
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:**Pre-Lab Equilibrium Questions:**
1) **In Figure 1 in manual:**
- \( F_1 = 185.0 \, \text{gm-wt} \)
- \( F_2 = 205.0 \, \text{gm-wt} \)
- \( \theta_1 = 35.0 \, \text{degrees} \) and \( \theta_2 = 56.0 \, \text{degrees} \)
a) Determine the magnitude and direction of \( F_3 \).
2) **In figures 3 and 4, \( AM = 14.4 \, \text{cm} \):**
- \( F_2 = 165 \, \text{gm-wt} \) and \( \theta_2 = 56.0 \, \text{degrees} \)
Calculate torque of \( F_2 \) about the point \( A \) and sense of rotation.
3) **In figures 3 and 4, \( AN = 13.4 \, \text{cm} \):**
- \( F_3 = 75 \, \text{gm-wt} \) and \( \theta_3 = 79.0 \, \text{degrees} \)
Calculate torque of \( F_3 \) about the point \( A \) and sense of rotation.
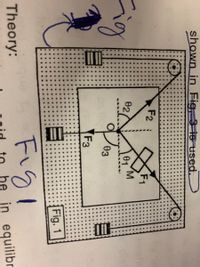
Transcribed Image Text:## Transcription for Educational Website
### Theory:
The diagram labeled as Fig. 1 illustrates a physical setup involving forces and angles. This setup is used to demonstrate the conditions required for equilibrium in a system.
### Diagram Explanation:
1. **Diagram Elements:**
- There are three forces, denoted as \( F_1 \), \( F_2 \), and \( F_3 \).
- The forces converge at a point labeled \( M \).
- Angles \( \theta_1 \), \( \theta_2 \), and \( \theta_3 \) are formed between the forces and the lines connecting them.
- The system includes pulleys depicted as circles with ropes looping around them.
2. **Setup Configuration:**
- \( F_1 \) is directed towards the bottom right corner, creating angle \( \theta_1 \) with the horizontal.
- \( F_2 \) points upwards and to the right, forming angle \( \theta_2 \).
- \( F_3 \) is directed horizontally to the left, along \( \theta_3 \).
3. **Additional Details:**
- The diagram includes shading to differentiate sections, suggesting a surface or base.
- The illustration might be part of a lab experiment aimed at exploring mechanical equilibriums, where vector addition or balancing is required.
This setup highlights the principles of equilibrium, demonstrating how forces interact in a balanced system and the significance of angles and directions in vector analysis.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- K, F, & T are shown below. K 37, F = 47, & T = 48. Let R = SK - 9F + ST. Determine the com You are expected to know how to draw vectors and may be asked to do so on a test. Vector K Vector F Vector T R Direction of R Submit Answer KU 50 ||Fx = | 50 60* Ry o relative to the HORIZONTAL in quadrant - Choose quadrant - Vector R 11arrow_forwardItem 15 Review Part A Let vectors A (2,1, 4). B (3,0,1). and C Calculate the following: (-1,-1,2) View Available Hintis) A.B Subni Part B What is the angle 0An behween A and B? Express your answer using one significant figure View Available Hint(s) radians Subrnitarrow_forwardA object is moving from ground at 70 meter per second and an angle of 75 degrees from horizontal. what is the horizontal dispalcement when the object reaches the ground? a. 226 m b. 154 m c. 250 m d. 125 m e. 233 marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON