
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
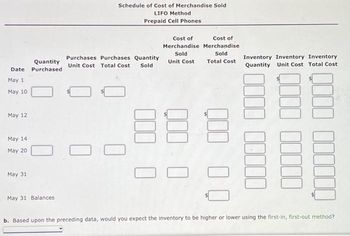
Transcribed Image Text:Date
May 1
May 10
May 12
May 14
May 20
May 31
Quantity
Purchased
May 31 Balances
Schedule of Cost of Merchandise Sold
LIFO Method
Prepaid Cell Phones
Purchases Purchases Quantity
Unit Cost Total Cost Sold
Cost of
Cost of
Merchandise Merchandise
Sold
Sold
Unit Cost
Total Cost
88 8
0
Inventory Inventory Inventory
Quantity Unit Cost Total Cost
b. Based upon the preceding data, would you expect the inventory to be higher or lower using the first-in, first-out method?
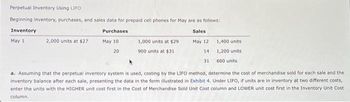
Transcribed Image Text:Perpetual Inventory Using LIFO
Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales data for prepaid cell phones for May are as follows:
Inventory
Purchases
Sales
May 12
May 1
May 10
20
14
31
2,000 units at $27
1,000 units at $29
900 units at $31
1,400 units
1,200 units.
600 units
a. Assuming that the perpetual inventory system is used, costing by the LIFO method, determine the cost of merchandise sold for each sale and the
inventory balance after each sale, presenting the data in the form illustrated in Exhibit 4. Under LIFO, if units are in inventory at two different costs,
enter the units with the HIGHER unit cost first in the Cost of Merchandise Sold Unit Cost column and LOWER unit cost first in the Inventory Unit Cost
column.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- You have the following information for Ivanhoe Inc. for the month ended October 31, 2025. Ivanhoe uses a periodic system for inventory. Date Oct. 1 Oct. 9 Oct. 11 Oct. 17 Oct. 22 Oct. 25 Oct. 29 (a1) (a2) Description Beginning inventory 55 Purchase Sale Purchase Sale Purchase Sale Ending inventory Cost of goods sold Gross profit Units Unit Cost or Selling Price $26 $ tA 140 tA 100 1.LIFO. 2. FIFO. 3. Average-cost. (Round answers to O decimal places, e.g. 125.) 100 55 65 110 Calculate ending inventory, cost of goods sold, and gross profit under each of the following methods. LIFO tA $ 28 LA 45 29 50 31 50 FIFO tA tA tA AVERAGE-COSTarrow_forwardcompany's inventory records show the following data for the month of July. Date July 1 July 5 July 10 July 20 July 25 July 1 Date Activities Beginning inventory Purchase Sale Purchase Sale July 5 Average cost July 5 July 10 July 20 200 units @ $50 If the company uses the weighted average method and the perpetual inventory system, what would be the cost of its ending inventory? Average cost July 20 July 25 Total July 25 Goods purchased Number of Cost per units unit 50 at $ 75.00 Units Acquired at Cost Units Sold at Retail 100 units @ $72 = $7,200 50 units @ $75 = $3,750 225 at $ 77.00 225 units @ $77 = $17,325 Number of units sold Cost of Goods Sold Cost per Cost of Goods Sold unit 75 at $ 50.00 = 200 at $ 50.00 $ 75 units @ $50 $ $ 3,750.00 10,000.00 10,000.00 Number of units 100 at Inventory Balance 100 at 50 at 150 at Cost per unit Inventory Balance 7,200.00 7,200.00 3,750.00 10,950.00 $ 175 at $ $ $ 75 at 150 at 225 at $ 375 at $ 50.00 = $ +73.00 = 77.00 = 75.40 75.00 = 55 72.00 = $…arrow_forwardPlease help me make a perpetual FIFO, perpetual LIFO, Weighted Average, and Specific ID chart. Thank youarrow_forward
- i need solution step by steparrow_forwardB66's transactions involving inventory for the month are shown below. Calculate the dollar amount of Sales, Cost of Goods Sold, Gross Margin and Ending Inventory using the three cost allocation methods (FIFO, LIFO, and Weighted Average) with perpetual inventory updating. Number of Units Unit Cost Sales Beginning Inventory 100 $66 Sold 50 $120 Purchased 80 $75 Sold 25 $125 Ending Inventory 105 Show your calculations and clearly label your solution. Submit your work as an attachment to this assignment.arrow_forwardPerpetual Inventory Using Weighted Average Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales for WCS12 are as follows: Oct. 1 Inventory 310 units at $12 13 Sale 160 units 22 Purchase 350 units at $15 29 Sale 200 units a. Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the weighted average method, determine the weighted average unit cost after the October 22 purchase. Round your answer to two decimal places.$fill in the blank 1per unit b. Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the weighted average method, determine the cost of goods sold on October 29. Round your "average unit cost" to two decimal places.$fill in the blank 2 c. Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the weighted average method, determine the inventory on October 31. Round your "average unit cost" to two decimal places.$fill in the blank 3arrow_forward
- Perpetual Inventory Using Weighted Average Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales for WCS12 are as follows: Oct. 1 Inventory 350 units at $14 13 Sale 160 units 22 Purchase 310 units at $15 29 Sale 200 units a. Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the weighted average method, determine the weighted average unit cost after the October 22 purchase. Round your answer to two decimal places.$fill in the blank 1per unit b. Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the weighted average method, determine the cost of goods sold on October 29. Round your "average unit cost" to two decimal places.$fill in the blank 2 c. Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the weighted average method, determine the inventory on October 31. Round your "average unit cost" to two decimal places.arrow_forwardPerpetual inventory using LIFO and FIFO In the spaces provided below, determine the cost of good sold and ending inventory under the FIFO and LIFO method for Kimbrell Corporation which uses a perpetual inventory system. Below is the data for the October: Beginning inventory 120 units @ $39 each October 2 purchase 100 units @ $41 each October 8 sale 80 units October 15 purchase 200 units @ $42 each October 22 sale 250 units FIFO Purchases Cost of Goods Sold Inventory Balance Quantity Unit Cost Total Cost Quantity Unit Cost Total Cost Quantity Unit Cost Total Cost…arrow_forwardPlease help me. Thankyou.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education