
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
Can anyone do second part?

Transcribed Image Text:Positive sample
negative sample
5. Unbound labeled antibody is washed away and a colorimetric substrate is added. Draw this below
Positive sample
negative sample
6. The enzyme cleaves the substrate causing a color change of the substrate solution. The intensity of
the color is quantified using a spectrophotometer and is proportional to the amount of antibody
how to do that?).
present in the sample. (Obviously, a standard curve would have to be generated. Could you think of
Positive sample
negative sample
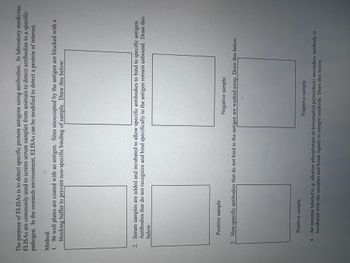
Transcribed Image Text:The purpose of ELISAS is to detect specific protein antigens using antibodies. In laboratory medicine,
ELISAS are commonly used to screen serum samples from animals to detect antibodies to a specific
pathogen. In the research environment, ELISAS can be modified to detect a protein of interest.
Method:
1. 96 well plates are coated with an antigen. Sites unoccupied by the antigen are blocked with a
blocking buffer to prevent non-specific binding of sample. Draw this below:
2. Serum samples are added and incubated to allow specific antibodies to bind to specific antigen.
Antibodies that do not recognize and bind specifically to the antigen remain unbound. Draw this
below:
Positive sample
Negative sample
3. Non-specific antibodies that do not bind to the antigen are washed away. Draw this below.
Positive sample
Negative sample
4. An enzyme labeled (e.g. alkaline phosphatase or horseradish peroxidase) secondary antibody is
incubated with the samples and binds tightly to sample antibody. Draw this below.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
Can you do the first part?
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Question

Transcribed Image Text:Method:
1. 96 well plates are coated with an antigen. Sites unoccupied by the antigen are blocked with a
blocking buffer to prevent non-specific binding of sample. Draw this below:
2. Serum samples are added and incubated to allow specific antibodies to bind to specific antigen.
Antibodies that do not recognize and bind specifically to the antigen remain unbound. Draw this
below:
Positive sample
Negative sample
3. Non-specific antibodies that do not bind to the antigen are washed away. Draw this below.
Positive sample
Negative sample
4. An enzyme labeled (e.g. alkaline phosphatase or horseradish peroxidase) secondary antibody is
incubated with the samples and binds tightly to sample antibody. Draw this below.
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
Can you do the first part?
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Question

Transcribed Image Text:Method:
1. 96 well plates are coated with an antigen. Sites unoccupied by the antigen are blocked with a
blocking buffer to prevent non-specific binding of sample. Draw this below:
2. Serum samples are added and incubated to allow specific antibodies to bind to specific antigen.
Antibodies that do not recognize and bind specifically to the antigen remain unbound. Draw this
below:
Positive sample
Negative sample
3. Non-specific antibodies that do not bind to the antigen are washed away. Draw this below.
Positive sample
Negative sample
4. An enzyme labeled (e.g. alkaline phosphatase or horseradish peroxidase) secondary antibody is
incubated with the samples and binds tightly to sample antibody. Draw this below.
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- According to the text,, what is deep one-handed effleurage called?arrow_forwardA woman in substantial pain called her doctor and explained (between sobs) that she was about to have her baby "right here:' The doctor calmed her and asked how she had come to that conclusion. She said that her water had broken and that her husband could see the baby's head. (a) Was she right? If so, what stage of labor was she in? (b) Do you think that she had time to make it to the hospital 60 miles away? Why or why not?arrow_forwardthe middle menix is the?arrow_forward
- Standard 7a Rodents can make vocalizations that humans can hear, such as a squeal. But they also can communicate during social interactions using ultrasonic vocalizations - vocalizations at a frequency higher than the human ear is capable of hearing. Sex differences in vocal communication, similar to observations in songbirds, are observed In rats, with adult male rats eliciting a typical type of ultrasonic vocalizations not observed in females. As noted elsewhere in this Problem Set, FOXP2 is involved in the development and neural control of vocalizations in a broad spectrum of species, including rodents. In humans it is linked to human speech and language disorders. In rats, FOXP2 has been related to sex-specific vocalizations, like the male-typical ultrasonic vocalizations. FOXP2 expression in neurons in the brain is greater in males than females. Further, recent research demonstrated that FOXP2 is a target of activated androgen receptors (Le specialize receptors that bind androgens…arrow_forwardwhat stage of development does the ‘baby’ implant asarrow_forwardWhat do you mean by labium?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education