
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
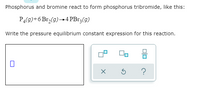
Transcribed Image Text:Phosphorus and bromine react to form phosphorus tribromide, like this:
PĄ(9)+6 Br,(9)→4 PB13(9)
Write the pressure equilibrium constant expression for this reaction.
?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A sealed 3.5 L container initially holds 0.0127 moles of hydrogen gas, 0.084 moles of solid iodine, and 0.0581 moles of hydrogen iodide gas. When equilibrium is reached, the concentration of hydrogen is 0.0065 M. Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant, Keq, for the reaction H2(g)+I2(s)⟶2HI(g). For the equilibrium constant, use a 1.0 M standard state, not a 1.0 atm standard state. Keq= ?arrow_forwardThe reaction A(g) ──> 2B(g) has an equilibrium constant Kc = 1.0 at a given temperature. If a reaction vessel contains equal amounts, in moles, of A and B does the direction in which the reaction proceeds depend on the volume of the vessel?arrow_forwardC6-6arrow_forward
- Predict the equilibrium concentration of NH in the reaction described below (for which Kc = 1.210 at the reaction temperature) by constructing an ICE table, writing the equilibrium constant expression, and solving for the equilibrium concentration. Complete Parts 1-3 before submitting your answer. = NHSH(s) NH¸(g) + H₂S(g) Using the data from your ICE Table (Part 1), construct the expression for the equilibrium constant, Kc. Each reaction participant must be represented by one tile. Do not combine terms. KC = II = 1.2 × 10-4 RESET [x] [2x] [2x]² [1.2 × 104+x] [1.2 × 104-x] [1.2 × 104 + 2x] [1.2 × 104 -2x] [1.2 × 10+ + x]² [1.2 × 10+ - x]² [1.2 × 10+ + 2x]² [1.2 × 104 -2x]²arrow_forwardConsider the reaction: N2(g) + 3H2(g) 2NH3(g) where Kc = 0.500 at 400 °C. If 50.0 L reaction vessel contains 1.000 mole N₂; 3.000 mole H₂ and 0.050 mole NH3, which of the following is TRUE? The reaction based on the following parameters is in equilibrium. More ammonia will be produced as the reaction approaches equilibrium. Data provided is not enough to warrant a conclusion regarding equilibrium. More ammonia will dissociate as the reaction approaches equilibrium.arrow_forwardThe equilibrium constant for the chemical equation N,(g) + 3 H, (g) 2 NH,(g) is K, 0.356 at 197 °C. Calculate the value of the K, for the reaction at 197 °C. K.arrow_forward
- The equilibrium constant for the chemical equation N,(g) + 3 H, (g) = 2 NH, (g) is Kp = 0.402 at 267 °C. Calculate the value of K. for the reaction at 267 °C. K. =arrow_forwardMost reaction do not go to completions. Equilibrium is established between the reactants and products. For the reaction of A with B to produce C and D, we can write the chemical equation as: аА + bв + сс + dD where + represents equilibrium between the reactants and products. The extent to which the reaction proceeds to product formation, at a given temperature, is given by the equilibrium constant, Kę. The equilibrium constant is written mathematically (for the above equation) as: [C[[D]* K. = [A]°[B]" where, a, b, c, and d are the stoichiometric coefficients from the balanced chemical equation and the brackets, [ ], indicate molar concentration. 1. For the following reaction: 2A + В + 3с calculate the equilibrium constant, K, if at equilibrium the concentration of A is 0.15M, the concentration of B is 0.20M, and the concentration of C is 0.10M.arrow_forwardThe equilibrium constant for the synthesis of ammonia N2(g) + 3 H2(g) --> 2 NH3(g) has the value K = 3.19 × 10^-4 at 400°C. Calculate the equilibrium partial pressures of N2(g), H2(g), and NH3(g) if the total pressure is 1.00 atm and the H:N atomratio in the system is 3;1. (Hint: Try the approximationthat PN2 and PH2 > PNH3 and see if the resulting equationsare simpliied.)arrow_forward
- Write the pressure equilibrium constant expression for this reaction. 2 CO,(g)+4 H,O(g)→2CH;OH(1)+3 O2(9)arrow_forwardWrite the equilibrium expression, in terms of pressure, for the formation of ammonia equilibrium.arrow_forward(a) What does it mean when the reaction quotient, Q, is numerically equal to the equilibrium constant, Kc? (b) What does it mean when it is less than the equilibrium constant? (c) What does it mean when it is less than the equilibrium constant?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY