
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
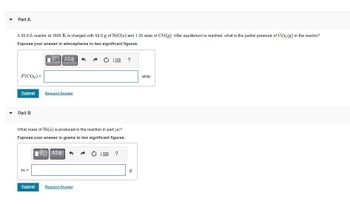
Transcribed Image Text:Part A
A 55.0-L reactor at 1600 K is charged with 50.0 g of NiO(s) and 1.30 atm of CO(g). After equilibrium is reached, what is the partial pressure of CO₂ (g) in the reactor?
Express your answer in atmospheres to two significant figures.
VE ΑΣΦΑ
P(CO₂) =
Submit
Part B
What mass of Ni(s) is produced in the reaction in part (a)?
Express your answer in grams to two significant figures.
ΨΕ ΑΣΦ
m =
Request Answer
Submit
Request Answer
?
?
04
g
atm
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Calculate the Keg from the given concentrations, all are gases. C2H6 1.000 M 2 Cl2 1.000 M C2H4CI2 + 0.000 M 0.250 M + 2 HCI start: 0.000 M equilibrium: 0.750 M 0.500 M 0.500 M 0.500 M used First put in the chemicals, then put in the numbers. The concentrations for both Cl2 and HCl are squared due to their coefficients. [ Kea %3D Keg = a. H3O*1 b. Он1 c. C2H6 d. C2HĄCI2 e. Cl2 f. HCI g. H2SO3 h. HC2H3O2 i. C2H3O21 j. H2S k. HS-1 I. s2 m. HX п. X1 o. 0.750 р. 2 q. 1 r. 0.250 s. 0.500 t. 0.333 u. 8.00 х 10-5 v. 1.75 x 10-6 w. 1.11 x 10-8 x. 5.5 x 10-2 у. О.7000 z. 1.60 x 10-5 aа. 1.143 х 10-5 bb. 0.6000 СС. 1.104 х 10-5 dd. 0.7100 ее. 1.26 х 10-5 ff. 4.901 gg. 7.93 hh. 4.942 ii. 4.957arrow_forward1.3 3 (i) In the Haber process for the production of ammonia, the following reaction occurs: 2 (g) + 3H₂(g) 2NH3(g) = DH is negative If the equilibrium concentrations for all the reactants and products at 600°C are: [N₂] = 0.40 mol/dm³, [H₂] = 1.20 mol/dm³ and [NH₂] = 0.20 mol/dm³ Construct an expression for K and calculate the numerical value of the equilibrium constant, K с (ii) At 500°C K. 0.062 mol 2dm. Compare this value to the one you calculated in 3(i) above and state whether the yield of ammonia is greater at 500°C or 600°C and briefly explain your choice.arrow_forwardA student ran the following reaction in the laboratory at 1080 K: 2SO3(g) 2S02(g) + O₂(g) When he introduced SO3(g) at a pressure of 0.886 atm Into a 1.00 L evacuated container, he found the equilibrium partial pressure of SO3(g) to be 0.340 atm. Calculate the equilibrium constant, Kp, he obtained for this reaction. Kp = Submit Answer 44 $ T R F V/ % 5 Retry Entire Group 9 more group attempts remaining T Cengage Learning Cengage Technical Support F5 G ^ 6 MacBook Air Y H & 7 RN U * 0 J ► 11 F8 M ( 9 ►► K F9 O 1 F11 + { Save and Exit = F12 11arrow_forward
- The equilibrium constant, Kc, for the following reaction is 1.25 at 659 K. 2NH3 (9) N2(g) + 3H₂(g) When a sufficiently large sample of NH3(g) is introduced into an evacuated vessel at 659 K, the equilibrium concentration of H₂(g) is found to be 0.609 M. Calculate the concentration of NH3 in the equilibrium mixture. [NH3] = Submit Answer Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. M Submit Answer Retry Entire Group 8 more group attempts remaining [Review Topics] [References] Use the References to access important values if needed for this question A student ran the following reaction in the laboratory at 679 K: H₂(g) + I₂(g) → 2HI(g) When she introduced 0.208 moles of H₂(g) and 0.237 moles of I2 (g) into a 1.00 liter container, she found the equilibrium concentration of I2 (g) to be 0.0625 M. Calculate the equilibrium constant, Kc, she obtained for this reaction. Kc = | Retry Entire Group 8 more group attempts remaining'arrow_forwardConsider the following reaction where Kc = 1.29×10-² at 600 K: ? COCI₂ (9) co (g) + Cl₂ (9) A reaction mixture was found to contain 0.107 moles of COCI₂ (g), 5.31×10-² moles of CO (g), and 3.63×10-² moles of Cl₂ (g), in a 1.00 liter container. Indicate True (T) or False (F) for each of the following: F 1. In order to reach equilibrium COCI₂(g) must be produced. 2. In order to reach equilibrium K must decrease . 3. In order to reach equilibrium CO must be produced. Ⓒ 4. Qc is less than Kc. Ⓒ 5. The reaction is at equilibrium. No further reaction will occur.arrow_forwardConsider the following reaction where Kc = 55.6 at 698 K. H2(g) + I2(g) ----> 2HI(g) A reaction mixture was found to contain 4.26×10-2 moles of H2(g), 4.04×10-2 moles of I2(g) and 0.270 moles of HI(g), in a 1.00 liter container. Is the reaction at equilibrium?If not, what direction must it run in order to reach equilibrium?The reaction quotient, Qc, equals _____ The reaction (fill in the blank) ____ A. must run in the forward direction to reach equilibrium.B. must run in the reverse direction to reach equilibrium.C. is at equilibrium.arrow_forward
- Consider the following reaction where Kc = 1.29×10-2 at 600 K.COCl2(g) CO(g) + Cl2(g)A reaction mixture was found to contain 0.120 moles of COCl2(g), 4.54×10-2 moles of CO(g), and 4.37×10-2 moles of Cl2(g), in a 1.00 liter container.Is the reaction at equilibrium?If not, what direction must it run in order to reach equilibrium?The reaction quotient, Qc, equals .The reactionfill in the blank 2A. must run in the forward direction to reach equilibrium.B. must run in the reverse direction to reach equilibrium.C. is at equilibrium.arrow_forwardAs you are walking across your laboratory, you notice a 5.25 L flask containing a gaseous mixture of 0.0205 mole NO2 (9) and 0.750 mol N2O4 (q) at 25°C. 4 (g) Is this mixture at equilibrium? If not, will the reaction proceed towards forming more products, or more reactants? N2O4 4 (9) → 2NO2 (9) Ko = 4.61 x 103 at 25°Carrow_forwardDinitrogen tetroxide partially decomposes according to the following equilibrium: N204(g) = 2NO2(g) A 1.000-L flask is charged with 0.0300 mol of N204. At equilibrium, 0.0204 mol of N204 remains. Calculate the Kc for this reaction. (Enter only the numerical value to three significant figures without units.) Answer:arrow_forward
- Show work..don't give Handwritten answer....don't use Ai for answering thisarrow_forward5. Consider the equilibrium where Kc = 85.0 at 460°C. The following mixture was prepared in a reactor at 460 °C with the concentrations [SO2] = 0.0200 M; [NO2] = 0.0200 M; [NO] = 0.100 M; [SO3] = 0.100 M. What will the concentrations of the four gases be when equilibrium is reached? SO2 (g) + NO2 (g) - NO (g) + S03 (g); Ke = 85.0 I 0.02 O. 02 C -x E 6.02- 0,02-0 0.ltx 0.lto 一× +x 十 LNOJ CSOPJ ) T02=x)co-02-) కంటె CN6 kcarrow_forwardConsider the following reaction at equilibrium. 4CuO (s) + CH4 (8) CO₂ (g) + 4Cu (s) + 2H₂O(g) AH = -514 kJ Le Châtelier's principle predicts that the equilibrium partial pressure of H₂O(g) can be decreased by removing Cu adding CH4 decreasing the reaction temperature decreasing the reactor volume adding an inert gasarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY