
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Please answer part 2 and refer to 12.6 for it. figure is attached
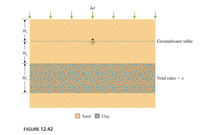
Transcribed Image Text:The diagram illustrates a layered soil profile, showing three distinct layers composed of sand and clay.
- **Layer 1 (Top Layer)**: This is a sand layer represented with a light orange color. It is subjected to an applied stress denoted by \( \Delta \sigma \) with arrows indicating downward force. The thickness of this layer is labeled as \( H_1 \).
- **Groundwater Table**: This horizontal dashed line indicates the level of the groundwater table within the top sand layer.
- **Layer 2 (Middle Layer)**: This layer consists of clay, represented with a combination of brown and blue colors. Its thickness is labeled as \( H_2 \). The void ratio of this clay layer is marked as \( e \).
- **Layer 3 (Bottom Layer)**: Similar to the top layer, this bottom layer is made up of sand and is depicted using the same light orange color. Its thickness is labeled as \( H_3 \).
The legend identifies the color coding used to differentiate between sand (light orange) and clay (brown with blue specks).
This figure (Figure 12.42) provides a visual representation of soil stratification used in geotechnical studies to understand layering and material properties influencing soil behavior under stress.

Transcribed Image Text:**Part 2**
Refer to Problem 12.6, what would be the average degree of consolidation (U) of the clay layer 180 days after the application of distributed load on the ground surface (∆σ) is applied? Given \( C_v = 2.8 \times 10^{-6} \, \text{m}^2/\text{min} \).
---
**12.6**
Refer to Figure 12.42. Given: \( H_1 = 2.5 \, \text{m}, \, H_2 = 2.5 \, \text{m} \),
\( H_3 = 3 \, \text{m}, \text{ and } \Delta\sigma = 100 \, \text{kN/m}^2 \). Also,
Sand: \( e = 0.64, \, G_s = 2.65 \)
Clay: \( e = 0.9, \, G_s = 2.75, \, LL = 55 \)
Estimate the primary consolidation settlement of the clay layer assuming that it is normally consolidated.
---
The problem requires the calculation of the average degree of consolidation and the primary consolidation settlement for a clay layer under an applied distributed load, given specific parameters for the sand and clay involved.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning