
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
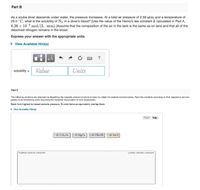
Transcribed Image Text:Part B
As a scuba diver descends under water, the pressure increases. At a total air pressure of 2.59 atm and a temperature of
25.0 °C, what is the solubility of N3 in a diver's blood? [Use the value of the Henry's law constant k calculated in Part A,
6.26 x 10-4 mol/(L·atm).JAssume that the composition of the air in the tank is the same as on land and that all of the
dissolved nitrogen remains in the blood.
Express your answer with the appropriate units.
• View Available Hint(s)
HẢ
?
solubility =
Value
Units
Part C
Tha following solutions are propared by dissolving the requisite amount of solute in water to obtain the desirad concentrations. Rank the solutions according to their respactive osmatic
pressures in decreasing order assuming the complete dissociation of ionic compounds.
Rank from highest to lowest osmotic pressure. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them.
• View Available Hint(s)
Reset
Help
1M C, HO, 1M MGCL 2 M CH,OH 1 M NaCI
Highest osmotic pressure
Lowest osmotic pressure
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1) What is the molality of a solution prepared by dissolving 78.8 g of ethylene glycol, HOCH2CH2OH, in 1.45 L of water? Assume the density of water is 1.00 g/mL. 2)The concentrations of Al and K in a sample of riverwater are 0.0500 mg/kg and 1.30 mg/kg, respectively. Express the concentration in molality. 3) What molality of nonvolatile solute is needed to lower the melting point of camphor by 1.050°C? (Kf = 39.70ºC/m) 4) Determine the melting point of an aqueous solution containing 193 mg of saccharin (C7H5O3NS) added to 1.00 mL of water (density of water = 1.00 g/mL, Kf = 1.86°C/m). 5) Which one of the following aqueous solutions should have the lowest freezing point? a. 0.0150 m Na2SO4 b. 0.0300 m KBr c. 0.00500 m C6H12O6 5) From your predicted value of the van't Hoff factor, calculate the boiling point of a 1.64 m aqueous solution of barium nitrate, Ba(NO3)2. The Kb of water is 0.52°C/m.arrow_forwardThe partial pressure of CO2, gas above the liquid in a bottle of champagne at 20 °C is 5.2 atm. What is the solubility of CO2, in champagne? Assume the Henry's law constant for CO2, is the same in champagne as it is in water: at 20 °C, kH =3.7 × 10^-2 mol Be sure to use the correct number of significant figures.arrow_forwardAt 25.0 °C, 100.0 mL of an aqueous solution containing 45.2 mg of a molecular solute has an osmotic pressure of 18.4 Torr. The molar mass of the solute is ___ g/mol.arrow_forward
- The freezing point of water H₂O is 0.00 °C at 1 atmosphere. A nonvolatile, nonelectrolyte that dissolves in water is antifreeze (ethylene glycol). How many grams of antifreeze, CH₂ OHCH₂OH (62.10 g/mol), must be dissolved in 268.0 grams of water to reduce the freezing point by 0.450 °C? Refer to the table for the necessary boiling or freezing point constant. Solvent Formula Kb(°C/m) Kf(°C/m) Water H₂O 0.512 Ethanol CH3 CH₂ OH 1.22 Chloroform CHCl3 3.67 Benzene C6H6 2.53 Diethyl ether CH3 CH₂ OCH2 CH3 2.02 Mass= g 1.86 1.99 5.12arrow_forwardI just can't find molarity. THIS IS NOT GRADED CHECKS ARE JUST LETTING ME KNOW RIGHT OR WRONG.arrow_forwardOmotic Pressure is a technique used to find the length of a polymer using its Molar Mass. If a 32.25 mg sample of PVC (polyvinyl chloride) is dissolved in benzene to 25.00 mL total solution at 30.00 oC, its osmotic pressure is 7.268 mm Hg. What is the Molar mass of the PVC? = i MRT760 mm Hg = 1.00 atmR = 0.08206 L-atm / mol K arrow_forward
- The vapor pressure of diethyl ether (ether) is 463.57 mm Hg at 25 °C. A nonvolatile, nonelectrolyte that dissolves in diethyl ether is aspirin.Calculate the vapor pressure of the solution at 25 °C when 10.18 grams of aspirin, C9H8O4 (180.1 g/mol), are dissolved in 239.0 grams of diethyl ether.diethyl ether = CH3CH2OCH2CH3 = 74.12 g/mol.VP(solution) = mm Hgarrow_forwardThe dispersed phase of a certain colloidal dispersion consistes of spheres of diameter 1.0 x 102 nm. What are the volume and surface area of each sphere? V = _ and SA = _ How many spheres are required to give a total volume of 1.0 cm3? What is the total surface area of these spheres in square meters? _ spheres, total SA = _ m2 The dispersed phase of a certain colloidal dispersion consistes of spheres of diameter 1.0 x 102 nm.arrow_forwardArterial blood contains about 0.25 g of oxygen per liter at 37°C and standard atmospheric pressure. Under these conditions, the Henry's law constant is kH = 3.7 ×× 10–2 mol/(L • atm), and the mole fraction of O2 in the atmosphere is 0.209. Part1:Calculate the solubility (in M) of O2 in the blood of a climber on Mt. Everest, where Patm = 0.35 atm.___M Part2: Calculate the solubility (in M) of O2 in the blood of a scuba diver at a depth of 100 feet, where Patm = ~3 atm.___Marrow_forward
- As a scuba diver descends under water, the pressure increases. At a total air pressure of 2.69 atm and a temperature of 25.0 °C, what is the solubility of N2 in a diver's blood? [Use the value of the Henry's law constant k calculated in Part A, 6.26 x 10-4 mol/(L· atm).JAssume that the composition of the air in the tank is the same as on land and that all of the dissolved nitrogen remains in the blood. Express your answer with the appropriate units.arrow_forwardThe vapor pressure of diethyl ether (ether) is 463.57 mm Hg at 25 °C. A nonvolatile, nonelectrolyte that dissolves in diethyl ether is aspirin.Calculate the vapor pressure of the solution at 25 °C when 10.17 grams of aspirin, C9H8O4 (180.1 g/mol), are dissolved in 151.7 grams of diethyl ether.diethyl ether = CH3CH2OCH2CH3 = 74.12 g/mol. The vapor pressure of diethyl ether (ether) is 463.57 mm Hg at 25°C.How many grams of estrogen (estradiol), C18H24O2, a nonvolatile, nonelectrolyte (MW = 272.4 g/mol), must be added to 192.1 grams of diethyl ether to reduce the vapor pressure to 452.63 mm Hg ?diethyl ether = CH3CH2OCH2CH3 = 74.12 g/mol.arrow_forwardI dont know how to do this questionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY