
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780134753119
Author: Sheldon Ross
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
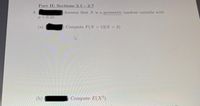
Transcribed Image Text:Part II: Sections 2.1 - 2.7
8.
Assume that X is a geometric random variable with
p=0.32.
(a)
Compute P(X > 13[X > 3).
(b)
Compute E(X²).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Random variables X and Y have CDF Fx(x) and Fy(y). Is F(x, y) = Fx(x)Fy(y) a valid CDF? Ex- plain your answer.arrow_forwardI just want the correct answer (A or B or C or D)I do not want the solution steps in the answerarrow_forwardI am struggling with this problem because I don't understand it can you do it step by step and can you label the parts as well.arrow_forward
- A random walk (RW) {Sn}n>o is a sum of id r.v.s X1, X2, •• , Xn,withP(X1 = a) = p, P(X1 = b) = 1 -p= q.Find the expectation E(Snl and variance var(Sn) of Sn for any n.arrow_forwardPart II: Sections 2.1-2.7 6. Let X be a binomial random variable with n = 20 and p= 0.75. What is the moment generating function of X? No work (a) is required for this part. (b) bilities, compute Using the attached table of cumulative binomial proba- P(X < 12).arrow_forwardLet Y be a discrete random variable with generating function 4 Gy (s) 6 - s What is E(Y) (in decimal)? Answer:arrow_forward
- 5 Calculate XkYk for the n = 5 data points (×₁,Y₁ ) = (2,4), (×2,Y₂) = (3,5), (×3,Y3) = (4,8), (×4,Y4) = (5,10), and k=1 (X5,5) = (6,14). 5 Σ xxYk = [ k=1 (Simplify your answer.)arrow_forwardA random variable X has a N(0,1) distribution. Use the moment generating function of X to compute (a) the third and (b) fourth moments of X, i.e., E(X³) and E(X4).arrow_forwardLet X be a random variable taking positive values and assume that E(X) exists. Which of the following statements are true? • (i) E(X*) > (E(X))*. • (ii) E(1/X²) > 1/E(X²). • (ii) E(e-3X) > e°arrow_forward
- Part II: Sections 2.1 2.7 7. Suppose that X is a discrete random variable with pmf f(x) =D c.14-피 . 뉴- 21 for r=-3, 3, 6, where c is a constant. (a) Find c. Compute E ( ~LX +) (b) 3.arrow_forward2. Let the independent random variables X1 and X2 have Bin(0.1,2) and Bin(0.5, 3), respectively. (a) Find P(X1 = 2 and X2 = 2). (b) Find P(X1 + X2 = 1). (c) Find E(X1 + X2). (d) Find Var(X1 + X2).arrow_forwardI roll a die with 10 faces numbered 0-9 and obtain a score X. What is E(X)? In order to obtain a random number between 0 and 99 I roll the die twice obtaining scores X and Y, then set Z = 10X + Y (i.e., the first roll determines the "tens", the second roll the "ones"). Is it true to say that E(Z) = 10E(X) + E(Y)?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)ProbabilityISBN:9780134753119Author:Sheldon RossPublisher:PEARSON
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)ProbabilityISBN:9780134753119Author:Sheldon RossPublisher:PEARSON

A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Probability
ISBN:9780134753119
Author:Sheldon Ross
Publisher:PEARSON
