
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
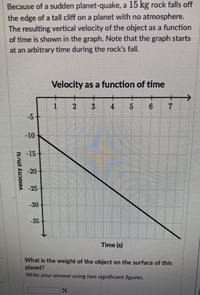
Transcribed Image Text:Because of a sudden planet-quake, a 15 kg rock falls off
the edge of a tall cliff on a planet with no atmosphere.
The resulting vertical velocity of the object as a function
of time is shown in the graph. Note that the graph starts
at an arbitrary time during the rock's fall.
Velocity as a function of time
6.
-5
-10
-15
-20
-25
-30
-35
Time (s)
What is the weight of the object on the surface of this
planet?
Write your answer using two significant figures.
Is/w) kupoiaA
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- You are an astronaut on a rotating space station. Your station has an inside diameter of 3.00 km a) Draw a system diagram and FBD of your body as you stand on the interior surface of the station b) Determine the speed you need to have if your apparent weight is to be equal in magnitude to your Earth -boundweight. c) Determine your frequency of rotation, both in hertz and in revolutions per minute.arrow_forward-For the differential equation dv/dt=-pv-g What is the expression for the terminal speed? What is the physical meaning of the terminal speed, for a falling object? -What is the formula for gravitational force as a function of distance, from Newton's law of gravitation? -arrow_forward2) A roller coaster is going over a hill with a radius of 20 m. a. How fast does it have to go for the passengers to feel weightless at the top? b. Suppose the roller coaster was running on the Moon, where the acceleration of gravity is only 1.7 m/s^2. How fast would it need to travel for you to feel weightless there?arrow_forward
- 13. On a distant planet, an astronaut drops a steel ball from a height of 150 meters. He observes that it takes 10 seconds for the ball to reach the surface of the planet. The distance that the ball falls from the starting point is recorded with the instruments that he carries in his spaceship, with this, he generates the table shown below. Using the data provided, determine the gravitational acceleration corresponding to the planet the astronaut is on. Write the answer using two significant figures. Heigh m // time seconds 0 0 6 2 24 4 54 6 96 8 150 10arrow_forward5. A ball is thrown with an initial velocity of 8.5 m/s at an angle of 30.0⁰ from the horizontal. How long the ball is in flight? (assume g = 9.81 m/s²) 6. The planet A has a mass of 1.972-1024 kg and the planet B has a mass of 5.348-1024 kg. What is the distance between the planet A and planet B if the force of gravity between them is 2.111-1022 N?. (assume G = 6.670-10-¹¹ Nm²/kg²) 1770arrow_forward(a) What is the acceleration (in m/s2) of gravity on the surface of the moon? m/s2 (b) What is the acceleration (in m/s2) of gravity on the surface (or outer limit) of Mars? The mass of Mars is 6.42 × 1023 kg and its radius is 3.37 x 106 m. m/s2arrow_forward
- 2-D star cluster puzzle Find the net gravitational force for v) A regular heptagon Let m=mass of the star = 1.99 x 10^30 kg, l=earth to star distance=149.6 x 10^6 km, G=6.67 x10^-11 N m^2/kg^2. Note that the masses of each star are the same. Also, it is advised to use vectors and components. And you can just find the gravitational net force of one of the stars in the shapearrow_forwardAn astronaut of mass m experiences a weight of mg upon the surface of the moor of radius R. Identify the gravitational force exerted on the astronaut by the moon in orbit a distance of 3R above the surface of the moon. A. 1/16 mg B. 16mg C. 1/9 mg D. mg E. (1/3)mgarrow_forwardOn another planet whose radius is four times that of Earth and whose mass is three times that of Earth, your weight on this planet is times your weight on Earth. Hint: What equation should you use to answer this question? Recall in Ch. 4 the calculation of the magnitude of g. A. 1/16 = 0.0625 B. 3/16 0.1875 C. 3/4 0.750 D. 9/16 0.5625 E. 4/3 = 1.333 F. 3 A B C D E LL Farrow_forward
- A planet was discovered which is twice as massive as Earth and has twice Earth's radius. How does the value of the gravitational field strength on the surface of that planet compare to the value of the gravitational field strength on the surface of Earth (gEarth)? 1/2gEarth 1/8gEarth gEarth 1/4gEarth 2gEarth 4 g Eartharrow_forward4. Astronomers use a telescope to watch a small moon orbit a planet in our solar system. They find that it takes the moon 14 days to go around the planet once, and they estimate the radius of the moon's orbit is about 4.2 x 10² meters. a. From this information, estimate the mass of the planet. b. Using the mass you found in part (a), estimate the free-fall acceleration on the planet's surface if it has a radius of 3.8 x 106 meters.arrow_forwardAn asteroid starts at rest infinitely far from an Unknown planet. The asteroid has a mass of 5.00×104 kg. The mass of the planet, and the radius of the planet are given below. MAsteroid= 5.00x104 kg MPlanet-8.60x1025 kg Rplanet= 2.50x107 m What is final velocity when the asteroid hits the planet? 4.3 m/s 9180 m/s 5050 m/s 21400 m/s 1.15 x 103 m/sarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON