
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
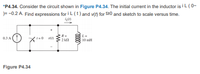
Transcribed Image Text:*P4.34. Consider the circuit shown in Figure P4.34. The initial current in the inductor is i L (0-
)= -0.2 A. Find expressions for i L (t) and v() for t20 and sketch to scale versus time.
R=
2 kl
L=
0.3 A
10 mH
Figure P4.34
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the circuit shown in Figure P4.50. The initial current in the inductor is i s ( 0+)=0. Write the differential equation for i s(t) and solve. [Hint: Try a particular solution of the form i sp ( t )=A cos( 300t )+B sin( 300t ).]arrow_forward4.61 In the circuit shown in Figure P4.61: VS1 = 15 V Vs2 = 9 V Rs1 = 130 Q R$2 = 290 22 R₁ = 1.1 kQ2 R₂ = 700 Q L = 17 mH C = 0.35 µF Determine the voltage vc across the capacitor and the current i, through the inductor as t → ∞o. Rs1 Vsi t=0 iL LR₁ Figure P4.61 CVC R$2 с +21 ww R₂ V s2arrow_forwardP4.23. Solve for the steady-state values of i1, i2, i3, i4, and vc for the circuit shown in Figure P4.23, after the switch has been closed for a long time. i iz 14 1 H 500 2 100 V 50 2 100 2 vc 100 µF Figure P4.23arrow_forward
- P4.34. Consider the circuit shown in Figure P4.34. The initial current in the inductor is iL (0-) 0. Find expressions for i (t) and v(t) for t> 0 and sketch to scale versus time. 0.1 A (1) R = v(t) 1 k2 t = 0 1 mH Figure P4.34arrow_forwardQuestion 4. In the circuit below I is a DC current, and v. is a sinusoidal signal. Given the diode has vo-0.75V at ip=1.5mA, calculate both the AC and DC voltage across the diode (v.) when I=1mA, R=5002, and Vs=100cos(10*n*t). Assume the capacitors are very large. R₂ www -0 ▷ +1₁ 15 B ANarrow_forwardWhat is a capacitor and how do they work? What is it about capacitors that make them unique? What is the formula for one time constant? How many time constants does it take to fully charge a capacitor? Show illustrations. What other electronic component(s) are commonly found with a capacitor…especially in timing circuits? What types of capacitors are there? What are the formulas for series and parallel capacitors? If three 30 uF capacitors were connected in parallel what would the net capacity be? How about the net value if the capacitors in Q7 were connected in series? If you were to connect a 5K-ohm resistor in series as in Q7… what would the first time constant be? What about time to full charge? Describe the difference between AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current). Use illustrations. Why is voltage generated and distributed in AC? What type of circuit(s) would change AC to DC? How about DC to AC?arrow_forward
- ASAP plzarrow_forwardDetermine expressions for and sketch is(t) toscale versus time for -0.2 … t … 1.0 s for thecircuit of Figure P4.37 using a differential equation.arrow_forwardP4.17. In the circuit of Figure P4.17, the switch instantaneously moves back and forth between contacts A and B, spending 1 s in each position. Thus, the capacitor repeatedly charges for 1 s and then discharges for 1 s. Assume that vc(0) = 0 and that the switch moves to position A at t = 0. Determine vc(1), vc(2), vc(3), and vc(4). Figure P 218 Chapter 4 Transients R *P4.22 CO der the cireuit shown in FILe P4.22. hat is the steady-state vale of er iteh opens? Determine how long it er the switch opers before vo is w rcent of its steav-state value. 2 ΜΩ 10 V c 1 µF Figure P4.17arrow_forward
- 4.50 Determine iz(t) in the circuit shown in Figure P4.50. Assume: i(1) = 100 cos(@t + 4) mA %3D i3(t) = 80 sin(@t – 1.2) mA - i4(1) = 150 sin(wt + 2) mA %3D W = 377 rad/s i4 Figure i3 +. Vs Z3 ZA Figure P4.50arrow_forwardThe voltage across and the current through acapacitor are shown in Figure P4.21. Determine thevalue of the capacitance.arrow_forward1. Consider the system below x(t) System-1 v(t) y(t) System-2 The input and output relationship of the two systems are v(t) = h₁ (t) * x(t), where h₁ (t) = r(t) and y(t) = ſtv(t)dt and the System-2 is linear. a) Show that System-2 is time invariant. b) Is the overall system linear and time invariant? Justify. c) Determine the impulse response of System-2. d) Determine the overall impulse response of the system. Note: just write code in matlab for the given question (code for implementation) Write code for at least 1 or 2 questions in the given questionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,