
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696527
Author: J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
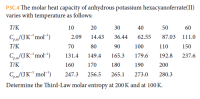
Transcribed Image Text:P3C.4 The molar heat capacity of anhydrous potassium hexacyanoferrate(II)
varies with temperature as follows:
T/K
10
20
30
40
50
60
Cpm/(J K"'mol")
14.43
2.09
36.44
62.55
87.03
111.0
P.m
T/K
70
80
90
100
110
150
Cpam/(JK"mol")
131.4
149.4
165.3
179.6
192.8
237.6
P.m'
T/K
160
170
180
190
200
Cpam/(JK mol")
247.3
256.5
265.1
273.0
280.3
Determine the Third-Law molar entropy at 200K and at 100 K.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 2.19 The heat capacity of sulphuric acid in Btu/(lb-mol °R) is given by Cp = 23.06 + 2.071 × 10-2T where T is in °R. What is the equivalent expression if heat capacity is given in (a) kJ/(kmol K) and T is in K (b) kcal/(kmol °C) and temperature in °C.arrow_forwardGiven the following formula for the heat capacity of CO: Cp [cal/(mol^ * C)] = 6.890 + 0.001436T(^ C) derive one that has units of [Btu/(lb-mole^ F)] .arrow_forwardCalculate the total energy in kJ for 198 g of liquid dimethyl ether (C2H6O) at -48.0 oC heated to 75.0 oC. The heat capacity for liquid dimethyl ether is 137 J/(mole⋅oC) and the heat capacity for dimethyl ether gas is 102 J/(mole⋅oC). The heat of vaporization for dimethyl ether is 21.5 kJ/mole. The boiling point for dimethyl ether is -24.0 oC. Group of answer choices 128.9 kJ 57.6 kJ 122.4 kJ 149.9 kJ 6910 kJarrow_forward
- Exercise 7.2.1: Heat from a generic reaction. A balance stoichiometric reaction 2D + 0.5E 3.8F with Ah-(100°C, 1 atm) = -48 kJ/mol. (a) If 62 mol/s of component F are produced at 100°C and 1 atm, how much heat (kW) is produced by the reaction?arrow_forwardA thermocouple lead consists of a small sphere of constantan (a Cu-Ni alloy) having a diameter of 1 mm. Constantan has a density (ρ) of 8920 kg/m3 , a thermal conductivity (k) of 24 W/(m.K), and a heat capacity (Cp) of 410 J/(kg.K). The thermocouple lead is initially at 20 ºC. It is placed into a hot air stream at 200 ºC. The heat transfer coefficient, h between the thermocouple lead and the air is 300 W/(m2 .K). a) Determine which resistance controls the heat transfer process. b) Determine the time required for the thermocouple reading to reach 95% of its total temperature change.***Do not copy from chegg. That one is not correct.arrow_forwardAn unfrozen food product has a specific heat of 4 kJ/kg°C and a latent heat of fusion of330 kJ/kg. Once it is frozen its specific heat is 1.98 kJ/kg°C. Its freezing point is -2°C.Determine the total amount of heat (W) to be removed to freeze 100 kg/h of the productfrom an initial temperature of 8°C to -18°C.arrow_forward
- Q.3 Two formulas for the heat capacity of CO are given here: C,(cal/(mol-"C)] = 6.890 + 0.0014367(°C) C,(Btu/(lb-mole "F)] = 6.864 + 0.00079787('F) Starting with the first formula, derive the second. (Recall Section 2.5, and remember that the tem- perature unit in the denominator of C, refers to a temperature interval.)arrow_forwardA stream flowing at a rate of 30kgmol/h containing 30% (mole) N₂ and 70% (mole) H₂. This is to be heated from 300 K to 470 K. Calculate the amount of heat transferred using the C data given below. CP N₂ = 29.57 - 5.43 × 10-³T + 13.17 x 10-672, kJ/kgmol -K CHH₂ = 28.65 +1.02 x 10-³T-0.15 x 10-672, kJ/kgmol - Karrow_forwardA CHM student completing the calorimetry experiment mixes 20.0 mL of 1.10 M HCl (aq) with 20.0 mL of 1.05 M NaOH (aq), and observes the temperature increase of 6.611∘∘C. Assume that the density of each solution is 1.02 g/mL, and the specific heat for the resulting solution is 4.02 J/g∙℃. Calculate the change in enthalpy for this reaction (ΔHrxn) in kJ/mol H2O. Use the correct sign (+ or -) and significant figures.arrow_forward
- 2. Fruit is impeded from ripening when it reaches high temperatures (>32°C). Farmer Joe is roo worried that Princeton's summer heat wave will affect the ripening of his ground cherries. The spherical fruit (1 cm in diameter) is surrounded by a spherical papery husk (husk = 0.3 W/m K) with an inner diameter of 2 cm and an outer diameter of 2.1 cm. The air in between the fruit and the husk is stagnant (air = 0.03 W/m K). On a calm day in July, the Princeton air (outside of the husk) is very warm, with a temperature of ~38°C and a heat transfer coefficient of hPrinceton,calm = 10 W/m².K. (a) Sketch the system, labeling all temperatures, dimensions, and proportionality constants.arrow_forwardWhat is the final temperature of a 200.00 gram sample of water (c = 4.18 J/g°C) that absorbs 5,000 Joules of heat energy after starting with a temperature of 20°C?arrow_forwardThe heat capacity (Cp) of an halogenated organic compound, chloroform is given by the follow equation. Equation (1) Cp (J/mol K) = 19.8 +0.22 T – 0.00026 T² (a) Obtain a new equation that uses T in Fahrenheit (b) Calculate the Cp of chloroform at 300 K using Equation (1) (c) Calculate the Cp of chloroform at 80 °F using the equation you derived in (a)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The