
Answer p1 and
Part 2:
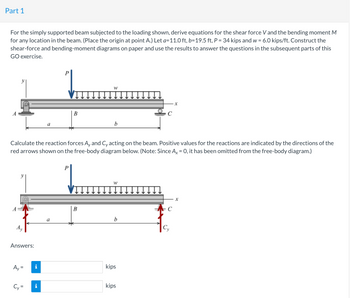
Determine the shear force acting at each of the following locations:
(a) x = 11.0- ft (i.e., just to the left of point B)
(b) x = 11.0+ ft (i.e., just to the right of point B)
(c) x = 28.5 ft
Note that x = 0 at support A. When entering your answers, use the shear-force sign convention detailed in Section 7.2.
Answers:
a) V = ____ kips
b) V = ____ kips
c) V = ____ kips
Part 3:
Determine the bending moment acting at each of the following locations:
(a) x = 11.0 ft (i.e., at point B)
(b) x = 28.5 ft
Note that x = 0 at support A. When entering your answers, use the bending-moment sign convention detailed in Section 7.2.
Answers:
a) M = ____ kips-ft
b) M = ____ kips-ft
Part 4:
Use your shear-force and bending-moment diagrams to determine the maximum bending moment, Mmax, and its location, xmax. Use the bending-moment sign convention detailed in Section 7.2.
Answers:
Mmax = ____ kips-ft
xmax = ____ ft
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

- Problem 4.1arrow_forwardThe assembly supports a uniform distributed load = 1.65 kN/m as shown. Part A Determine the resultant internal loadings at cross sections at point on the assembly. Express your answers, separated by commas, to four significant figures. V AZO NE=, VE =, ME = Submit Request Answer Part B Determine the resultant internal loadings at cross sections at point F on the assembly. Express your answers, separated by commas, to four significant figures. Np. Vp, Mp= Submit Provide Feedback VO ALO 63 12 Request Answer 1? kN, KN, KN-m kN, KN, KN-m D E 0.5 m 0.5 m 0.5 m B Im -1.5 m 2 marrow_forwardRequired information NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. Consider the given figure. B 100 mm 100 mm 100 mm C 120 mm K A E -280 mm F D Knowing that the turnbuckle has been tightened until the tension in wire AD is 375 N, determine the internal forces at the point K. The shear force Vis 255.86 N. 274.14 N. 1 The axial force Fis The bending moment Mis 84.068 N-m in the counter-clockwise direction.arrow_forward
- Civil engineers often use the straight-line equation, = b 0 + b 1x, to model the relationship between the shear strength y of masonry joints and precompression stress, x. To test this theory, a series of stress tests were performed on solid bricks arranged in triplets and joined with mortar. The precompression stress was varied for each triplet and the ultimate shear load just before failure (called the shear strength) was recorded. The stress results for n = 7 resulted in a Coefficient of Determination of 0.8436. Given that r 2= 0.8436, give a practical interpretation of r 2, the coefficient of determination for the least squares model. a. We expect to predict the shear strength of a triplet test to within about 0.8436 tons of its true value. b. About 84.36% of the total variation in the sample of y-values can be explained by (or attributed to) the linear relationship between shear strength and precompression stress. c. In repeated sampling, approximately 84.36% of…arrow_forwardQUESTION 4 The following figure represents a cross section through a long opening. The magnitudes of the plane components of the field stresses are o,= 13.75 MPa, o, = 19.25 MPa, Ty = 4.76 MPa, expressed relative to the reference axes !! shown. 1. Calculate the maximum and minimum boundary stresses in the excavation perimeter, defining the locations of the relevant points. 2. If the strength of the rock mass is defined by a maximum shear strength criterlon, and the shear strength is 20 MPa, estimate the extent of boundary failure, in terms of the angular range over the perimeter.arrow_forwardThe wooden frame is constructed from wooden 2” X 4” Lumber (Nominal size; Actual size: 1 ½” X 3 ½”) and bears a uniform distributed load. All connections are pin connected. If wo = 100 lb/ft, and L = 9 ft. Note that the distributed load is the force per unit length in the horizontal direction. A) Find the vertical reaction force at A. 747 450 248 900 563 B) Find the normal stress perpendicular to the grain at point D. -26.4 -33.9 -85.7 -21.4 -66.9 C) Find the shear force, V, on the cross-section at E. 106 900 159 150 35arrow_forward
- When the two forces are placed on the beam, the diameter of the A-36 steel rod BC decreases from 40 mm to 39.96 mm. (Figure 1) Figure -1 m -1 m P -1 m- B 0.75 m 1 m Part A Determine the magnitude of each force P. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. P = μA Value KN Submit Previous Answers Request Answer Provide Feedback ? X Incorrect; Try Again; 2 attempts remainingarrow_forwardPlease help. Written on paper not typed on computer or keyboard please. Need help on all questions. Please include all units, steps to the problem and information such as its direction or if it is in compression or tension. Thx.arrow_forwardPlease solve in a handwritten format. Don't use chatgpt. Mechanical engineeringarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





