
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
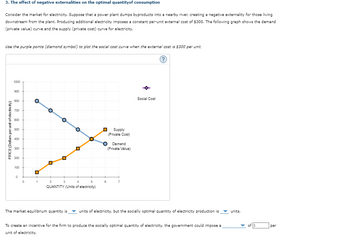
Transcribed Image Text:3. The effect of negative externalities on the optimal quantity of consumption
Consider the market for electricity. Suppose that a power plant dumps byproducts into a nearby river, creating a negative externality for those living
downstream from the plant. Producing additional electricity imposes a constant per-unit external cost of $300. The following graph shows the demand
(private value) curve and the supply (private cost) curve for electricity.
Use the purple points (diamond symbol) to plot the social cost curve when the external cost is $300 per unit.
1000
900
800
700
600
500
400
300
200
PRICE (Dollars per unit of electricity)
100
ப
0
0
1
2
°
3
0
°
4
°
QUANTITY (Units of electricity)
5
6
Supply
(Private Cost)
Demand
(Private Value)
Social Cost
?
The market equilibrium quantity is
units of electricity, but the socially optimal quantity of electricity production is
units.
To create an incentive for the firm to produce the socially optimal quantity of electricity, the government could impose a
unit of electricity.
per
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The following graph shows the demand (marginal private benefits) and supply (marginal private costs) curves for a good. The dashed drop lines on the graph reflect the market equilibrium price and quantity for this good. Suppose that a positive externality arises as a result of the production of this good. Adjust the following graph by shifting one of the curves to reflect the presence of the positive externality. PRICE AND COST The market fails in that it overproduces underproduces Supply Demand the good. Demand Supply (?)arrow_forwardUse the following supply and demand graph to answer the question below. S₁ S₂ Price J E 0 A B с Quantity D₂ -D₁ S₁ and D₁ represent the current market supply and demand, respectively. S2 and D2 represent the socially optimal supply and demand. The positions of the graphs indicate that there is (are) external Multiple Choice costs from production and consumption of the product. costs from production and external benefits from consumption of the product.arrow_forwardConsider a market with the following supply and demand. (It may help to draw a graph for these questions.) P 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 QS 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 1100 QD 800 750 700 650 600 550 500 450 400 350 If there is an external cost of $3, what is the efficient quantity? 500 (already answer) If there is an external benefit of $3, what is the efficient quantity? 700 (already answer) For the remaining questions assume that there is a $3 external COST. If the government wants to get the efficient quantity with a per/unit tax, how much should the tax be? 3 (already answer) Now imagine that they use tradable allowances. If they cap the quantity at 400 what would the value of these allowance be in the market? (Assume the…arrow_forward
- Compared to a good with no externalities, a good with a negative externality appear to have experienced a will at each corresponding price. OIncrease in Supply ODecrease in Supply OIncrease in Demand ODecrease in Demandarrow_forwardThe Cemex plant in Davenport produced cement. The production of cement created dust which traveled through the air and landed on the nearby area. Testing at an elementary school and fire department near the plant showed toxic levels of Chromium 6 resulting from the dust. Using the concept of externalities and the graph below, explain what kind of externality this event created and the effects this had on economic efficiency. Be sure to indicate any differences between market price and quantity for cement and the efficient price and quantity.arrow_forwardThe supply and demand conditions facing a firm that makes widgets and generates a negative externality by dumping a highly toxic sludge in a nearby river is given in the table below. Price Quantity Demanded Quantity Supplied without Paying Social Costs Quantity Supplied after Paying Social Costs 100 0 120 75 80 10 100 50 55 30 90 30 40 55 85 25 30 80 80 20 20 100 65 15 The equilibrium price and quantity when social costs are taken into account are Question 12 options: Price = $55, Quantity = 30 Price = $40, Quantity = 55 Price = $30, Quantity = 20 Price = $30, Quantity = 80arrow_forward
- Consider the market for electricity. Suppose that a power plant dumps byproducts into a nearby river, creating a negative externality for those living downstream from the plant. Producing additional electricity imposes a constant per-unit external cost of $240. The following graph shows the demand (private value) curve and the supply (private cost) curve for electricity. Use the purple points (diamond symbol) to plot the social cost curve when the external cost is $240 per unit. PRICE (Dollars per unit of electricity) 800 720 640 560 480 400+ 320 240 Supply (Private Cost) Demand (Private Value) 160 [- 80 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 QUANTITY (Units of electricity) Social Cost ? The market equilibrium quantity is units of electricity, but the socially optimal quantity of electricity production is units. To create an incentive for the firm to produce the socially optimal quantity of electricity, the government could impose a unit of electricity. of perarrow_forwardConsider a market with the following supply and demand. (It may help to draw a graph for these questions.) P 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 QS 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 1100 QD 800 750 700 650 600 550 500 450 400 350 If there is an external cost of $3, what is the efficient quantity? If there is an external benefit of $3, what is the efficient quantity? For the remaining questions assume that there is a $3 external COST. If the government wants to get the efficient quantity with a per/unit tax, how much should the tax be? Now imagine that they use tradable allowances. If they cap the quantity at 400 what would the value of these allowance be in the market? (Assume the market is perfectly competitive and that "one allowance" lets you…arrow_forwardAn intermediate microeconomics questionarrow_forward
- You have the following supply and demand curves for an industry: QSX = -100 + 3 * PX for PX >= $40 QDX = 300 – 2 * PX However, this industry causes pollution damage to third parties. Each quantity produced creates pollution that causes equal damage, such that the marginal external cost is a constant $20 per unit (MEC= $20). a) Calculate the price quantity combinations for both the perfectly competitive and the efficient solution. Graphically show both solutions as well. Make sure you label all curves and axes. b) What efficient tax would move the competitive market to the efficient solution?arrow_forwardThe graph above shows the market for paper. The marginal social cost is higher than the marginal private cost A)since the marginal social cost includes all the costs of production, including the value of the externality B)since the marginal private cost includes all the costs of production, including the value of the externality C)because there is no externality in this market D)because for each level of production the social cost is less than the private costarrow_forwardThe market for seasonal flu shots is depicted in the graph. As more people receive flu shots, fewer people catch the flu and potentially pass it on to others. Therefore, the chance of catching the flu decreases for everyone, even those who do not purchase a flu shot. This is an example of a positive externality. The graph contains the private demand curve (D1) and the supply curve. D1 does not take into consideration the social benefit of people getting flu shots. Graph the social demand curve by placing the end points of D2 at the correct locations. Then, indicate the dead weight loss to society by placing the DWL triangle in the correct location on the graph. The Market for Flu Vaccinations D2 (marginal soeial benefit) DWL supply D1 (marginal private benefit) Quantity of flu shots Price ($)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education