
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
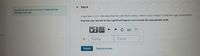
Transcribed Image Text:Part A
You look at yourself in a shiny 8 4-cm diameter
Christmas tree ball
If your face is 23.0 cm away from the ball's front surface, where is your image? Follow the sign conventions.
Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units.
HA
di =
Value
Units
Submit
Request Answer
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Spherical Mirror 1 You wish to create an image that is 10 meters from an object. This image is to be inverted and half the height of the object. You wish to accomplish this using one spherical mirror ▾ Part A What is the focal length f of the mirror that would accomplish this? Express your answer in meters, as a fraction or to three significant figures. ▸ View Available Hint(s) f= for Paina Ferdo for Part redo foart Are Submit Part B Complete previous part(s) Part A keyboard shortcuts for Part A help for Part A marrow_forwardAn object O is placed at the location shown in front of a concave spherical mirror. Use ray tracing to determine the location and size of the reflected image. As you work, keep in mind the following properties of principal rays: Part A Trace the path of a ray emitted from the tip of the object through the focal point of the mirror and then the reflected ray that results. Start by extending the existing ray emitted from the tip of the object. Then create the reflected ray. 1. A ray parallel to the axis, after reflection, passes through the focal point Fof a concave mirror or appears to come from the (virtual) focal point of a convex mirror. 2. A ray through (or proceeding toward) the focal point Fis reflected parallel to the axis. 3. A ray along the radius through or away from the center of curvature C intersects the surface normally and is reflected back along its original path 4. A ray to the vertex Vis reflected, forming equal angles with the optic axis. Draw the vector for the…arrow_forwardTwo converging lenses with focal lengths of 50 cm and 19 cm are 12 cm apart. A 3.5-cm-tall object is 25cm in front of the 50-cm-focal-length lens.arrow_forward
- Constants upright, real and reduced O inverted, real and reduced A shaving or makeup mirror is designed to magnify your face by a factor of 1.35 when your face is placed 20.5 cm in front of it. Submit Previous Answers v Correct Part C Calculate the required radius of curvature for the mirror. Follow the sign conventions. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. HA 144 cm Submit Previous Answers Request Answer X Incorrect; Try Again; 7 attempts remainingarrow_forwardplease explain parts d, e, and farrow_forwardA concave cosmetic mirror has a focal length of 30 cm. A 5.0-cm-long mascara brush is held upright 15 cm from the mirror. Part A Use ray tracing to determine the location of its image. Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. Enter a positive value if the image is on the other side from the lens and a negative value if the image is on the same side. s = 30 Submit O Part B μA Previous Answers Request Answer X Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remaining Check your sign. The image is on the other side from the mirror as an object. Part C cm What is the height of the image? Use ray tracing to determine. Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. μA h=| Value Submit Request Answer ? Units ?arrow_forward
- Part A A 2.6-cm-tall object is 30 cm to the left of a lens with a focal length of 15 cm . A second lens with a focal length of 5.0 cm is 40 cm to the right of the first lens. Calculate the distance between the final image and the second lens. Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. ) ) ? d = Value cm Part B Calculate the image height. Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. HA ? h' = Value cmarrow_forwardTwo converging lenses with focal lengths of 40 cm and 21 cm are 12 cm apart. A 4.0-cm-tall object is 15 cm in front of the 40-cm-focal-length lens. Part A Calculate the position of the final image (relative to the 21-cm-focal-length lens). Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. Enter a positive value if the image is on the other side from the lens and a negative value if the image is on the same side. Submitarrow_forward2 points Save Answer You have a concave mirror with a focal length of 345 mm. You point the mirror at an object, and you find an image of size -6.63 cm at a distance of 46.1 cm in front of the mirror. What is the size of the object in centimeters? (State answer with correct sign and with 1 digit right of the decimal. Do not include unit in answer.) A Moving to the next question prevents changes to this answer.arrow_forward
- CM-1 An object is placed 15.0 cm from a concave mirror with a focal length of 25.0 cm. a) Draw a diagram, showing 3 rays originating from the object reflecting off the mirror, and where they converge to form the image. b) What is the image distance? c) What is the total lateral magnification of the image? d) Is the image real or virtual? e) Is the image upright or inverted?arrow_forwardPart A A dentist uses a curved mirror to view the back side of teeth in the upper jaw. Suppose she wants an upright image with a magnification of 1.5 when the mirror is 1.9 cm from a tooth. Should she use a convex or a concave mirror? O She should use a convex mirror. O She should use a concave mirror. Submit Previous Answers v Correct Part B What focal length should it have? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. HA ? f = Value Units Submit Request Answerarrow_forwardK Solve for the indicated variable. Assume all variables are positive. QV₁ QV₂ T. L T₂ ; for T₁ (Simplify your answer.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON