
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
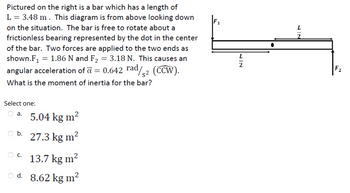
Transcribed Image Text:Pictured on the right is a bar which has a length of
L = 3.48 m . This diagram is from above looking down
on the situation. The bar is free to rotate about a
frictionless bearing represented by the dot in the center
of the bar. Two forces are applied to the two ends as
shown.F₁ = 1.86 N and F₂ = 3.18 N. This causes an
angular acceleration of a = 0.642 rad/2 (CCW).
What is the moment of inertia for the bar?
Select one:
a.
b.
5.04 kg m²
27.3 kg m²
C.
13.7 kg m²
O d. 8.62 kg m²
L
2
F₂
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Link 2 is isolated from a kinematic diagram and shown in the figure below. The link is rotating counterclockwise at a rate of 263 rpm. Determine the velocity of points A and B. Use y = 53° and ẞ= 72° A 8" γ B B 18" Enter the angular velocity, rounded to two decimal places, in rad/s. Answer: Check Enter the speed of point A, rounded to the nearest unit, in in/s. Answer: your answer must be a positive acute angle Checkarrow_forwardFA b b Pivot F, In the figure above, 4 forces of equal magnitude act on a uniform thin metal plate. The plate has a hinge (pivot) set up at one corner as shown. Rank the four forces in order, from the least amount of torque to the greatest amount of torque generated about the pivot point. Note: Dashed lines are merely drawing aids. F3, F2, F1, F4 F3, F1, F2, F4 F4, F3, F2, F1 F2, F1, F3, F4 F4, F3, F1, F2arrow_forwardA 3 kilogram solid sphere with a radius of 15 centimeters rolls without slipping down a rough incline with a 35 degree angle. If the sphere rolls from rest from a height of 45 centimeters, determine the sphere's translational speed at the bottom of the incline. Also, draw the free body diagram. Also see the attached picture that goes with the problem. Thank you.arrow_forward
- Use the worked example above to help you solve this problem. A merry-go-round modeled as a disk of mass M = 8.50 x 10¹ kg and radius R = 2.30 m is rotating in a horizontal plane about a frictionless vertical axle (see figure). (a) After a student with mass m = 80.0 kg jumps onto the merry-go-round, the system's angular speed decreases to 2.10 rad/s. If the student walks slowly from the edge toward the center, find the angular speed of the system when she reaches a point 0.490 m from the center. Your response differs significantly from the correct answer. Rework your solution from the beginning and check each step carefully. rad/s (b) Find the change in the system's rotational kinetic energy caused by her movement to the center. X Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. J (c) Find the work done on the student as she or= 0.490 m.arrow_forwardA solid, uniform, spherical boulder (I=(2/5) MR2) starts from rest and rolls down a 75.0 [m] hill, as shown at the figure at the right. The top half of the hill is rough enough to cause the boulder to roll without slipping, but thelower half is covered with ice and there is no friction. What is the translational speed of the boulder when it reaches the bottom of the hill?arrow_forwardPlease show formula's used and do step for step, please don't cut out any algebraarrow_forward
- For question 4 answer A and B 4. A grinding wheel is spinning at a rate of 20.0 revolutions per second. When the power to the grinder is turned off, the grinding wheel slows with constant angular acceleration and takes 80.0 s to come to a rest. (a) What was the angular acceleration of the grinding wheel as it came to rest? (b) How many rotations did the wheel make during the time it was coming to rest?arrow_forwardMII-1 Consider a solid disk of mass M and radius R, which has a uniform density. a) The disk is rotated about an axis that goes through its center and is perpendicular to its face, as shown in the diagram below on the left. Find a formula for its moment of inertia. Your answer should be a symbolic expression that only depends on the variables M and R. Hint: you will need to divide the disk into infinitesimal mass elements (dm) and then perform the integral: r?dm b) Suppose the radius of the disk is 12.5 cm and the mass is 1.75 kg. Use the formula from part a) to calculate a numerical value for the moment of inertia, in kg m2. c) Now the axis of rotation is moved from the center of the disk to the end of the disk, as shown in the diagram below on the right. Find an expression for its moment of inertia. Hint: theorem. As before, your answer should only depend on the variables M and R. d) Suppose the radius of the disk is 12.5 cm and the mass is 1.75 kg. Use the formula from part c) to…arrow_forwardJust explain concepts, formulas, theories as if you were to solve.... A hoop and a solid disk both have the same radius and mass and negligible thickness. Assume that they are both rotating with the same constant angular speed. Which has the higher rotational kinetic energy? If you see an object rotating, is there necessarily a net nonzero torque acting on it? Why or why not? A skater rotates quickly on the ice. He pushes his arms out. What happens to his angular speed? Why? A 100 gram meter stick has a wad of clay on one end of it. The stick is supported from a fulcrum point 33 1/3 cm from the clay. What is the clay's mass? A student sits on a rotating stool holding two 3.0 kg objects. When his arms are extended horizontally, the objects are 1.0 m from the axis of rotation and he rotates with an angular speed of 0.75 rad/s. The moment of inertia of the student plus stool is 3.0 kg m2 and is assumed to be constant. The student then pulls in the objects horizontally to 0.30 m…arrow_forward
- PLEASE ANSWER ASAP!!!!!!!!! VERY URGENT!!!!!!!!!!!!!arrow_forwardThe 4.0 m long bar shown in the figure is fixed so that it can rotate freely around point O at the end of the bar. Three forces are applied along the bar at the positions and angles shown. Use the convention that a counter-clockwise spin is positive. Which of the following forces creates zero torque on the bar? Mark all that apply. 27 N 16 N 30 +3.0 m→ 45° - 4.0 m- 33 N The 33 N force The 16 N force The 27 N force Nonearrow_forwardA disk is rotating on a horizontal axis as shown in the figure. Answer the following questions if you pull out at A and push in at B along the axis of the disk.What is the direction of the torque acting on the disk? What is the direction of the initial angular momentum vector for the disk? The applied torque causes the wheel's axis (or angular momentum vector) to move. From the front view, what is the direction of motion of the L vector? A disk is rotating on a vertical axis as shown in the figure. Answer the following questions if you push in at A and pull out at B along the axis of the disk. What is the direction of the torque acting on the disk? What is the direction of the initial angular momentum vector for the disk? The applied torque causes the wheel's axis (or angular momentum vector) to move. From the front view, what is the direction of motion of the L vector?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON