time interval during which the rockets must be fired if each…arrow_forwardGrab a meter stick or any uniform thin piece of wood about 1m in length. (e.g. the handle of a broom with the head removed). Place your index fingers at either end so that you are holding the stick up with just two fingers. Move your fingers slowly together. Where do they end up? Describe the motion of your fingers. Explain why this happens.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios