
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
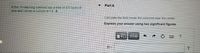
Transcribed Image Text:Part A
A thin 11-cm-long solenoid has a total of 470 turns of
wire and carries a current of 1.8 A
Calculate the field inside the solenoid near the center.
Express your answer using two significant figures.
B-
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 2. Consider the two cases shown below. How does the magnitude of the induced current in Case 1, compare to the magnitude of the induced current in Case 2? Assume S₂ =3S₁. Case I L $2 Case II Larrow_forwardPoint A in (Figure 1) is 6.0 mm from the wire. Assume that the wire is very long and that all other wires are too far away to contribute to the magnetic field. Figure ww 20 Ω 60 V + 100 Ω . A < 30 Ω 1 of 1 www Part A What is the magnetic field strength at point A? Express your answer with the appropriate units. BA= Submit 2² Provide Feedback μА Value Request Answer Units ?arrow_forwardThe magnetic field at the earth's surface can vary in response to solar activity. During one intense solar storm, the vertical component of the magnetic field changed by 2.8 μT per minute, causing voltage spikes in large loops of the power grid that knocked out power in parts of Canada. Part A What emf is induced in a square 180 km on a side by this rate of change of field? Express your answer with the appropriate units. E = Submit μA Value Provide Feedback Request Answer Units ? Review | Constants | Periodic Table Next >arrow_forward
- Problem 3 A square loop whose sides are 8 cm long is made with copper wire of radius 9 mm, assuming resistivity of copper is 1.72 x 10-8 Ohm x m. If a magnetic field perpendicular to the loop is changing at a constant rate of 6 mT/s, what is the current in the loop? A This problem is open source, to find it download for free at https://openstax.org/details/books/university-physics-volume-2.arrow_forwardTwo long, parallel wires are separated by a distance of 3.40 cm. The force per unit length that each wire exerts on the other is 4.60x10-5 N/m, and the wires repel each other. The current in one wire is 0.640 A. Part A What is the current in the second wire? Express your answer in amperes. I = for Part A for Part A undo for Part A redo for Part A reset for Part A keyboard shortcuts for Part A help for Part A Submit Part B Request Answer Are the two currents in the same direction or in opposite directions? In the same direction In opposite direction Submit Previous Answers ✓ Correct Aarrow_forward- Part A How much energy is stored in a 2.60-cm-diameter, 14.0-cm-long solenoid that has 190 turns of wire and carries a current of 0.790 A? Express your answer with the appropriate units. UL = 2.82 Submit μA J Previous Answers Request Answer ? X Incorrect; Try Again; One attempt remainingarrow_forward
- A solenoid is designed to produce a magnetic field of 3.80x10-2 T at its center. It has a radius of 1.80 cm and a length of 47.0 cm, and the wire can carry a maximum current of 13.0 A . For related problem-solving tips and strategies, you may want to view a Video Tutor Solution of Field of a solenoid. Part A What minimum number of turns per unit length must the solenoid have? Express your answer in inverse meters. n = Submit Part B L = ΑΣΦ What total length of wire is required? Express your answer in meters. G| ΑΣΦ Submit Request Answer Request Answer W ? m -1 marrow_forwardReview I Constants The 10-turn loop of wire shown in the figure(Figure 1) lies in a horizontal plane, parallel to a uniform horizontal magnetic field, and carries a 2.0 A current. The loop is free to rotate about a nonmagnetic axle through the center. A 50 g mass hangs from one edge of the loop. Part A What magnetic field strength will prevent the loop from rotating about the axle? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure 1 of 1 HẢ ? Value B 10 turns 5.0 cm Units 10.0 сm Submit Request Answer 50 g Provide Feedback Next >arrow_forwardA current loop in a motor has an area of 1.95 cm² . It carries a 240 mA current in a uniform field of 0.62 T. 1 Part A What is the magnitude of the maximum torque on the current loop? Express your answer with the appropriate units. T= BHA μÅ S Value → C Units ?arrow_forward
- A single loop of wire with an area of 0.0680 m² is in a uniform magnetic field that has an initial value of 3.80 T, is perpendicular to the plane of the loop, and is decreasing at a constant rate of 0.210 T/s. For related problem-solving tips and strategies, you may want to view a Video Tutor Solution of Emf and current induced in a loop. Part A What emf is induced in this loop? Express your answer in volts. —| ΑΣΦ lɛl = Submit Part B Request Answer I = ? If the loop has a resistance of 0.450 , find the current induced in the loop. Express your answer in amperes. —| ΑΣΦ V ? Aarrow_forwardA 6.70 - partice moves through a region of space where an lectric field of magnitude 1250 N/C points in the positive direction, and a magnetic field of magnitude 1.22 T points in the Positive direction Part A the net force acting on the particle is 621x10-N in the positive x direction, find the components of the particle's velocity. Assume the particle's velocity is in the x-y plane Enter your answers numerically separated by commas. Vx, Vy, Vz= ? m/s Submit Request Answerarrow_forwardA potential difference of 0.055 V is developed across the 10-cm-long wire of (Figure 1) as it moves through a magnetic field perpendicular to the plane of the figure. Figure 10 cm 5.0 m/s |+++ 1 of 1 Part A What is the strength of the magnetic field? Express your answer with the appropriate units. B = Submit Part B Value μÀ O to the right Request Answer What is the direction of the magnetic field? Submit out of the page to the left O into the page Provide Feedback Request Answer B Units ?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON