
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
Choose your colors! help
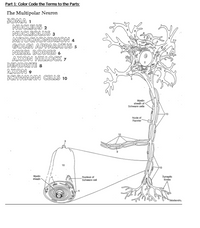
Transcribed Image Text:# Understanding the Structure of the Multipolar Neuron
This educational guide focuses on the structure of the multipolar neuron, a type of nerve cell, by color coding its key components. Below is the list of parts with reference numbers used in the diagram:
1. **Soma**
2. **Nucleus**
3. **Nucleolus**
4. **Mitochondrion**
5. **Golgi Apparatus**
6. **Nissl Bodies**
7. **Axon Hillock**
8. **Dendrite**
9. **Axon**
10. **Schwann Cells**
## Diagram Explanation
### Main Diagram
The diagram represents the multipolar neuron with various labeled parts:
- The central part of the neuron is the **soma (1)**, or cell body, containing the **nucleus (2)** and the **nucleolus (3)**.
- **Dendrites (8)** extend from the neuron, allowing it to receive signals from other neurons.
- Leading away from the soma is the **axon hillock (7)**, transitioning into the **axon (9)**, which transmits impulses away from the cell body.
- The **Nissl bodies (6)** are dispersed within the soma, indicating the presence of rough endoplasmic reticulum for protein synthesis.
### Axonal Structure
- Surrounding the axon are **Schwann cells (10)**, which form the **myelin sheath** facilitating efficient signal transmission. The **myelin sheath** is discontinuous, with gaps known as **Nodes of Ranvier**.
- A detailed view of a **Schwann cell** is provided, highlighting the **nucleus of the Schwann cell**.
### Ending Structures
- At the end of the axon are **synaptic knobs**, where neurotransmitters are released to signal other neurons or muscles.
## Additional Visualization
The diagram also includes a magnified view of a Schwann cell to illustrate the layering of the myelin sheath and its relationship with the axon. This emphasizes the role of Schwann cells in neuronal insulation and signal propagation.
By studying this detailed diagram and the numbered parts, learners can gain a comprehensive understanding of neuron anatomy and its significance in the nervous system.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- B D LLUI — F H J K L ΣΤΟ M- N P dc ve and submit. Click Save All Answers to save all answers. 1 Save All Answarrow_forwardI need to make a paper assignment on why sports people collapse because of heart problems. can you give me some topics about?arrow_forwardPLEASE do as many as you can.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education