
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
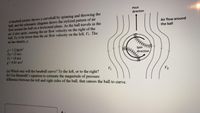
Transcribed Image Text:Pitch
direction
A baseball pitcher throws a curveball by spinning and throwing the
ball, and the schematic diagram shows the stylized pattem of air
flow around the ball on a horizontal plane. As the ball travels in the
air, it also spins, causing the air flow velocity on the right of the
ball, Vz, to be lower than the air flow velocity on the left, VL. The
air has density, p.
Air flow around
the ball
p-12 kg/m
VR 15 m/s
V 18 m/s
g-9.81 m/s
Spin
direction
(a) Which way will the baseball curve? To the left, or to the right?
(b) Use Bernoulli's cquation to estimate the magnitude of pressure
difference between the left and right sides of the ball, that causes the ball to curve.
VL
VR
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 1.2 kg object is oscillating in simple harmonic motion at the end of an ideal horizontal spring ir the frictionless air track. Its position as a function of time t is given by r(t) = (0.045 m)cos[(15 rad/s)t - /8). a) What is the spring constant? k= N/m b) What are the frequency and period of the oscillation? f= Hz T= c) What is the maximum speed that the object reaches? vmax= m/s What is the particle's position when the velocity is maximum? d) What is the maximum acceleration that the object reaches? amax= m/s? What is the particle's position when the acceleration is maximum? e) What is the maximum energy of the system? KE= J f) Find the acceleration of the object when the object is at x=0.025 m. m/s2 a=arrow_forwardI need the solution with an explanation of the steps, and please do not solve it in a paperarrow_forwardThe pressure altimeter is an aneroid barometer that measures the pressure of the atmosphere at the level where the altimeter is located. Consider a jet airliner moving at 447 mph in a direction 60 degrees cast of north, has a speed relative to the ground of 503 mph due east. Recall from physics I that a plane has both an absolute speod relative to the ground, and a speed relative to the air. The values are different in the presence of wind. Draw a cartesian vector diagram of the jet, both with respect to the Earth and ait. a) Caleulate thex and y components of the geostrophic wind the plane is flying in. Use 3 sig figs for all. b) If the pilot simply flies along the pressure surface, calculate the rate of change in altitude of the plane using the characteristic Coriolis parameter defined in clas Vg x: type your answer. Vg y: type your answer. Rate of change of altitude (in m/km): type your answerarrow_forward
- 2 Problem Norm the Niner throws up a football with a speed v0 = 10 m/s and at an angle relative to the vertical on a windy day. The wind affects the football by creating a horizontal acceleration of 0.7 m/s² to the left (the wind has no vertical acceleration). At what angle 9 must the ball be thrown so that its path forms a loop and returns to Norm? Assume no drag acts on the football. [Hint: because the football follows a "loop" the velocity profile will be antisymmetric, such that the veloc- ity vector at the end (when catching the ball at some time T) is the negative of the velocity vector when initially throwing the ball. There is a particular angle 0 that makes this true. You should also review your trignometric identities, since one is needed for this problem.] WINDarrow_forwardHI, Please see acttached imagearrow_forwardThe data presented in the figure shows a generic 2.5MW wind turbine power curve and a wind speed data at hub height. 2500 0.25 2000 0.20 1500 0.15 1000 0.10 50 0.05 0.00 o 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 Wind speed (m/s) wWind speed frequency Power generated by wind turbine Estimate the Annual Energy Production that this wind turbine is able to generate. Power (MW) ksuanbay paads puMarrow_forward
- A 1000 kg spacecraft is approaching Jupiter (which is at the origin). The position of the spacecraft is given by the vector RSC = (0.0,-2.533) x 106km. The velocity is given by VSC= (+6.00, +8.00) km/sec. The mass of Jupiter, (MJ=318 MEarth) and MEarth = 5.97 x 1024 kg. A) What is the potential and kinetic energy of the spacecraft (write each to 3 sig figs.) What is the total energy of the spacecraft? Call the total energy Ei. B) Can it escape Jupiter? Justify your answer. C) What is the angular momentum of the spacecraft around Jupiter? Call this Li.arrow_forwardhi Vo Vo V₁ = R - he A ball will be thrown from the initial position (pictured in green) to strike a target (pictured in red) while avoiding contact with the ceiling. The initial height is hi - 5 m, the ceiling is he - 25 m tall, and the target = = is ht = 20 m above the ground. The target is R = 40 ht m away, horizontally. Find the minimum initial speed V₁ that can achieve this m/sarrow_forwardHow do we add velocities in a one-dimensional motion?arrow_forward
- I need the answer as soon as possiblearrow_forwardSOLVE CAREFULLY!! Please Write Clearly and Box the final Answer for Part A, and Part B , with THE CORRECT UNITS) Thank you. Express your answer to three significant figures and include appropriate units. DRAW the kinematic diagram and label it for this problem as well Thank youarrow_forward1. [-/2 Points] DETAILS SERCP8 3.P.035. MY NOTES ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER A jet airliner moving initially at 300 mi/h due east enters a region where the wind is blowing at 105 mi/h in a direction 35.0° north of east. What is the new velocity of the aircraft relative to the ground? o north of east mi/h atarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY