
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
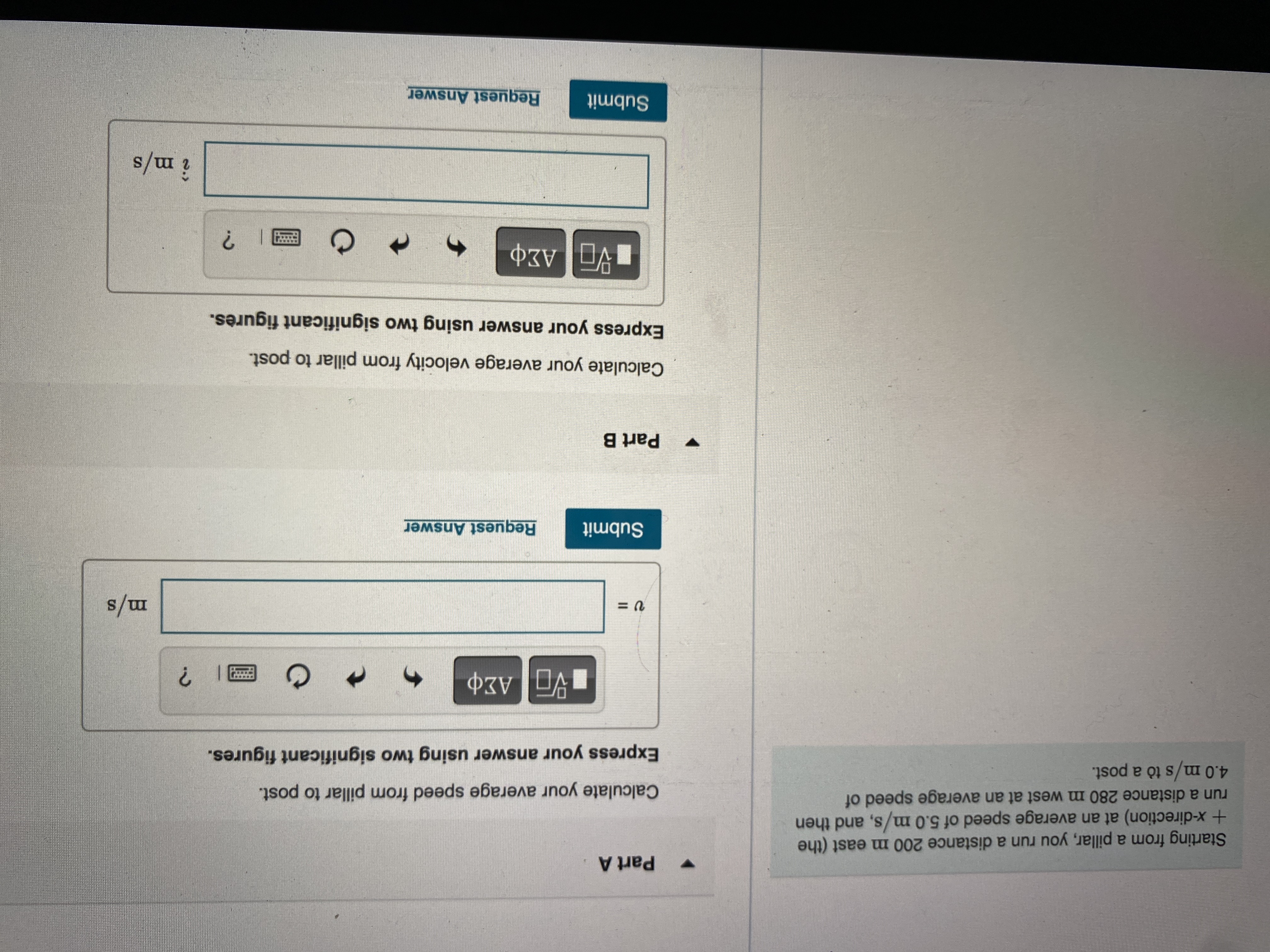
Transcribed Image Text:Part A
Starting from a pillar, you run a distance 200 m east (the
+x-direction) at an average speed of 5.0 m/s, and then
run a distance 280 m west at an average speed of
4.0 m/s tò a post.
Calculate your average speed from pillar to post.
Express your answer using two significant figures.
s/w
Submit
Request Answer
Part B
Calculate your average velocity from pillar to post.
Express your answer using two significant figures.
î m/s
Submit
Request Answer
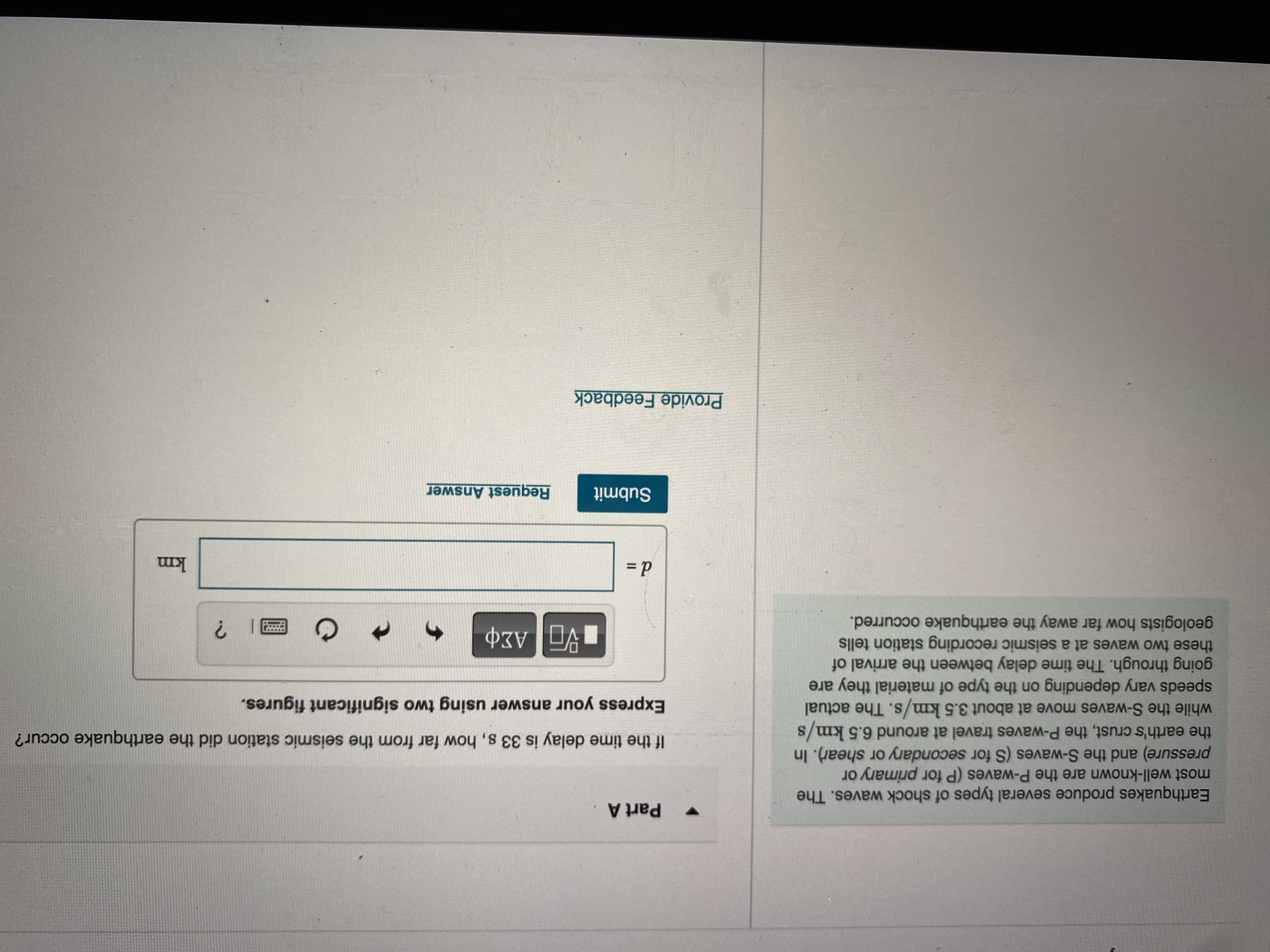
Transcribed Image Text:Part A
Earthquakes produce several types of shock waves. The
most well-k are the P-waves (P for primary or
pressure) and the S-waves (S for secondary or shear). In
If the time delay is 33 s, how far from the seismic station did the earthquake occur?
while the S-waves move at about 3.5 km/s. The actual
S.
speeds vary depending on the type of material they are
going throu The time delay between the arrival of
Express your answer using two significant figures.
these two waves at a seismic recording station tells
geologists how far away the earthquake occurred.
|| ?
km
Submit
Request Answer
Provide Feedback
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A student travels along some path. Which of the following statements is true about the total distance travelled by the student and the magnitude of the displacement from their starting position to their ending position? The total distance travelled can be either larger or smaller or equal to the magnitude of the displacement. O The total distance traveled must always be equal to the magnitude of the displacement. O The total distance traveled must be smaller than or equal to the magnitude of the displacement. O The total distance travelled must be larger than or equal to the magnitude of the displacement.arrow_forwardA high diver leaves the end of a 5.5 mm high diving board and strikes the water 1.2 ss later, 3.5 mm beyond the end of the board. Considering the diver as a particle, Part C Determine the maximum height reached. Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. Part D Determine the magnitude of the velocity v⃗fwith which she enters the water. Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. Part E Determine the angle of the velocity v⃗f with which she enters the water. Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units.arrow_forwardAt highway speeds, a particular automobile is capable of an acceleration of about 1.8 m/s². Part A At this rate, how long does it take to accelerate from 55 km/h to 120 km/h? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units.arrow_forward
- A particle moves along a straight path with an acceleration of a = (4/s) m/s², where s is in meters. ▼ Part A Determine the particle's velocity when s= 7 m, if it is released from rest when s = 1 m. Express your answer three significant figures and include the appropriate units. V= Value Submit 5 Request Answer Units ?arrow_forward9 ΔΔΔ Δ Δ ΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΔΑ What is the approximate total displacement based on the graph below? use 2 sfs. Approximate the values on each axis to the best of your ability. 560 (velocity mis 50 2240 30 P 10 123 I 3 4 5 Time (s) 1 678 9 2arrow_forwardWhen the motorcyclist is at A, he increases his speed along the vertical circular path at the rate of v = (0.04s) ft/s² where s is in ft. Take p = 270 ft. ▼ Part A V If he starts at V₁ = 2 ft/s where s = 0 at A, determine the magnitude of his velocity when he reaches B. = Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. μÅ Value Units Submit Part B = P 0 O μà 60° Submit Also, what is his initial acceleration? Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Value Units Request Answer P Request Answer ? ?arrow_forward
- You shoot an arrow into the air. Two seconds later (2.00 s) the arrow has gone straight upward to a height of 31.0 m above its launch point. Part A What was the arrow's initial speed? V ΑΣφ vo = m/s Submit Request Answerarrow_forwardIn this problem, you will apply kinematic equations to a jumping flea. Take the magnitude of free-fall acceleration to be 9.80 m/s². Ignore air resistance. Part A A flea jumps straight up to a maximum height of 0.410 m. What is its initial velocity vo as it leaves the ground? Express your answer in meters per second to three significant figures. ▸ View Available Hint(s) 20 2.83 m/s Submit ✓ Correct Part B Previous Answers How long is the flea in the air from the time it jumps to the time it hits the ground? Express your answer in seconds to three significant figures. ► View Available Hint(s) time in air = Submit 1951 ΑΣΦ Previous Answers Request Answer wood ? Sarrow_forwardPart A At an air show, a jet plane has velocity components v₂ = 725 km/h and v₁ = 455 km/h at time 4.85 s and v = 843 km/h and vy = 385 km/h at time 7.47 s. For this time interval, find the component of the plane's average acceleration. ΑΣΦ ax = 45.04 ? km/h² You have already submitted this answer. Enter a new answer. No credit lost. Try again. Submit Previous Answers Request Answer Part B For this time interval, find the y component of the plane's average acceleration. ΑΣΦ ay = -26.72 Submit Previous Answers Request Answer × Incorrect; Try Again Part C ? km/h² For this time interval, find the magnitude of its average acceleration. a = ΑΣΦ Submit Request Answer Part D ? km/h² For this time interval, find the direction of its average acceleration. θα ΑΣΦ ? ° clockwise from +x axisarrow_forward
- You're driving down the highway late one night at 20 m/s when a deer steps onto the road 35 m in front of you. Your reaction time before stepping on the brakes is 0.50 s, and the maximum deceleration of your car is 10 m/s². Part A How much distance is between you and the deer when you come to a stop? Express your answer in meters. ΨΗ ΑΣΦ 340 EPPINE ? Previous Answers Request Answer Submit X Incorrect; Try Again. m 27arrow_forward2. V A particle moves according to the equation ¤ = 10t², where is in meters and t is in seconds. (a) Find the average velocity for the time interval from 2.00 s to 3.00 s. (b) Find the average velocity for the time interval from 2.00 to 2.10 s.arrow_forwardA small object moves along the x-axis with acceleration a₂ (t) = -(0.0320 m/s³) (15.0 s-t). At t=0 the object is at x = -14.0 m and has velocity Voz = 8.20 m/s. Part A What is the x-coordinate of the object when t = 10.0 s? Express your answer with the appropriate units. x= μА Value 4 m ? X Incorrect; Try Again; 2 attempts remainingarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON