
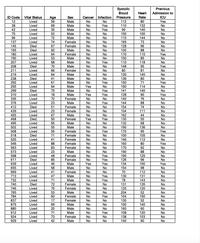
PART II: Now, consider only those who do not have an infection. Repeat #1 - #5 above for these subjects. For #1, make your stemplot back-to-back with the previous stemplot. For #5, make your boxplots side-by- side.
PART II: Now, consider only those who do not have an infection. Repeat #1 - #5 above for these subjects. For #1, make your stemplot back-to-back with the previous stemplot. For #5, make your boxplots side-by- side.
1. For these subjects only, construct a stemplot for the variable “heart rate”. (We will be making this into a back-to-back stemplot later, so leave room on the left side.)
2. Discuss the shape of your stemplot. Is it symmetric? Positively skewed? Negatively skewed? None of these? Are there any outliers?
3. How would you describe the center and the spread of this distribution?
4. Find the five-number summary.
5. Construct a box plot.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

- Find the chara oderietin palynourel of the amatrex 3. 2.arrow_forwardBarry has several Christmas Cactus houseplants. He heard a rumor that they will bloom better if they are put in a dark room from October to November. What experiment could Barry design to test his hypothesis?arrow_forwardPlease share the solution for the last 2 parts (c & d) in bold. The first three parts answered by your team. In a study of the Gouldian finch, Griffith et al. (2011) looked at stress caused by having an incompatible mate.There are two genetically distinct types of Gouldian finches, one having a red face and the other having a black face. Previous experiments have shown that female finches have a strong preference for mating with males with the same face color as themselves , and that when different face types of finch mate with one another, their offspring are less likely to survive than when both parents are the same type. Researchers paired females sequentially with males of both types in random order,In other words, each female bred twice once with a compatible male and once with an incompatible male.Each time, females produced a brood of young with the assigned male.For each pairing, the researchers measured the blood corticosterone concentration (in units of ng/ml) as an index…arrow_forward
- Continuing on with the four plants. Find each pairwise comparison using the Bonferoni correction. To do that you will first need to find the number of comparisons, and then the alpha level for each comparison if the overall alpha level is 0.05. g. Find the number of comparisons and the alpha level for each comparison. Write out the math needed to find these numbers. h. Continuing on with the four plants. Find each pairwise comparison using the Bonferoni correction. To do that you will first need to find the number of comparisons, and then the alpha level for each comparison if the overall alpha level is 0.05. g. Find the number of comparisons and the alpha level for each comparison. Write out the math needed to find these numbers. h. Continuing on with the four plants. Find each pairwise comparison using the Bonferoni correction. To do that you will first need to find the number of comparisons, and then the alpha level for each comparison if the overall alpha level is…arrow_forwardMeghan is a psychology major who is testing a maze for a group of mice to navigate. In order for it to be productive for a class project, she would like the average time for a mouse to complete the maze to be 90 seconds. She randomly selects 28 mice and has each mouse complete the maze. Meghan records the time, in seconds, that each mouse needed to complete the maze. The results are provided in the accompanying data table. Based on research and previous results, Meghan assumes that the population is normally distributed and the population standard deviation is 5.80 seconds. Use Excel to test whether the mean amount of time a mouse completes the maze is 90 seconds, and then draw a conclusion in the context of the problem, where α=0.10. Time (seconds) 85.71 93.16 87.00 89.71 94.26 92.05 86.16 82.16 94.76 HelpCopy to ClipboardDownload CSV Select the correct answer below:…arrow_forwardA certain affects virus 0.4% of the population (in a population of 100,000 people, 400 will be infected with the virus). A test used to detect the virus in a person is positive 87% of the time if the person has the virus (true positive) and it is positive 14% of the time if the person does not have the virus (false positive). Fill in the remainder of the following table and use it to answer the questions below. Infected Not Infected Total Positive Test Negative Test Total 400 99,600 100,000arrow_forward
- Can a person train to become better at holding their breath? An experiment was designed to find out. Twelve volunteers were randomly assigned to 1 of 2 groups. The 6 volunteers assigned to group 1 were given breath-holding exercises to perform for 2 weeks. The other group was not given any information about the experiment. At the end of the 2 weeks, all 12 volunteers were individually tested to determine how long they could hold their breath. Here are the data (in seconds). Group 1: 90, 88, 70, 110, 75, 105 Group 2: 40, 48, 35, 50, 55, 62 The researcher would like to determine if these data provide convincing evidence that the true mean amount of time volunteers who were given training held their breath is greater than volunteers without training. Let ₁ = the true mean amount of time that volunteers who were given training held their breath and ₂ = the true mean amount of time that volunteers without training held their breath. What are the appropriate hypotheses? Ho: U1 - U2 = 0, Ha:…arrow_forwardAs humans we consume food. The body extracts good things such as proteins and vitamins and throws away waste. A typical waste product is uric acid. High levels of uric acid can be an indication of conditions such as gout, kidney disease, and cancer. For females a high level of uric acid is 6 mg/dL or more and for males a high level of uric acid is 7 mg/dL or more. Suppose, over a period of months, an adult female was given 5 blood tests for uric acid. The results of each blood test are shown below. results 6.75 6.68 12.07 10.29 6.68 The distribution of uric acid in healthy adult females is normally distributed with known population standard deviation, σ=2.09σ=2.09 mg/dl.Find a 95% confidence interval for the population mean of uric acid in this adult female's blood. Assume the sample of blood tests were given in a way that's equivalent to a simple random sample. (Round your answers to two decimal places.)margin of error mg/dLlower limit mg/dLupper limit mg/dLDoes this…arrow_forwardElaine is interested in determining if men are more satisfied in their jobs than women in the healthcare industry. She administers a job satisfaction questionnaire to 20 men and 20 women working in hospital administration. Her grouping variable is gender and dependent variable is job satisfaction. The job satisfaction scale consists of 8 items measured using a 5-point rating scale. A higher score on this scale would indicate high job satisfaction. The maximum score that can be obtained on the scale is 40. We can assume that job satisfaction scores are normally distributed. Use the appropriate T test with a significance level of 0.05 to test the hypothesis. Research Question Do the mean job satisfaction scores differ for men and women working in the hospital administration department? Hypothesis The mean job satisfaction scores do not differ for men and women working in the hospital administration department. Compute an independent sample t test on these data. Report…arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





