
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
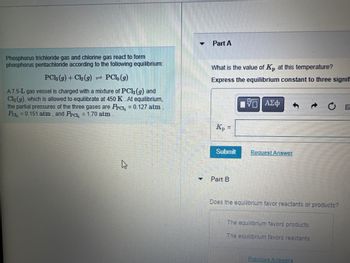
Transcribed Image Text:Phosphorus trichloride gas and chlorine gas react to form
phosphorus pentachloride according to the following equilibrium:
PC1, (g)
A7.5-L gas vessel is charged with a mixture of PC13 (g) and
Cl₂(g), which is allowed to equilibrate at 450 K. At equilibrium,
the partial pressures of the three gases are Prc, = 0.127 atm
Pa₂ = 0.151 atm, and Prc, = 1.70 atm
PC13 (g) + Cl₂ (g)
=
♥
-
Part A
What is the value of Kp at this temperature?
Express the equilibrium constant to three signif
15. ΑΣΦ
Kp =
Submit
Part B
Request Answer
Does the equilibrium favor reactants or products?
The equilibrium favors products.
The equilibrium favors reactants.
Previous Answers
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The equilibrium constant, Kp , for the following reaction is 1.04×10-2 at 548 K.NH4Cl(s) NH3(g) + HCl(g)If an equilibrium mixture of the three compounds in a 6.28 L container at 548 K contains 1.00 mol of NH4Cl(s) and 0.224 mol of NH3(g), the partial pressure of HCl(g) is atm.arrow_forwardWrite the expression for the equilibrium constant K, for the following reaction. Enclose pressures in parentheses and do NOT write the chemical formula as a subscript. For example, enter (PNH3 ) as (P NH3). If either the numerator or denominator is 1, please enter 1 2 Nb2O5(s) +→ 4 NbO2(s) + O2(g) K =arrow_forwardThe equilibrium constant, Kc, for the following reaction is 1.20×10-2 at 500 K.PCl5(g) PCl3(g) + Cl2(g)Calculate the equilibrium concentrations of reactant and products when 0.259 moles of PCl5(g) are introduced into a 1.00 L vessel at 500 K. [PCl5] = M [PCl3] = M [Cl2] = Marrow_forward
- The equilibrium constant, Kc, for the following reaction is 6.30 at 723 K. 2NH3 (9) ⇒ N₂ (9) + 3H₂ (9) If an equilibrium mixture of the three gases in a 12.8 L container at 723 K contains 0.496 mol of NH3(g) and 0.448 mol of N₂, the equilibrium concentration of H₂ is M.arrow_forwardNitrogen monoxide, NO, reacts with bromine, Br2, to give nitrosyl bromide, NOBr.arrow_forwardConsider the following reaction where Kc NH4Cl(s) ⇒ NH3(g) + HCl(g) A reaction mixture was found to contain 0.0531 moles of NH4Cl(s), 0.00147 moles of NH3(g), and 0.00226 moles of HC1(g), in a 1.00 liter container. Is the reaction at equilibrium? If not, what direction must it run in order to reach equilibrium? The reaction quotient, Q, equals = Submit Answer -6 5.10 x 107 at 548 K. The reaction O must run in the forward direction to reach equilibrium. O must run in the reverse direction to reach equilibrium. O is at equilibrium. Use the References to access important values it needed for this question. Retry Entire Group 9 more group attempts remainingarrow_forward
- A sample of N₂H6CO₂ weighing 22.5 grams is heated to 80°C in a 1.0 L container. All of the salt sublimes into NH3(g) and CO₂(g) according to the following equilibrium process. N₂H6CO₂ (s) + CO₂ (g) + 2NH3 (g) Determine the partial pressure of the NH3(g) in the system in atmospheres. This discussion is closed. M CAL -:00- 0:50- CI 2:00 Submit Answer Tries 0/99 3 F1 @ 2 ост 21 9: F2 3 80 F3 $ 4 10 a F4 % 5 S F5 6 tv A MacBook Air C F6 & 7 F7 ( Î DII FB F9 F10 F11 54 F13 Send 22arrow_forwardThe equilibrium constant, Kp, for the following reaction is 1.04x10-² at 548 K. NH4CI(S) NH3(g) + HCl(g) If an equilibrium mixture of the three compounds in a 6.78 L container at 548 K contains 2.85 mol of NH4Cl(s) and 0.113 mol of NH3(g), the partial pressure of HCI(g) is atm.arrow_forwardA chemical engineer is studying the following reaction: 2 NO(g)+2H2(g) → N,(9)+2H2O(g) At the temperature the engineer picks, the equilibrium constant K, for this reaction is 0.0038. The engineer charges ("fills") four reaction vessels with nitrogen monoxide and hydrogen, and lets the reaction begin. She then measures the composition of the mixture inside each vessel from time to time. Her first set of measurements are shown in the table below. Predict the changes in the compositions the engineer should expect next time she measures the compositions. reaction compound pressure expected change in pressure vessel NO 7.58 atm f increase I decrease (no change) H2 8.02 atm f increase I decrease (no change) A N, 4.16 atm f increase I decrease (no change) H,0 2.79 atm f increase I decrease O (no change) NO 8.89 atm ↑ increase I decrease (no change) H2 9.33 atm f increase I decrease (no change) В N2 3.51 atm f increase I decrease (no change) H,0 1.48 atm f increase I decrease (no change) NO…arrow_forward
- Calcium oxide and carbon dioxide react to form calcium carbonate, like this: CaO(s)+CO,(g)→CaCO3(s) At a certain temperature, a chemist finds that a 8.1 L reaction vessel containing a mixture of calcium oxide, carbon dioxide, and calcium carbonate at equilibrium has the following composition: compound amount СаО 43.8 g CO2 40.9 g CaCO3 55.4 g Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant K, for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. K = 0 x10arrow_forwardThe equilibrium constant, Ke, for the following reaction is 10.5 at 350. K. 2CH₂Cl₂ (9) CH₂(g) + CCL4 (9) Calculate the equilibrium concentrations of reactant and products when 0.359 moles of CH₂Cl₂ (g) are introduced into a 1.00 L vessel at 350. K [CH₂Cl₂]-[ [CH]-[ [CCL]-[ M M M 3arrow_forwardThe equilibrium constant, K., for the following reaction is 83.3 at 500 K. PCI3(g) + Cl2(9)=PCI5(g) Calculate the equilibrium concentrations of reactant and products when 0.242 moles of PCI3 and 0.242 moles of Cl, are introduced into a 1.00 L vessel at 500 K. [PCI3] =| [Cl2] = [PCI5] = M Marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY