
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
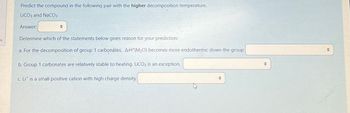
Transcribed Image Text:Predict the compound in the following pair with the higher decomposition temperature.
LICO3 and NaCO3
Answer:
+
Determine which of the statements below gives reason for your prediction:
a. For the decomposition of group 1 carbonates, ArH (M₂O) becomes more endothermic down the group
b. Group 1 carbonates are relatively stable to heating. LiCO3 is an exception.
c. Lit is a small positive cation with high charge density
→
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Calculate the heat of reaction per mole of water if addition of 25.0 mL of 0.101 M H,SOA to 50.0 mL of 0.103 M NaOH causes the temperature to rise by 0.99°C.arrow_forwardGiven the standard enthalpy changes for the following two reactions:(1) N2(g) + 2O2(g) -> 2NO2(g)...... ΔH° = 66.4 kJ(2) 2N2O(g) -> 2N2(g) + O2(g)......ΔH° = -164.2 kJwhat is the standard enthalpy change for the reaction:(3) 2N2O(g) + 3O2(g) -> 4NO2(g)......ΔH° = ?_____ kJarrow_forwardplease help with the following! I believe the answer can either be 881, -881, or 852arrow_forward
- 1. How many kJ of energy are released by 34.65 g of boron? Ti + 2 B -> TiB2 △ H = 316 kJ/mol 2. How much energy in kJ is released when 14.17 g of aluminum react with an excess of copper oxide? 3 CuO + 2 Al -> 3 Cu + Al2O3 △ H = 1190 kJ/mol 3. If 36.26 grams of aluminum is heated from 18 oC to 26 oC how much energy was required? sAl = 0.897 J/(gK)arrow_forwardPart A Calculate the enthalpy of the reaction 2NO(g) + O2(9)–→2NO2(9) given the following reactions and enthalpies of formation: A N2(9) + O2(g)→NO2(9), AfH = 33.2 kJ mol 1 B. N2 (9) + ¿O2(9)→NO(g), AfHß = 90.2 kJ mol 1 Express your answer with the appropriate units. • View Available Hint(s) ? A¢H° = Value Units Submitarrow_forwardCalculate the heat of reaction per mole of water if addition of 25.0 mL of 0.101 M A H2SO4 to 50.0 mL of 0.103 M NaOH causes the temperature to rise by 0.99°C. Assume that for both solutions the density is 1.00 g/mol and the specific heat (s) = 4.184 J/g°C. %3Darrow_forward
- Using the thermodynamic tables find the enthalpy of formation for BaCO3 (s) a. none of these b. – 1.29 x 103 kJ c. + 314.4 kJ d. – 1219 kJ e. – 628.8 kJ f. – 5.16 x 103 kJ g. – 314.4 kJarrow_forwardThe reaction of CH3OH(g) with N2(g) to give HCN(g), NH3(g), and O2(g) requires 164 kJ/mol of CH3OH(g). Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction. Include the phases of all species in the reaction. How much heat is involved in the reaction of 65.0 g of CH3OH(g) with excess N2(g) to give HCN(g) and NH3(g) in this reaction?arrow_forward2. Please calculate the standard enthalpy of reaction (AHrxn, in kJ/mol) for the preparation of nitrous acid, HNO2, using the thermodynamic data given below. Preparation of nitrous acid: HCl(g) + NaNO2(s) → HNO2(1) + NaCl(s) 2NaCl(s) + H₂O(l) → 2HCl(g) + Na₂O(s) NO(g) + NO₂(g) + Na2O(s) → 2NaNO2 (s) NO(g) + NO₂(g) → N₂O(g) + O₂(g) 2HNO2(1)→ N₂O(g) + O2(g) + H₂O(g) H₂O(1)→ H₂O(g) ΔΗ = 507.31 kJ/mol AH = -427.14 kJ/mol AH = - 42.68 kJ/mol 34.35 kJ/mol ΔΗ ΔΗ = 44.012 kJ/mol =arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY