
Practise Post Lab Questions for Heating under reflux-Wintergreen oil
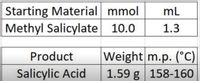
HERE IS A LITTLE BACKGROUND INFORMATION AND SEE PICTURE FOR DATA COLLECTED
Background Information:
PURPOSE
- Convert wintergreen oil into salicylic acid using aqueous base.
- Hydrolyze esters under basic conditions
- Reflux a reaction
- Perform a vacuum filtration
Esters can be converted to
Since the pKa value for salicylic acid is 2.98, the pH needs to be substantially lower than this to maximize the amount of salicylic acid that is recovered. After acidification, the mixture can be cooled briefly and collected by vacuum filtration. The identity of the product will be confirmed by melting point.
PROCEDURE
Add 10.0 mmol of methyl salicylate to a 50 mL round-bottom flask. Then, add 15 mL of 6 M sodium hydroxide to the same flask. Assemble an apparatus for reflux and attach the flask to the condenser. Be sure to grease all joints and use Keck clips as needed. Using a heating mantle, heat the reaction mixture to reflux and allow the reaction to continue to reflux for 30 minutes. At this point, the reaction mixture should no longer be cloudy. If it is still cloudy, continue to reflux for an additional 10-15 minutes. Once the mixture is no longer cloudy, remove the flask from the heat source.
When the flask is cool enough to handle, transfer the reaction mixture to a 125 mL beaker. Slowly add 16 mL of 3.0 M sulfuric acid to the beaker and carefully stir the mixture with a glass rod. Dip a clean pipet or stir rod into the mixture and touch the pipet to a small piece of pH paper. The pH should be close to 2 or lower to ensure that the carboxylate has been protonated. Add a little more acid if needed. At this point, the mixture should also be cloudy. Cool the mixture in an ice bath for 10-15 minutes, then collect the product by vacuum filtration. Allow the product to dry until the following lab period, then determine the yield and melting point.
Clean up and waste disposal: The filtrate can be disposed of in the acidic inorganic waste. All of the glassware can be rinsed with water then acetone. The dry glassware can be returned to the drawer or kit.
TABLE OF PROPERTIES
|
Compound |
MM (g/mol) |
mp (oC) |
Density |
|
Wintergreen oil (methyl salicylate) |
152.1 |
--- |
1.17 g/mL |
|
Salicylic acid |
138.1 |
159 |
--- |
1. Practise question: From the picture of the final data collection. Determine the yields and melting point.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 1 images

- Which of the following statements is false with respect to this reaction? Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer. a) this is an example of an oxidation b) mCPBA is an oxidant c) mCPBA is a carboxylic acid d) the ketone is being oxidized to an ester e) the product is an esterarrow_forwardWrite TRUE if the statement is correct, FALSE if otherwise. 11. Both fats and oils are mixtures of esters containing both saturated and unsaturated compounds. 12. Fats and oils are esters made from glycerol and long chain carboxylic acids. 13. Potassium iodide is used as a solubilizing agent. 14. The greater the iodine number, the greater the number of double bonds. 15.Butter, beef fat and lard have high iodine numbers.arrow_forwardI need help pleasearrow_forward
- What starting material is needed to form a secondary alcohol using H2/Pt? A. Aldehyde B. Ester C. Amide D. Alkene E. Ketone F. Carboxylic acid 2. Which starting material is/are a needed to form an anode and water using the reagent H+/ heat ( choose all that apply) - carboxylic acid - amine - ketone -aldehyde -carboxylate ion -ammonium ion alcoholarrow_forwardFunctional Groups 1. In squares below, hand-draw chemical structures of the following, circle bolded functional groups. Acetoacetic acid Ethyl butyrate Trimethylamine (carboxylic acid) (ester)arrow_forwardWhy are esters popular? Give examples of where you can find these compounds.arrow_forward
- Create balanced chemical reactions for the following reactions. Organic reactions should be written with the line-angle drawing of each structure. 1. Reacting salicylic acid with acetic anhydride to form acetylsalicylic acid, with the use of sulfuric acid as a catalyst. 2. Water reacting with acetic anhydride to form acetic acid.arrow_forward4. Assume that an esterification reaction is done using 0.10 moles of a carboxylic acid and 1.0 moles of an alcohol. What is the theoretical yield (in moles) for the reaction? (You can write a generic esterification reaction to help answer this question and recognize the limiting reagent.) 5. A student completes the reaction described in question 4 and obtains 5.3 g of the product (the product has a molecular mass of 74.0 g/mol). a) What is the actual yield (the moles of product obtained)? Show your calculation, including units. 5.3 g product X mol products b) Calculate the % yield for the reaction. Show your calculation, including units.arrow_forwardChoose the products that can be made when using an ester as the starting material. You may assume that necessary reagents are present. Choose all that apply. carboxylic acid acid anhydride amide ester alkenearrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





