
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
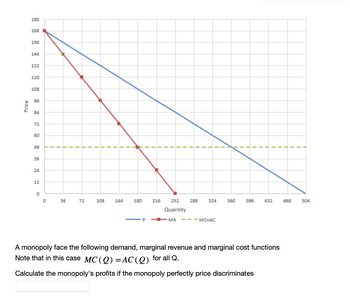
Transcribed Image Text:**Educational Content: Monopoly Economics**
**Graph Explanation:**
The graph illustrates the demand, marginal revenue, and marginal cost functions for a monopoly.
- The **blue line** represents the demand curve (P), which is downward sloping, indicating that as quantity increases, the price decreases.
- The **red line** is the marginal revenue (MR) curve. It lies below the demand curve and also slopes downward.
- The **green dashed line** represents both the marginal cost (MC) and average cost (AC) curve, as stated in the description. This line is horizontal, indicating constant marginal and average costs for all quantities.
**Key Concept:**
- In this scenario, the marginal cost is equal to the average cost for all quantities (MC(Q) = AC(Q)).
**Task:**
Calculate the monopoly's profits if the monopoly perfectly price discriminates.
**Note:**
In the context of perfect price discrimination, the monopoly can charge each consumer the maximum price they are willing to pay, capturing all consumer surplus as additional profit.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Costs & Revenue INELASTIC MARKET ELASTIC MARKET COMBINED MARKET X2 X1 P2 P1 AR Y1 MC .. MC1 MC2 -MC ATC Y2 AR AR MR MR Output Q1 Q2 Capyright: www.economicsonline.co.uk MR a) Looking from the price perspective what kind of monopoly is presented cumulatively in all three diagrams? b) explain what are the diagrams are explaining? Support them with the example of your choice.arrow_forwardYou have been granted a monopoly in the avocado market. The market demand for avocados is Q = 2000 – 2P. Your cost structure is such that your total costs are TC = 1000+ 400Q. (limit: whatever needed) What is your profit maximizing price and quantity? Explain this in words and show it graphically. What are the profit, producer surplus and consumer surplus? The government is thinking about breaking your monopoly into ten identical firms and giving ownership to 10 random people. Correspondingly, each firm would have a fixed cost of $1000 and a marginal production cost of $400 per unit. In this perfectly competitive environment, what would be the equilibrium price and quantity? Explain this in words and show it graphically. What are the profit per firm, producer surplus and consumer surplus that correspond to your answer to part d)? How much would you be willing to pay to keep the government from taking your monopoly away? Explain.arrow_forwardThe accompanying graph depicts the marginal revenue (MR), demand (D), and marginal cost (MC) curves for a monopoly a. Place point Pi at the profit maximizing price and quantitvy assuming that the monopolist can only charge a single price. 100 95 90 85 80 75 70 65 2 60 b. What are the profits of the firm if it charges a single price? 50 45 Suppose the monopolist able to successfully price discriminate between two groups by charging one group $60 and charging $35 to the other group. c. What are the firm's profits if it charges the two prices as mentioned above? 35 30 25 20 15 10 MR 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95100 Quantityarrow_forward
- Suppose a monopolist faces a demand equation given by P=20-Q, and a marginal revenue equation given by MR = 20-2Q, and MC=AVC=ATC=$6. What is the deadweight loss associated with the monopolist? a) $8.5 b) $33.25 c) $24.5 d) $12.5arrow_forwardThe figure below represents the cost and revenue structure for a monopoly firm. Cost and Revenue($) Pot Q₂ Q₂ Q₂Q₂ Quantity A profit-maximizing monopoly's total revenue is equal to: a. P3 x Q₂ b. P₂ x Q4 C. (P3-Po) x Q₂ d. (P3-Po) x Q4arrow_forwardIf a monopoly firm can sell 12 items per day at a price of $150 each, and to increase sales by one (marginal) item per day, the monopolist must lower price to $148, calculate the marginal revenue of the 13th item:arrow_forward
- Consider the local telephone company, a natural monopoly. The following graph shows the demand curve for phone services, the company's marginal revenue curve (labeled MR), its marginal cost curve (labeled MC), and its average total cost curve (labeled AC). (Hint: Click a point on the graph to see its exact coordinates.) PRICE (Dollars per month) 160 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 0 1 MR 2 3 4 567 QUANTITY (Thousands of households per month) AC MC D 8 (?)arrow_forwardYou operate a monopoly with demand, marginal revenue and marginal cost depicted in the graph below. What price and quantity (approximately) should you charge if you want to maximize profit? 10 9 7 MC 6 D 1 MR 1 4 9. 10 Quantity Q* = 5.8 and P* = 4.2 Q 5.8 and P* 2.9 %3D Q = 3.5 and P* 3 Q 3.5 and P* = 6.5 Price 4.arrow_forwardWhich lettered point (i.e. A,B,C,D) is at the price-quantity combination that would exist under an unregulated monopoly? Which lettered point (i.e. A,B,C,D) is at the price-quantity combination that would be efficient, from society’s perspective? Which lettered point (i.e. A,B,C,D) is at the price-quantity combination that, in theory, the regulator aims for? Send to: Everyonearrow_forward
- Refer to the table below. What is the total cost if the monopoly operates at the profit - maximizing output? Price($) Quantity TR ($) TC ($) 5 2 10 8 4 4 16 10 3 6 18 12 2 8 16 18 1 10 10 25arrow_forwardAnswer everything in the photo please.arrow_forward↑ If a monopoly faces an inverse demand curve of p=270-Q has a constant marginal and average cost of $90, and can perfectly price discriminate, what is its profit? What are the consumer surplus, welfare, and deadweight loss? How would these results change if the firm were a single-price monopoly? Profit from perfect price discrimination (x) is $ 16.200 (Enter your response as a whole number) Corresponding consumer surplus is (enter your response as whole numbers): welfare is and deadweight loss is CS=$ W-s OWL-Sarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education