
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
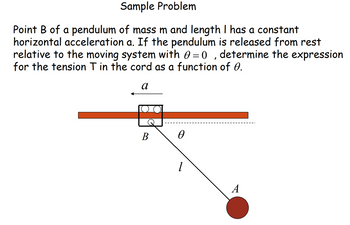
Transcribed Image Text:Sample Problem
Point B of a pendulum of mass m and length I has a constant
horizontal acceleration a. If the pendulum is released from rest
relative to the moving system with = 0, determine the expression
for the tension T in the cord as a function of 0.
а
B
Ꮎ
1
A
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1) A loaded wheelbarrow is pulled to the left with an acceleration a = 2 m / s? by a force P. In this motion, the wheelbarrow does not rotate and the force of friction as well as the effect of the rotation of the wheel may be neglected. The combined mass of the wheelbarrow and its load is 250 kg with center of mass at G. For this instant, determine the horizontal and vertical components of the force P and the normal reaction at B. a P G beal 60 cm 50 cm 1 m 20 cmarrow_forwardThe slider of mass m is released from rest in position A and slides without friction along the vertical‐plane guide shown. Determine the height h such that the normal force exerted by the guide on the slider is zero as the slider passes point C. For this value of h, determine the normal force as the slider passes point B.arrow_forward3/169 The 3-kg sphere is carried by the parallelogram linkage where the spring is unstretched when = 90°. If the mechanism is released from rest at 0 = 90°, calculate the velocity v of the sphere when the position = 135° is passed. The links are in the vertical plane, and their mass is small and may be neglected. 0 I.. 500 mm www 3 kg wˇˇˇˇˇˇˇˇˇˇwwwwww k = 100 N/m 500 mm I.. 500 mm Problem 3/169arrow_forward
- 4. A loading car is at rest on a track forming an angle of 25° with the vertical when a force is applied to the cable attached at C. The gross weight of the car and its load is 5465 lb WG, and it acts at point G. Know the tension in the cable connected at C is 5000 Ib Tc. Neglect friction between the car and the track. Determine how far the car travels in 15 seconds. Model this as a particle at G. 24 in. B 25 in. 30 in. 25 in.arrow_forwardA force of P = 340 N is applied to the 70-kg cart. The mass center of the cart is at G Determine the reaction at both the wheels at A. Determine the reaction at both the wheels at B. What is the acceleration of the cart?arrow_forwardA simple pendulum of mass m = 10 kg and length r= 1 m is mounted on the flatcar, which has a constant horizontal acceleration a = 1 m/s as shown. If the pendulum is released from rest relative to the flatcar at the position 0 = 0 deg, determine the expression for the tension Tin the supporting light rod for 0 = 45 deg and A = 90 deg.arrow_forward
- The weights of block A and cylinder B of Fig. are WA = 250 lb and Wg = 100 lb. If the coefficient of friction is 0.35 for all surfaces, determine the minimum force P required for equilibrium. B 30arrow_forwardThe slender bar AB with a mass of 60 kg and a length of 4 m is secured by a cable at C, and pivoted to the back of a truck at A. When the truck starts from rest creating an acceleration of 5 m/sec² on the bar in the direction of the arrow, calculate the magnitude of the tension in the cable. Present your answer in Newtons using 3 significant figures. В. 4 m 60° A -2 marrow_forwardA simple pendulum is pivoted at O and is free to swing in the vertical plane of the plate. If the plate is given a constant acceleration a = 2.7 m/s? up the incline e = 26°, find the steady angle ß assumed by the pendulum after all initial start-up oscillations have ceased. Neglect the mass of the slender supporting rod. Answer: B = iarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY