
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
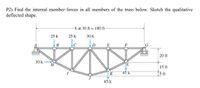
Transcribed Image Text:P2) Find the internal member forces in all members of the truss below. Sketch the qualitative
deflected shape.
6 at 30 ft = 180 ft-
25 k
25 k
30 k
to
B
E
F
20 ft
30 k
H.
15 ft
45 k
5 ft
K
45 k
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 7 steps with 7 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Using mcd plsarrow_forward2- Find the vertical deflection of the point C. Beam: A=5000 mm2, 1-60e6 mm4, E-70 GPa Bar: A= 500 mm2, E=70 GPa A D Bar 4 2 m 3 B Beam 4m C P=2 KNarrow_forwardThe simply supported beam consists of a W21 × 44 structural steel wide-flange shape [E = 29,000 ksi; I = 843 in.4]. Assume that the support at D can provide resistance either up or down. For a loading of w = 7.8 kips/ft, determine:(a) the beam deflection vA at point A.(b) the beam deflection vC at point C.Assume LAB = 10 ft, LBC = 8 ft, LCD = 8 ft, LDE = 7 ft.arrow_forward
- PROBLEM 2: Determine the horizontal deflection at the joint C (A) due to the 20-kip load applied at joint C. The truss has pin supports at A and B. All truss members are steel bars with E=29,000 ksi and A=0.75 in². 20 kips C AX 4 ft D 3 ft 3 ftarrow_forwardCalculate for the following member forces of the frame shown below using Portal Method. a. Shear at column KJ in kN. b. Axial at beam FJ in kN. 36kN D H 3 m 28.9kN G K 3 m 34.8kN B F J 4.5 m E I 5 m 4 marrow_forwardThe cantilever beam shown is subjected to a concentrated load of P. The cross-sectional dimensions of the wide-flange shape are also shown, where bf = 7.00 in., d = 12.5 in., tf = 0.475 in., tw = 0.250 in.(a) Compute the value of Q that is associated with point K, which is located yk = 3.0 in. above the centroid of the wide-flange shape.(b) If the allowable shear stress for the wide-flange shape is τallow= 12 ksi, determine the maximum concentrated load P than can be applied to the cantilever beam. Calculate the cross-sectional area of the top flange (1), the bottom flange (2), and the web (3).Answers:A1 = in.2.,A2 = in.2.,A3 = in.2. Part 2 Determine the location of the y direction centroids of the top flange (1), the bottom flange (2), and the web (3), with respect to the bottom of the cross-section.Answers:y1 = in.,y2 = in.,y3 = in. Part 3 Determine the centroid location in the y direction for the cross-section…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning