Question
Please answer question in 20 mintues of this question post. Thank you
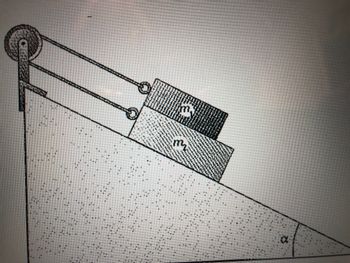
For the system shown, what is the critical angle α (the angle at which the system just begins to move)? Assume that the coefficient of friction between all flat surfaces is 0.06000 and that the pulley is frictionless and massless. The mass of m1=70.0 kg and m2=167 kg. Express the answer in radians.
Transcribed Image Text:**
***
*****
**
******
im
C
****
wwww.
****
www.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
First, construct free-body diagrams of each object involved in the problem (figures that show all the forces acting on each object) in order to solve problems involving rough inclined planes. When necessary, this helps visualize the situation and balance forces.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Please don't provide handwritten solution ....arrow_forwardEach problem requires a proper FBD and separate kinematic diagram.arrow_forwardA bicycle mechanic is checking a road bike's chain. He applies force FF = 21 NN to a pedal at the angle shown in (Figure 1) while keeping the wheel from rotating. The pedal is 17 cmcm from the center of the crank; the gear has a diameter of 16 cmcm. What is the tension in the chain?arrow_forward
- In the setup shown in the figure, ?1=27.0kg, ?=220N, ?= 35°, and ?2=7.0kg. The frictionless pulley has a 0.1 m radius and its moment of inertia is 0.20 kg m^2. The coefficient of kinetic friction between ?1 and the table is 0.2. Calculate the acceleration of ?1.arrow_forwardThe angular position as a function of time of a rotating cylinder is giving by: θ(t) = 2.50(rad/s2)t2 – 0.60(rad/s3)t3. Find the maximum angular speed of the cylinder. Use calculus. show full work when differentiating.arrow_forwardPlease answer fastarrow_forward
- A thin- walled cylinder of radius 50 cm, mass 1.0 kg, is mounted on a frictionless, horizontal axle as in Figure 1 . A light cord wrapped around the wheel supports an object of mass 2 kg. When the wheel is released, the object accelerates downward, the cord unwraps off the wheel, and the wheel rotates with an angular acceleration. Find the angular acceleration of the wheel, , and the tension in the cord.arrow_forwardAs shown in the figure below, two blocks are connected by a string of negligible mass passing over a pulley of radius 0.350 m and moment of inertia I. The block on the frictionless incline is moving with a constant acceleration of magnitude a - 1.80 m/s². (Let m₂ = 14.5 kg, m₂ = 18.5 kg, and 8 = 37.0°) From this information, we wish to find the moment of inertia of the pulley. T₂ (a) What analysis model is appropriate for the blocks? O particle in equilibrium O particle under constant acceleration particle under constant speed particle under constant angular acceleration O particle in simple harmonic motion (b) What analysis model is appropriate for the pulley? O particle in equilibrium particle under constant acceleration particle under constant speed particle under constant angular acceleration O particle in simple harmonic motion (c) From the analysis model in part (a), find the tension T₁. N (d) From the analysis model in part (a), find the tension 7₂. N (e) From the analysis model…arrow_forwardIn the slider-crank mechanism, the slider block C is moving to the left with a linear velocity vc= 1.25 m/s. For the crank AB, find its corresponding angular velocity wAB at this instant. Given: a= 30 cm, b= 60 cm, 0= 30° and B= 53°. WAB aarrow_forward
- HELP WITH THIS PLEASE, DO NOT DO b ONLY THE OTHERarrow_forwardUse at least 4 significant figures throughout the entire problem. 9.80m/s2 for the acceleration due to gravity. Do not use 10 m/s2 for the acceleration due to gravity.arrow_forwardShow the complete solution. Please make sure that your handwritten is readable. Thank you.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios