
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
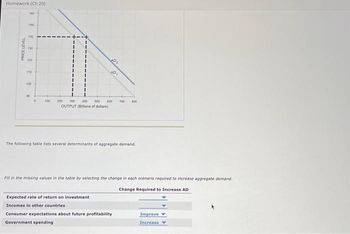
Transcribed Image Text:Homework (Ch 20)
PRICE LEVEL
160
150
140
130
120
110
100
8
II
II
II
II
AD₂
AD₁
0 100 200 300 400 500 000 700 800
OUTPUT (Billions of dollars)
The following table lists several determinants of aggregate demand.
Fill in the missing values in the table by selecting the change in each scenario required to increase aggregate demand.
Change Required to Increase AD
Expected rate of return on investment
Incomes in other countries
Consumer expectations about future profitability
Government spending
Improve
Increase
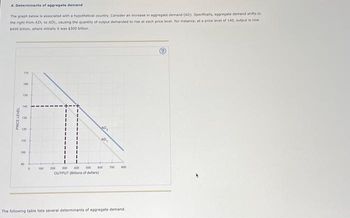
Transcribed Image Text:4. Determinants of aggregate demand
The graph below is associated with a hypothetical country. Consider an increase in aggregate demand (AD). Specifically, aggregate demand shifts to
the right from AD, to AD,, causing the quantity of output demanded to rise at each price level. For instance, at a price level of 140, output is now
$400 billion, where initially it was $300 billion
PRICE LEVEL
170
160
130
130
120
110
100
8
0
II
200
100
II
II
II
I
I
100
300 400
OUTPUT (Billions of dollars)
AD₁
600
700
800
The following table lists several determinants of aggregate demand.
(2)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Look at Figure 2. Assume this aggregate demand diagram represents an economy with government, where: a = exogenous consumption b = the marginal propensity to consume t = the tax rate |= investment G = government spending Y = income Figure 2 Aggregate demand AD, AD. 45° Income What is the equation for the aggregate demand schedule ADo? Select one: O ADO = b+ a(1 - t)G +1+ Y O ADO = a + b(1 – 1)Y + 1+ G O ADO = a + b(1 - t) I+ Y+ G O ADO = b+ a(1 – 1)Y + /+ G Next page > ( Previous page PHILIPSarrow_forward3. Determinants of aggregate demand The following graph shows an increase in aggregate demand (AD) in a hypothetical country. Specifically, aggregate demand shifts to the right from AD₁ to AD2, causing the quantity of output demanded to rise at all price levels. For example, at a price level of 140, output is now $400 billion, where previously it was $300 billion. 170 PRICE LEVEL 160 150 140 120 110 100 90 0 +--+ AD2 AD1 600 100 200 300 400 500 OUTPUT (Billions of dollars) 700 800arrow_forward1. Which of the following could cause a shift from AD to AD₁, ceteris paribus? PRICE LEVEL a a Figure 10.1 REAL OUTPUT ($ billions per year) B) an increase in exports A) a decrease in investment AD OC) an increase in consumer confidence OD) an increase in consumption AS 4arrow_forward
- 10-8. Assume that the position of a nation's aggregate demand curve has not changed, but the long-run equilibrium price level has declined. Other things being equal, which of the following factors might account for this event? a. An increase in labor productivity b. A decrease in the capital stock c. A decrease in the quantity of money in circulation d. The discovery of new mineral resources used to produce various goods e. A technological improvementarrow_forwardSuppose that the economy is initially in long-run equilibrium with the price level of 800. Now suppose that the Aggregate Demand (AD) curve shifts left from AD1 (blue) to AD2 (green). 1200 ADX 1100- 1000 Price Level ADX 900- 800 700 600 50% RASI 400* 300- 200 100- LRAS 400 500 600 700 100 200 300 Real GDP What is the new price level in the short-run as a result of this shift? 800 900 1000 1100 120 aarrow_forwardThe figure given below represents the equilibrium real GDP and price level in the aggregate demand and aggregate supply model. Figure 8.3 U.S. Price Level 100 m 9 AS₁ to AS3 AS₁ to AS₂ AD₂ toAD3 O AD₂ to AD₁ O AD₁ to AD₂ AS AS₁ 200 300 400 500 Real GDP (billions of dollars) AD AS₂ In Figure 8.3, which of the following shifts would result in stagflation (economic stagnation and inflation)?arrow_forward
- H1.arrow_forwardThe total expenditure in Macroland begins with these initial levels (in trillions of dollars): autonomous consumption=1, Investment = 2; Net Exports = 0, T=2, and MPC = 0.75. Assume that equilibrium has been achieved. Suddenly there is an external shock and as a result investment goes down to 1. What is the change in GDP? Use the base model to answer this question. Equilibrium GDP goes down by 1 Equilibrium GDP goes up by 1 Equilibrium GDP goes up by 4 Equilibrium GDP goes down by 4arrow_forwardDear expert bro hand written not allowed.arrow_forward
- 8. Which of the following explain why the Aggregate Demand curve is downward sloping? a) An increase in the price level decreases the purchasing power of money denominated wealth, which in turn causes a decline in on consumption spending. b) An increase in the price level decreases the purchasing power of money, which means that more money is needed to purchase goods. This causes buyers of investment and durable goods to require bigger loans to finance their purchases. This, in turn, causes an increase in the demand for loanable funds which leads to a higher interest rate. A higher interest rate will reduce the real purchases of investment and durable goods. c) An increase in the price level makes goods relatively more expensive to foreigners causing them to buy less which means that net exports will decline. d) All of the above. e) None of the above. 9. Which of the following explain why the Aggregate Supply curve is upward sloping?…arrow_forwardWhich of the following will increase the Aggregate Demand curve or shift it to the right? The government passes a big infrastructure improvement spending bill O Interest rates rise The raises personal income taxes The U.S. population experiences a significant contraction in population, decreasing the number of people working and consuming. Question 2 Which of the following will decrease the aggregate supply curve or shift it to the left? New international sanctions on Iranian oil raise the price of oil globally and oil is an input in production of many goods and services A 10 percent across the board reduction in personal income tax rates Business taxes fall A new networking technology increases productivity all over the economyarrow_forwardGraphically show the likely short-run impact on US real GDP and aggregate price level using the AD/AS model. Explain your prediction. Which curve in the AD/AS model would a change in US consumer consumption affect? Note:- Please avoid using ChatGPT and refrain from providing handwritten solutions; otherwise, I will definitely give a downvote. Also, be mindful of plagiarism. Answer completely and accurate answer. Rest assured, you will receive an upvote if the answer is accurate.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education