
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
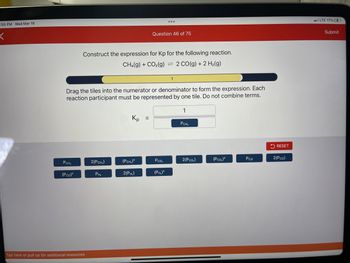
Transcribed Image Text::55 PM Wed Mar 15
<
PCH₂
(Pco)²
Construct the expression for Kp for the following reaction.
CH4(g) + CO₂(g)
2 CO(g) + 2 H₂(g)
Drag the tiles into the numerator or denominator to form the expression. Each
reaction participant must be represented by one tile. Do not combine terms.
Tap here or pull up for additional resources
2(PCH₂)
PH₂
Kp
(PCH₂)²
Question 46 of 75
2(PH₂)
=
Pco₂
-
(PH₂)²
1
PCH₂
2(Pco,)
(Pco,)²
Pco
RESET
2(PCO)
LTE 17%
Submit
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Nitrogen dioxide decomposes according to the reaction 2 NO2 (g) ⇌ 2 NO (g) + O2 (g) Where Kp = 4.48 x 10 ^ -13 at a certain temperature. If 0.40 atm of NO is added to a container and allowed to come to equilibrium, what are the equilibrium partial pressures of NO (g) and O2 (g)? P NO = atm NO P O2 = atm O2 Use correct significant figures.arrow_forwardWhat would be the equation for the following Kp expression: Kp= ( PHF) 2 I (PF2) (PH2)? H2 (g) = 2 HF (g) + F2 (g) 2F2 (g) + H2 (g) = 2 HF (g) O 2 HF (g) S H2 (g) + F2 (g) F2 (g) + H2 (g) = 2 HF (g)arrow_forwardFor which of these reactions will there be no effect on the relative amounts of the substances present at equilibrium when the pressure of the system is increased at constant temperature? O 2 sO, (g) + 0,(g) = 2 SO, (g) + heat heat + CO, (g) + NO(g) =CO(g) + NO, (g) heat + 2 Cl, (g) + 2 H,O(g) = 4 HCI(g) + 0, (g) N, (g) + 3 H, (g) = 2 NH, (g) + heatarrow_forward
- Consider the hypothetical reaction A(g) 2B(g). A flask is charged with 0.74 atm of pure A. after which it is allowed to reach equilibrium at 0 °C. At equilibrium the partial pressure of A is 0.37 atm Part A What is the total pressure in the flask at equilibrium? Express your answer using two significant figures. VS ΑΣΦ 4 P₁ = Submit Part B What is the value of Kp? Express your answer using two significant figures. K₂= Submit Part C Request Answer |VL ΑΣΦ Submit Request Answer What could we do to maximize the yield of B? → Request Answer [w] ? O Doing the reaction in a larger flask maximizes the yield of B. O Doing the reaction in a smaller flask maximizes the yield of B. atmarrow_forward5) At 25 °C the equilibrium constant of the reaction is Kel for the respective reactions and N₂(g) +3H₂(g) 2NH₂(g) (reaction 1) 3.5 x 108. What are the values Ke2 and Ke3 of the equilibrium constants = N2(g) +H₂(g) = NH₂(g) H₂(g) NH3(g), (reaction 2) 2NH3(9) N₂(g) + 3 H₂(g) 1 3 (reaction 3)?arrow_forwardIs this not 5.37?arrow_forward
- Consider the following reaction where K. = 10.5 at 350 K: 2 CH2C12 (g) CH4 (g) + CCI4 (g) A reaction mixture was found to contain 1.23×10²² moles of CH,Cl, (g), 5.29×10² moles of CH4 (g), and 4.07×102 moles of CCl, (g), in a 1.00 liter container. Indicate True (T) or False (F) for each of the following: O 1. In order to reach equilibrium CH2CI,(g) must be consumed . O 2. In order to reach equilibrium K. must decrease . 3. In order to reach equilibrium CH, must be consumed . O 4. Qç is greater than K.. O 5. The reaction is at equilibrium. No further reaction will occur.arrow_forward3. Given the chemical reaction A(aq) + 2B(aq) → C(aq) + 3D(aq) Initially, you have 2 moles of A and 3 moles of B dissolved in a total volume of 3 L. a. X moles of A reacted, and the solution reached equilibrium. Solve for the End state in term of x b. Write down the expression of the equilibrium constant (Keq) in term of x and volume.arrow_forwardIn an experiment to study the formation of HI(g),H2(g) + I2(g) ⇌ 2 HI(g)At equilibrium, {H2} = 0.0137, {I2} = 0.0627 and {HI} = 0.0268. Calculate the value of Kc.arrow_forward
- The reaction HCO₂H(g) CO(g) + H₂O(g) has Kp = 1.6 × 106 at 400 °C. What is the value of Kc for this reaction at this temperature? Kc = Harrow_forwardConsider the following chemical equilibrium: 4 NH; (g) + 3 0, (g) =2N, (g)+6H,0 (g) Now write an equation below that shows how to calculate K, from K, for this reaction at an absolute temperature T. You can assume T is comfortably above room temperature. If you include any common physical constants in your equation be sure you use their standard symbols, found in the ALEKS Calculator.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY