
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781305652231
Author: R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%

Transcribed Image Text:3. a. Define the following with an example;
i. paths
ii. simple graph
b. Draw the graph with the adjacency matrix
го
3
21
3
1
1
with respect to the
1
1
L2
1
2
ordering of vertices, a, b, c, d.
i. Find the degree of each vertex in your graph from
part (a) above.
ii. How many walks of length 2 are there from the
vertex c to c? How many of these walks are paths?
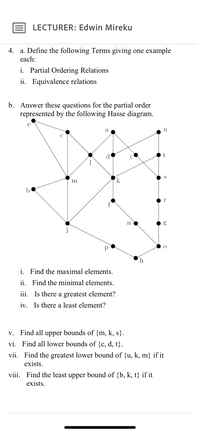
Transcribed Image Text:LECTURER: Edwin Mireku
4. a. Define the following Terms giving one example
each:
i. Partial Ordering Relations
ii. Equivalence relations
b. Answer these questions for the partial order
represented by the following Hasse diagram.
a
d
1
S
m
b
i. Find the maximal elements.
ii. Find the minimal elements.
iii. Is there a greatest element?
iv. Is there a least element?
V.
Find all upper bounds of {m, k, s}.
vi. Find all lower bounds of {c, d, t}.
vii. Find the greatest lower bound of {u, k, m} if it
exists.
viii. Find the least upper bound of {b, k, t} if it
exists.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, advanced-math and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which of these graphs have the property that the removal of any vertex and all edges incident with that vertex produces a planar graph? K7 K5 K4,4 K3,4arrow_forward. Sketch the complete graph with number of vertex 6.arrow_forwardA department wants to schedule final exams so that no student has more than one exam on any given day. The vertices of the graph below showthe courses that are being taken by more than one student, with an edge connecting two vertices if there is a student in both courses. Find a way tocolor the vertices of the graph with only four colors so that no two adjacent vertices have the same color and explain how to use the result to schedulethe final exams.arrow_forward
- A department wants to schedule final exams so that no student has more than one exam on any given day. The vertices of the graph below show the courses that are being taken by more than one student, with an edge connecting two vertices if there is a student in both courses. Find a way to colour the vertices of the graph with only four colours so that no two adjacent vertices have the same colour and explain how to use the result to schedule the final exams.arrow_forwardQ16. Consider the graph with the following vertices, edges, and weights (weights are stated as the third entry for each edge in E, with the first two entries representing the vertices joined by the edge): V = {a, b, c, d, e, f} E = {{a, b, 9}, {a, c, 6}, {a, d, 1}, {a, f, 4}, {b, c, 2}, {b, f, 8}, {c, d, 3}, {c, f, 5}, {d, e, 4}, {d, f, 8}} a Your Answer: 3 f What is the total weight of a minimum spanning tree of the graph? Answer d CDarrow_forwardConstruct a simple graph with vertices J, K, L, M whose degrees are 0, 2, 2, 2 What is the edge set?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:9781305652231
Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:Cengage Learning