
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Phoenix Company reports the following fixed budget. It is based on an expected production and sales volume of 15,500 units.
| PHOENIX COMPANY | |
| Fixed Budget | |
| For Year Ended December 31 | |
| Sales | $ 3,255,000 |
|---|---|
| Costs | |
| Direct materials | 1,007,500 |
| Direct labor | 232,500 |
| Sales staff commissions | 77,500 |
| 300,000 | |
| Supervisory salaries | 199,000 |
| Shipping | 217,000 |
| Sales staff salaries (fixed annual amount) | 251,000 |
| Administrative salaries | 611,750 |
| Depreciation—Office equipment | 196,000 |
| Income | $ 162,750 |
Required:
1&2. Prepare flexible budgets at sales volumes of 14,500 and 16,500 units.
3. The company’s business conditions are improving. One possible result is a sales volume of 18,500 units. Prepare a simple
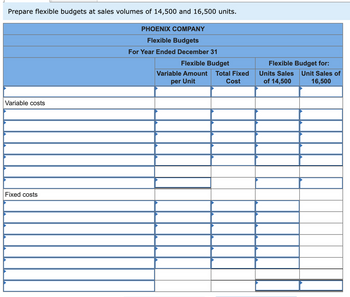
Transcribed Image Text:Prepare flexible budgets at sales volumes of 14,500 and 16,500 units.
Variable costs
Fixed costs
PHOENIX COMPANY
Flexible Budgets
For Year Ended December 31
Flexible Budget
Variable Amount Total Fixed
per Unit
Cost
Flexible Budget for:
Units Sales
of 14,500
Unit Sales of
16,500
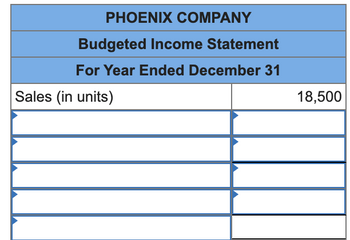
Transcribed Image Text:PHOENIX COMPANY
Budgeted Income Statement
For Year Ended December 31
Sales (in units)
18,500
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Tucker Inc. is preparing its Manufacturing Overhead Budget for the Quarter based on the following production in units. April May June QuarterProduction in units 20,000 10,000 15,000 45,000Tucker Inc. uses a variable manufacturing overhead rate of $2.50 per unit produced Fixed manufacturing overhad is $40,000 per month and includes $20,000 of non-cash costs (depreciation of plant assets). The total Variable Manufacturing Overhead cost for the quarter is: The total Fixed Manufacturing Overhead cost for the quarter is: Thet total Manufacturing Overhead costs for the quarter is: The total Cash disbursements for manufacturing overhead for the quarter isarrow_forwardPlease show calculationarrow_forwardClarks Company's master budget includes $360,000 for equipment depreciation. The master budget was prepared for an annual volume of 120,000 chargeable hours. This volume is expected to occur uniformly throughout the year. During September Clark performed 9,000 chargeable hours and recorded $28,000 of depreciation. Determine the flexible budget amount for equipment depreciation in September?arrow_forward
- The following information is available for Pioneer Company: Sales price per unit is $100. . November and December sales were budgeted at 3,060 and 3,420 units, respectively. Variable costs are 11 percent of sales (6 percent commission, 2 percent advertising, 3 percent shipping). Fixed costs per month are sales salaries, $5,700; office salaries, $2,900; depreciation, $2,600; building rent, $3,000; insurance, $1,500; and utilities, $700. Required: Determine Pioneer's budgeted selling and administrative expenses for November and December. Total Budgeted Selling and Administrative Expenses November Decemberarrow_forwardFlores Company budgeted total variable costs at P250,000 for the current year. In addition, they budgeted costs for (a) factory rent at P325,000; (b) depreciation of office equipment at P20,000; (c) office rent at P140,000; and (d) depreciation of factory equipment at P60,000. All of the above costs were based upon estimated 50,080 machine hours. At the end of the accounting period, the Factory Overhead Control had a balance of P650,625. Actual machine hours were 53,210. What was the over or underapplied factory overhead for the period?arrow_forwardCrane Corporation's master budget for the year is shown below: Sales (60,700 units) Cost of goods sold: Direct materials Direct labor Overhead (variable overhead applied at 45% of direct labor cost) Gross profit Selling expenses: Sales commissions (all variable) Rent (all fixed) Insurance (all short-term fixed) General expenses: Salaries (all short-term fixed) Rent (all short-term fixed) Depreciation (all short-term fixed) Operating income $ 212,450 497,740 247,000 Required 1 $ 160,248 47,000 37,000 Required 2 95,500 80,500 57,000 $ 2,306,600 957,190 $ 1,349,410 Required: 1. During the year, the company manufactured and sold 55,700 units of product. Prepare a flexible budget for this level of output. 2. Now suppose that the actual level of output was 65,700 units. Prepare a flexible budget for this output level. 477, 248 $ 872,162 Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. During the year, the company manufactured and sold 55,700 units of product. Prepare a…arrow_forward
- Compute the dollar amount of Direct Material "A" to be used in production during the year, given the following info: Budgeted Sales for the year = 640,000 units Estimated Beg. Inventory = 108,000 units Desired End. Inventory = 90,000 units The Quantities of Direct Materials expected to be used for each Unit of finished product are as follows: Material A = 0.5 lb. per unit @ $0.60 per lb. Material B 1.0 lb. per unit @ $1.70 per lb. Material C= 1.2 lb. per unit @ $1.00 per lb. O $186,600.00 $210,600.00 O$181,200.00 $240,000.00arrow_forwardStarts Inc. using production levels of 62,000, 67,200, and 69,300 units produced. The following additional information is necessary to complete the budget. Prepare a flexible production budget for the year ending December 31 for :Variable costs: Direct labor ($18.00 per unit) Direct materials ($5.00 per unit) Variable manufacturing costs ($8.00 per unit) Fixed costs: Supervisor’s salaries $27,000 Rent 18,000 Depreciation on equipment 82,000arrow_forwardSunland Company has accumulated the following budget data for the year 2022: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Sales: 29,200 units; unit selling price $82 Cost of one unit of finished goods: direct materials, 2 kg at $5 per kilogram; direct labour, 3 hours at $13 per hour; and manufacturing overhead, $5 per direct labour hour Inventories (raw materials only): beginning, 9,900 kg; ending, 15,700 kg Raw materials cost: $5 per kilogram Selling and administrative expenses: $219,000 Income taxes: 30% of income before income taxes Prepare a schedule showing the calculation of the cost of goods sold for 2022. SUNLAND COMPANY Computation of Cost of Goods Sold For the Year Ending December 31, 2022 Cost of goods sold Manufacturing overhead Beginning inventory Direct materials Ending inventory Number of units sold Selling and administrative expenses Direct labour Cost of one unit of finished goods eTextbook and Media $ $ $arrow_forward
- Waterway Industries has the following budgeted costs for the next year: Time Charges Material Charges Shop employees’ wages and benefits $120000 $ - Parts manager’s salary and benefits - 50000 Office employee’s salary and benefits 45000 15000 Other overhead 15000 40000 Invoice cost of parts and materials - 454000 Total budgeted costs $180000 $559000 Next year’s material loading charge, assuming a 30% markup on material cost is 48.78%. 53.00%. 30.00%. 18.78%. do not give solution in imagearrow_forwardGary Ltd. manufactures a product for which the budgeted capacity is 392,000 units per month. The following data is available for August 2019: Details Units Sales 320,000 Opening stock 60,000 Closing stock 160,000 Production 420,000 Cost Data Details $ Direct materials 55 Direct labour 22 Variable Production Overheads 41 Fixed administrative overheads were estimated at $ 600,000 while fixed selling overheads were estimated at $840,000. During the periods, the selling price per unit was $180 and Total Fixed Production Overheads were $5,880,000. Required: (a) Show the profit situation using Marginal costing principles (b) Show the profit situation using Absorption costing principlesarrow_forwardWharton Company has the capacity to produce 50,000 units per year. The company sells each unit for $125. Budgeted information is as follows: Revenues $5,612,000 Direct materials $1,932,000 Direct labor 552,000 Manufacturing overhead (fixed) 276,000 Manufacturing overhead (variable) 552,000 3,312,000 Total $2,300,000 A special order has been received for 5,000 units to be sold for $80 per unit. The company would incur an additional $60,000 in total fixed costs in order to lease a special machine in order to make a slight modification to the original product. Should the company accept the special order? A. Yes, the revenue will increase substantially. B. No, total costs would increase by $303,600. C. Yes, profit will increase by $36,400. D. No, accepting this order would decrease profits to $2,263,600.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education