
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
19
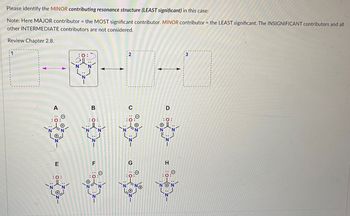
Transcribed Image Text:**Educational Content: Identifying the Minor Contributing Resonance Structure**
**Task:**
Please identify the **MINOR contributing resonance structure** (LEAST significant) in this case:
**Note:**
- MAJOR contributor = the MOST significant contributor.
- MINOR contributor = the LEAST significant.
- INSIGNIFICANT contributors and all other INTERMEDIATE contributors are not considered.
For further understanding, refer to **Chapter 2.8**.
**Diagram Explanation:**
There is a central resonance structure composed of three nitrogen (N) atoms and one oxygen (O) atom, with the resonance indicated by arrows showing the electron delocalization between different forms. The diagrams are labeled 1, 2, and 3 within dashed boxes, but appear empty except for box 2.
Below the primary structure, several potential resonance structures labeled A through H are presented. Each structure represents a different arrangement of electrons and charges around an N-O framework.
- Structures show variations in the positions of electrons (dots) and formal charges (positive and negative).
- Positive charges are indicated as (+) on certain nitrogen atoms, and negative charges (-) are on the oxygen atoms.
By comparing each structure's stability based on formal charges, octet satisfaction, and electron arrangement, determine which structure is the least stable, and thus the MINOR contributor.
This exercise requires understanding the principles of resonance stability, including electronegativity and charge distribution in resonance structures.
Remember to review Chapter 2.8 for a detailed breakdown of resonance principles and contributing factors for structure stability.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1: Writing the objective-
The objective of the question is to predict the minor contributing resonating structure.
The resonating structures are groups of two or more Lewis structures that show the delocalization of electrons.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which of these gemstones is formed in very high pressure conditions? Multiple Choice amethyst opal diamond emeraldarrow_forwardWhat is Indane?arrow_forwardIndique la estereoquímica de A y B respectivamente: F H3C A CH3 H Select one: O a. A: Z; B: E O b. A: Z; B: Z c. A: E; B: Z O d. A: E; B: E F H B Brarrow_forward
- M myMCC | Middlesex College x e Chapter 6 * OWLV2 | Online teaching and X b Answered: A 2.00 g sample o x h Hulu | Watch f → C A A https://east.cengagenow.com/ilrn/takeAssignment/takeCovalentActivity.do?locator=assignment-take G R Tp Apps P Pin FB M Matwa MCCMai Pay -zu:brar I Vitaurce Booksh. e SelfServ M myMCC b b M mail E Reading list P pay Other bookmarks >> Chapter 7 [References] Microwaves have frequencies in the range of 10° to 1012 /s (cycles per second), equivalent to between 1 gigahertz and 1 terahertz. What is the wavelength of microwave radiation whose frequency is 3.780 x 1010 /s? The speed of light is 2.998 × 10° m/s. Question 4 1 pt Question 5 O 1 pt Wavelength = m Question 6 O 1 pt Question 7 1 pt Submit Answer Try Another Version 6 item attempts remaining Question 8 O 1 pt Question 9 O 1 pt Question 10 1 pt Question 11 1 pt Visited Question 12 O 1 pt Question 13 1 pt Question 14 O 1 pt Question 15 1 pt Question 16 1 pt Question 17 O 1 pt Question 18 1 pt Question 19 1…arrow_forward20. What is the major organic product of the following reaction? S: Na* a. I b. 11 Br C. d. ||| ||| IV 'Brarrow_forwardDraw the products  formed when each of the air mites is treated with water and HCLarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY