
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Calculate the value of the deflection at point B due to concentrated load P in the form
Enter the numerator in the answer box below in kNm3 to three decimal places. Assume the positive direction of deflection in the positive direction of v axis.
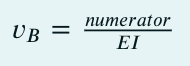
Transcribed Image Text:UB
=
numerator
ΕΙ
![The beam shown in Figure Q.2 consists of a W610 x 140 structural steel wide-flange shape [E = 200 GPa; /=
1120 x 106 mm4]. If w=59 kN/m and P= 129 kN, determine:
4.3, V
1.5 m
B
W
3.5 m
P
C
2.5 m
D
Figure Q.2
Part A: The reactions at A, B, and D. Choose the reaction force at B as the redundant; therefore, the
released beam is simply supported between A and D.](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/2f40e488-8d31-4ebf-93c2-8a5fabf31b11/d5779eb6-0366-4d95-a191-6cf604b328b3/qmzk63v_thumbnail.png)
Transcribed Image Text:The beam shown in Figure Q.2 consists of a W610 x 140 structural steel wide-flange shape [E = 200 GPa; /=
1120 x 106 mm4]. If w=59 kN/m and P= 129 kN, determine:
4.3, V
1.5 m
B
W
3.5 m
P
C
2.5 m
D
Figure Q.2
Part A: The reactions at A, B, and D. Choose the reaction force at B as the redundant; therefore, the
released beam is simply supported between A and D.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step 1: Introduce the problem statement
VIEW Step 2: Determine static indeterminacy
VIEW Step 3: Support reactions for beam subjected to external load and unit load
VIEW Step 4: Apply principle of virtual work
VIEW Step 5: Determine the value of redundant
VIEW Step 6: Determine support reactions
VIEW Solution
VIEW Step by stepSolved in 7 steps with 19 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A. Determine the magnitude of normal reaction at A B. Determine the x component of the reaction at B C. Determine the y component of the reaction at Barrow_forwardThe beam shown in Figure Q.2 consists of a W610 x 140 structural steel wide-flange shape [E= 200 GPa; /= 1120 x 106 mm4]. If w= 59 kN/m and P= 129 kN, determine: P y, v 1.5 m W 3.5 m с 2.5 m D HA Figure Q.2 Part A: The reactions at A, B, and D. Choose the reaction force at B as the redundant; therefore, the released beam is simply supported between A and D.arrow_forwardFigure shows a statically determinate beam under distributed loading conditions where C is the constant. 2x x? q(x) = C(- L AB A 2L/3 L/3 RA RB Figure 2 a) Determine the resultant of the distributed load where C is constant. Submit part Unanswered b) The magnitude and direction of the reactions at support B. Submit part Unanswered c) The magnitude and direction of the reactions at support A.arrow_forward
- The beam shown in Figure Q.2 consists of a W610 × 140 structural steel wide-flange shape [E = 200 GPa; I = 1120 × 106 mm4]. If w = 64 kN/m and P = 126 kN , determine: Part A: The reactions at A, B, and D. Choose the reaction force at B as the redundant; therefore, the released beam is simply supported between A and D. a) Calculate the value of the deflection at point B due to uniformly distributed load w in the form ??=??????????? Note: EI will cancel out in further calculations. Enter the numerator in the answer box below in kNm3 to three decimal places. Assume the positive direction of deflection in the positive direction of v axis.arrow_forwardThe beam shown in Figure Q.2 consists of a W610 x 140 structural steel wide-flange shape [E= 200 GPa;/= 1120 x 106 mm4]. If w= 59 kN/m and P= 129 kN, determine: P A Y, V 1.5 m B W 3.5 m с 2.5 m numerator EI D Figure Q.2 Part A: The reactions at A, B, and D. Choose the reaction force at B as the redundant; therefore, the released beam is simply supported between A and D. a) Calculate the value of the deflection at point B due to uniformly distributed load win the form UB = Note: E/will cancel out in further calculations. Enter the numerator in the answer box below in kNm³ to three decimal places. Assume the positive direction of deflection in the positive direction of v axis.arrow_forward10. A beam is loaded and supported as shown. Determine the components of the reactions at supports A and B.arrow_forward
- 10. A beam is loaded and supported as shown. Determine the components of the reactions at supports A and B.arrow_forwardA The beam weight is 40 lb/ft. 6 k 1 k/ft A 8' 8' 2' B 180 PROBLEM 4.30 4.31 A beam supports a nonuniformly distributed load as shown. Calculate the reaction at each support. Neglect the weight of the beam. A w = 3 kips/ft w = 7 kips/ft B L = 22'-0" ROBLEM 4.31 2 Calculate the reactions at each support for the beam show Neglect the weight of the beam. 3kN 900 N/marrow_forwardProblem 2: For the shown beam, 40 N 150 N 250 N knowing that distance d = 1.0 m: a. Calculate the reactions at the supports on the opposite beam. ......arrow_forward
- . a-The reaction at fixed end Rcy b-The bending moment at the fixed end Mc c- The shear force at B and bending moment at Barrow_forwardThe beam shown below is a simple span with an overhang. The beam supports a uniform distributed load. 0.5 kip/ft 16 ft 5 ft 1. Draw a free body diagram (FBD) of the beam and write the equations of equilibrium to solve for the support reactions. You do not have to include the horizontal reaction at A. Answer: RA 3.61 kip ↑, RB 6.89 kip ↑ 2. Draw an FBD of the beam showing the loads and the known magnitude and direction of the support reactions. 3. Draw the shear diagram for the beam. 4. Draw the bending moment diagram for the beam. 5. At what location along the beam does the maximum positive bending moment occur? 6. At what location along the beam does the maximum negative bending moment occur?arrow_forwardQ1. (а) Figure Q1(a) shows a beam loaded with a point load and a partially UTM uniform distributed load. respectively. support at A and B are roller 3 UTM The M 5 UTM (i) Draw the free body diagram of the structure. * UTM UTM Determine the support reactions at A and B by taking the (ii) structure in equilibrium condition. ITM O UTM - UTM 5 UTM O UTM 30kN 30° 10KN/m F = 840 N 2m 24 m 2m 4m A \3 m G UTM 15 m 2 m STMUTM 5 UTM FIGURE Q1(a) 10 ni FIGURE Q1(b) 一arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning