
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
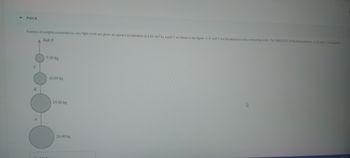
Transcribed Image Text:Part A
A series of weights connected by very light cords are given an upward acceleration of 4.00 m/s2 by a pull P, as shown in the figure. A, B, and C are the tensions in the connecting cords. The SMALLEST
A Pull P
B
A
5.00 kg
COLN
10.00 kg
15.00 kg
20.00 kg
free tensions A
i dosest to
614PM
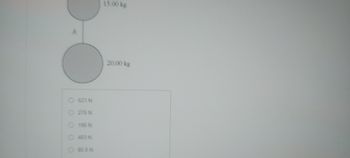
Transcribed Image Text:O 621 N
276 N.
O 196 N
483 N
80.0 N
15.00 kg
20.00 kg
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The end of a light rope ABCD are connected to the same horizontal beam at A and D. Masses of 1 kg are suspended at B and C. AB = CD BC and AD = 2 AB. Calculate the tension in each part of the rope using the method of components if A and D are in the same horizontal plane (use g = 9.81 m/s2). A.arrow_forwardIf the coefficient of kinetic friction between an object with mass M = 3.00 kg and a flat surface is 4 =0.410, what force will cause the object to accelerate at 2.50 m/s? The force is applied at an angle of 0 = 30.0* (see the figure below). M Hk F = ? 1) Calculate the force. N Submitarrow_forwardA physics major is cooking breakfast when he notices that the frictional force between the steel spatula and the Oiled Steel frying pan is only 0.150 N. Knowing the coefficient of kinetic friction between the two materials (0.03), he quickly calculates the normal force. What is it? Narrow_forward
- Don't use chat gpt Itarrow_forward5. A block of weight w = 100 N is suspended from a rope tied to two other ropes at point O. One rope is horizontally attached to a wall and the other is fastened to the ceiling. The angle between ceiling and the rope is 60°. Assume the weights of the ropes and the knot are negligible. Calculate the tension in each rope (T₁, T2, and T3). I T2 0 T3 W 60° Earrow_forwardI Review Part A Find the tension in the string connecting mj and m2. Assume the table is frictionless and the masses move freely. (Figure 1) Express your answer using two significant figures. Υ ΑΣΦ T = Submit Request Answer Figure 1 of 1 Part B m, = 1.0 kg m2 = 2.0 kg Find the tension in the string connecting m2 and m3. Express your answer using two significant figures. m, = 3.0 kg 0 ΑΣφ T2 = Pearsonarrow_forward
- Suppose a 66.5 kg gymnast climbs a rope. What is the tension in the rope if she climbs at a constant speed? tension: N What is the tension in the rope if she accelerates upward at a rate of 1.65 m/s? tension: Narrow_forwardA force in the +x-direction with magnitude F(x)= 18.0 N - (0.530 N/m) x is applied to a 6.40 kg box that is sitting on the horizontal, frictionless surface of a frozen lake. F(x) is the only horizontal force on the box. For related problemsolving tips and strategies, you may want to view a Video Tutor Solution of Motion with a varying force. ▼ Part A If the box is initially at rest at x = 0, what is its speed after it has traveled 17.0 m? Express your answer with the appropriate units. V = μA Value Submit Units Previous Answers Request Answer ? X Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remainingarrow_forwardAn object of mass m is constrained to move on a horizontal frictionless circular track of radius m starts fIrom rest at time t = 0 and thereafter is puushed by an external force with constant magnitude F, always horizontal and tangent to the track. The horizontal component of the force exerted by the track on the object is given by А. О В. F C. Ft/mR D. Ft2/mR E. F/mg ans: Darrow_forward
- A ladder of weight W stands on a rough floor and rests against a frictionless wall, illustrated above. It is only stable if the angle between the ladder and the ground is greater than theta (theta > 60 degree). a. Find the coefficient of static friction between the floor and the ladder. b. A child of weight 4W places the ladder against the wall at angle 70 degree(theta = 70 degree). Calculate how far up the ladder it is safe for the child to climb.arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardA monkey of mass m = 10.0 kg is holding on to two vines each of length l = 3.00 m. The vines form an angle with the horizontal of 40.0 degrees (see figure). The monkey is not moving and the vines are considered massless and not stretchable. a. What is the distance d between the mounting points of the vines at the top? b. Draw a free body diagram of the monkey and indicate all forces.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON