
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781133104261
Author: Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Answer parts c and d

Transcribed Image Text:Part (b) What is the angle, 0 in degrees, between one of the chains and the vertical where it contacts the chandelier?
Part (c) Write an expression for FTy, the magnitude of the y-component of the tension in one chain, in terms of the given information and variables
available in the palette.
Part (d) Using your previous results, find the tension, FT in Newtons, in one chain.
FT=
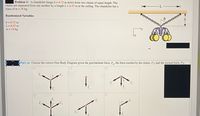
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 1: A chandelier hangs h = 0.72 m down from two chains of equal length. The
chains are separated from one another by a length L = 0.55 m at the ceiling. The chandelier has a
mass of m = 18 kg.
Randomized Variables
h = 0.72 m
L= 0.55 m
m = 18 kg
Part (a) Choose the correct Free Body Diagram given the gravitational force, Fe, the force exerted by the chains, FT, and the normal force, FN.
F.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The x and y coordinates of a 4.00-kg particle moving in the xy plane under the influence of a net force F are given by x = t4 6t and y = 4t2 + 1, with x and y in meters and t in seconds. What is the magnitude of the force F at t = 4.00 s?arrow_forwardA bag of cement weighing 325 N hangs in equilibrium from three wires as suggested in Figure P4.23. Two of the wires make angles 1 = 60.0 and 2 = 40.0 with the horizontal. Assuming the system is in equilibrium, find the tensions T1, T2, and T3 in the wires. Figure P4.23 Problems 23 and 24.arrow_forwardIf the vector components of the position of a particle moving in the xy plane as a function of time are x(t)=(2.5ms2)t2i and y(t)=(5.0ms3)t3j, when is the angle between the net force on the particle and the x axis equal to 45?arrow_forward
- The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO), with mass m = 1850 kg, maps the surface of the Moon from an orbital altitude of 50.0 km. What are the magnitude and direction of a. the force the LRO experiences due to the Moons gravity and b. the force exerted by the LRO on the Moon?arrow_forwardFor t 0, an object of mass m experiences no force and moves in the positive x direction with a constant speed vi. Beginning at t = 0, when the object passes position x = 0, it experiences a net resistive force proportional to the square of its speed: Fnet=mkv2i, where k is a constant. The speed of the object after t = 0 is given by v = vi/(1 + kvit). (a) Find the position x of the object as a function of time. (b) Find the objects velocity as a function of position.arrow_forwardStarting from rest, a rectangular toy block with mass 300 g slides in 1.30 s all the way across a table 1.20 m in length that Zak has tilted at an angle of 42.0 to the horizontal. a. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the toy block? b. What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the table? c. What are the magnitude and direction of the friction force acting on the block? d. What is the speed of the block when it is at the end of the table, having slid a distance of 1.20 m?arrow_forward
- A space station, in the form of a wheel 120 m in diameter, rotates to provide an artificial gravity of 3.00 m/s2 for persons who walk around on the inner wall of the outer rim. Find the rate of the wheels rotation in revolutions per minute that will produce this effect.arrow_forwardAn iron bolt of mass 65.0 g hangs from a string 35.7 cm long. The top end of the string is fixed. Without touching it, a magnet attracts the bolt so that it remains stationary, but is displaced horizontally 28.0 cm to the tight from the previously vertical line of the string. The magnet is located to the right of the bolt and on the same vertical level as the bolt in the final configuration. (a) Draw a free-body diagram of the bolt. (b) Find the tension in the string, (c) Find the magnetic force on the bolt.arrow_forwardJamal and Dayo are lifting a large chest, weighing 207 lb, by using the two rope handles attached to either side. As they lift and hold it up so that it is motionless, each handle makes a different angle with respect to the vertical side of the chest (Fig. P5.76). If the angle between Jamals handle and the vertical side is 25.0 and the angle between Dayos handle and the vertical side of the chest is 30.0, what are the tensions in each handle? FIGURE P5.76arrow_forward
- A 0.400-kg pendulum bob passes through the lowest part of its path at a speed of 3.00 m/s. (a) What is the tension in the pendulum cable at this point if the pendulum is 80.0 cm long? (b) When the pendulum reaches its highest point, what angle does the cable make with the vertical? (c) What is the tension in the pendulum cable when the pendulum reaches its highest point?arrow_forwardThe starship Enterprise has its tractor beam locked onto some valuable debris and is trying to pull it toward the ship. A Klingon battle cruiser and a Romulan warbird are also trying to recover the item by pulling the debris with their tractor beams as shown in Figure P5.25. a. Given the following magnitudes of the tractor beam forces, find the net force experienced by the debris: FEnt = 7.59 106 N, FRom = 2.53 106 N, and FKling = 8.97 105 N. b. If the debris has a mass of 2549 kg, what is the net acceleration of the debris? FIGURE P5.25arrow_forwardIn Example 2.6, we considered a simple model for a rocket launched from the surface of the Earth. A better expression for the rockets position measured from the center of the Earth is given by y(t)=(R3/2+3g2Rt)2/3j where R is the radius of the Earth (6.38 106 m) and g is the constant acceleration of an object in free fall near the Earths surface (9.81 m/s2). a. Derive expressions for vy(t) and ay(t). b. Plot y(t), vy(t), and ay(t). (A spreadsheet program would be helpful.) c. When will the rocket be at y=4R? d. What are vy and ay when y=4R?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning